An antianginal is a drug used in the treatment of angina pectoris, a symptom of ischaemic heart disease.
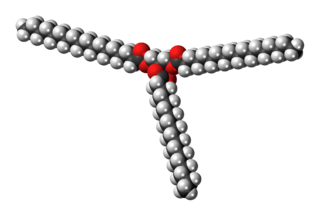
Stearin, or tristearin, or glyceryl tristearate is an odourless, white powder. It is a triglyceride derived from three units of stearic acid. Most triglycerides are derived from at least two and more commonly three different fatty acids. Like other triglycerides, stearin can crystallise in three polymorphs. For stearin, these melt at 54 (α-form), 65, and 72.5 °C (β-form).

Shasta Beverages is an American soft drink manufacturer that markets a value-priced soft drink line with a wide variety of soda flavors, as well as a few drink mixers, under the brand name Shasta. The company name is derived from Mount Shasta in northern California and the associated Shasta Springs.

Behenic acid (also docosanoic acid) is a carboxylic acid, the saturated fatty acid with formula C21H43COOH. In appearance, it consists of white solid although impure samples appear yellowish.
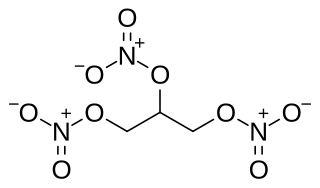
Nitroglycerin, also known as glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), is a medication used for heart failure, high blood pressure, anal fissures, painful periods, and to treat and prevent chest pain caused by decreased blood flow to the heart (angina) or due to the recreational use of cocaine. This includes chest pain from a heart attack. It is taken by mouth, under the tongue, applied to the skin, or by injection into a vein.

Monoglycerides are a class of glycerides which are composed of a molecule of glycerol linked to a fatty acid via an ester bond. As glycerol contains both primary and secondary alcohol groups two different types of monoglycerides may be formed; 1-monoacylglycerols where the fatty acid is attached to a primary alcohol, or a 2-monoacylglycerols where the fatty acid is attached to the secondary alcohol.

Lotion is a low-viscosity topical preparation intended for application to the skin. By contrast, creams and gels have higher viscosity, typically due to lower water content. Lotions are applied to external skin with bare hands, a brush, a clean cloth, or cotton wool.
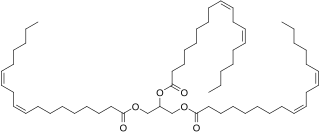
Linolein is a triglyceride in which glycerol is esterified with linoleic acid. It's a primary constituent of sunflower oil and multiple other vegetable fats. It is used in the manufacturing of biodiesel. Linolein is also an ingredient in some cosmetic products.
In enzymology, a (R)-2-hydroxy-fatty-acid dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.98) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Alkylglycerol monooxygenase (AGMO) is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydroxylation of alkylglycerols, a specific subclass of ether lipids. This enzyme was first described in 1964 as a pteridine-dependent ether lipid cleaving enzyme. In 2010 finally, the gene coding for alkylglycerol monooxygenase was discovered as transmembrane protein 195 (TMEM195) on chromosome 7. In analogy to the enzymes phenylalanine hydroxylase, tyrosine hydroxylase, tryptophan hydroxylase and nitric oxide synthase, alkylglycerol monooxygenase critically depends on the cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin and iron.
In enzymology, a phosphoglycerol geranylgeranyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Glycerol monostearate, commonly known as GMS, is a monoglyceride commonly used as an emulsifier in foods. It takes the form of a white, odorless, and sweet-tasting flaky powder that is hygroscopic. Chemically it is the glycerol ester of stearic acid It is also used as hydration powder in exercise formulas

A nitrovasodilator is a pharmaceutical agent that causes vasodilation by donation of nitric oxide (NO), and is mostly used for the treatment and prevention of angina pectoris.

Guam Memorial Hospital is located in Tamuning, Guam and is the public civilian hospital serving the island of Guam. The hospital has 158 licensed acute care beds, plus 40 beds at its off-site, long-term care Skilled Nursing Facility.
Lithium stearate is a chemical compound with the formula LiO2C(CH2)16CH3. It is formally classified as a soap (a salt of a fatty acid). Lithium stearate is a white soft solid, prepared by the reaction of lithium hydroxide and stearic acid.
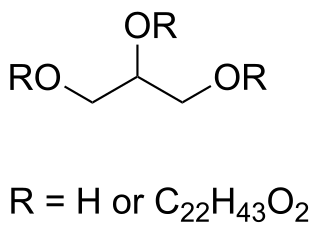
Glyceryl behenate is a fat used in cosmetics, foods, and oral pharmaceutical formulations. In cosmetics, it is mainly used as a viscosity-increasing agent in emulsions.
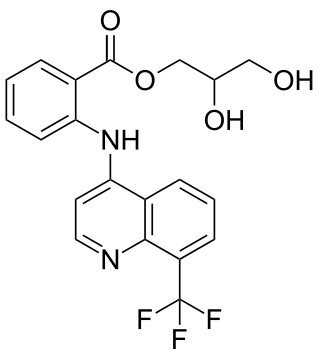
Floctafenine is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
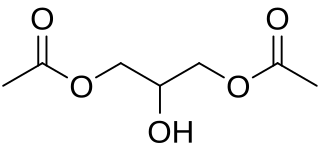
Glyceryl diacetate is a food additive with the E number E1517. This diglyceride is more generally known as diacetin. It is the diester of glycerol and acetylating agents, such as acetic acid and acetic anhydride. It is a colorless, viscous and odorless liquid with a high boiling point. Glycerol diaceate is typically a mixture of two isomers, 1,2-glyceryl diacetate and 1,3-glyceryl diacetate.

Glyceryl octyl ascorbic acid (GO-VC) is an amphipathic derivative of vitamin C consisting of two ether linkages: a 1-octyl at position 2 and a glycerin at position 3. The chemical name is 2-glyceryl-3-octyl ascorbic acid. The isomer in which these two groups are swapped is also known.













