Plymouth Sound, or locally just The Sound, is a deep inlet or sound in the English Channel near Plymouth in England.

The Battle of Trafalgar was a naval engagement that took place on 21 October 1805 between the British Royal Navy and the combined fleets of the French and Spanish Navies during the War of the Third Coalition of the Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815).

HMS Bellerophon, known to sailors as the "Billy Ruffian", was a ship of the line of the Royal Navy. A third-rate of 74 guns, she was launched in 1786. Bellerophon served during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, mostly on blockades or convoy escort duties. She fought in three fleet actions: the Glorious First of June (1794), the Battle of the Nile (1798) and the Battle of Trafalgar (1805). While the ship was on blockade duty in 1815, Napoleon boarded Bellerophon so he could surrender to the ship's captain, ending 22 years of almost continuous war between Britain and France.

HMS Defiance was a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built by Randall and Co., at Rotherhithe on the River Thames, and launched on 10 December 1783.

HMS Agamemnon was a 64-gun third-rate ship of the line of the British Royal Navy. She saw service in the American Revolutionary War, French Revolutionary, and Napoleonic Wars and fought in many major naval battles. She is remembered as Horatio Nelson's favourite ship, and she was named after the mythical ancient Greek king Agamemnon, the first ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name.

HMS Superb was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, and the fourth vessel to bear the name. She was launched on 19 March 1798 from Northfleet, and was eventually broken up in 1826. Superb is mostly associated with Richard Goodwin Keats who commanded her as captain from 1801 until his promotion in 1806. Keats famously spent only one night out of the ship during four and a half years out of a home port. She also served as his flagship from early 1808 until she was paid off in 1809.

HMS Royal Sovereign was a 100-gun first-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, which served as the flagship of Admiral Collingwood at the Battle of Trafalgar. She was the third of seven Royal Navy ships to bear the name. She was launched at Plymouth Dockyard on 11 September 1786, at a cost of £67,458, and was the only ship built to her design. Because of the high number of Northumbrians on board the crew were known as the Tars of the Tyne.
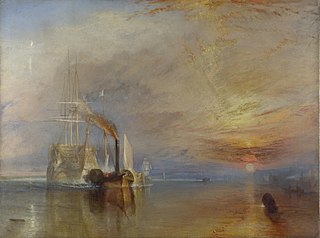
HMS Temeraire was a 98-gun second-rate ship of the line of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy. Launched in 1798, she served during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, mostly on blockades or convoy escort duties. She fought only one fleet action, the Battle of Trafalgar, but became so well known for that action and her subsequent depictions in art and literature that she has been remembered as The Fighting Temeraire.

HMS Polyphemus, a 64-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 27 April 1782 at Sheerness. She participated in the 1801 Battle of Copenhagen, the Battle of Trafalgar, and the Siege of Santo Domingo. In 1813 she became a powder hulk and was broken up in 1827.

HMS Pickle was a topsail schooner of the Royal Navy. She was originally a civilian vessel named Sting, of six guns, that Lord Hugh Seymour purchased to use as a tender on the Jamaica station. Pickle was at the Battle of Trafalgar, and though she was too small to take part in the fighting, Pickle was the first ship to bring the news of Nelson's victory to Great Britain. She also participated in a notable single-ship action when she captured the French privateer Favorite in 1807. Pickle was wrecked in 1808, but without loss of life.

Admiral Sir Richard Goodwin Keats GCB was a British naval officer who fought throughout the American Revolution, French Revolutionary War and Napoleonic War. He retired in 1812 due to ill health and was made Commodore-Governor of Newfoundland from 1813 to 1816. In 1821 he was made Governor of Greenwich Hospital in Greenwich, London. Keats held the post until his death at Greenwich in 1834. Keats is remembered as a capable and well respected officer. His actions at the Battle of Algeciras Bay became legendary.

The Battle of Trafalgar was fought between British and Franco-Spanish fleets on 21 October 1805. A force of 27 British ships of the line faced 33 allied ships. Both forces were formed in two columns; the British sailed parallel, the allied one following the other.

Achille was a Téméraire-class 74-gun French ship of the line built at Rochefort in 1803 after plans by Jacques-Noël Sané.

Captain John Richards Lapenotière was a British Royal Navy officer who, as a lieutenant commanding the tiny topsail schooner HMS Pickle, observed the Battle of Trafalgar on 21 October 1805, participated in the rescue operations which followed it and then carried the dispatches of the victory and the death of Admiral Nelson to Britain.

HMS Edgar was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, that saw service in the American Revolutionary, French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. Launched in 1779, she fought in the battles of Cape St Vincent and Copenhagen, two of the major naval engagements of the wars.

HMS Amazon was a 38-gun fifth-rate Amazon-class frigate of the Royal Navy. She served during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars under several notable naval commanders and played a key role in the Battle of Copenhagen under Edward Riou, who commanded the frigate squadron during the attack. After Riou was killed during the battle, command briefly devolved to John Quilliam. Quilliam made a significant impression on Horatio Nelson, who appointed Quilliam to serve on the flagship HMS Victory. Amazon passed to William Parker, who continued the association with Nelson with service in the Mediterranean and participation in the chase to the West Indies during the Trafalgar Campaign. Amazon went on to join Sir John Borlase Warren's squadron in the Atlantic and took part in the defeat of Charles-Alexandre Léon Durand Linois's forces at the action of 13 March 1806. During the battle, she hunted down and captured the 40-gun frigate Belle Poule.

Neptuno was an 80-gun Neptuno-class ship of the line of the Spanish Navy. She was built in 1795 and took part in the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. She fought with the Franco-Spanish fleet in the battle of Trafalgar, and was wrecked in its aftermath.

HMS Victory is a 104-gun first-rate wooden sailing ship of the line. With 246 years of service as of 2024, she is the world's oldest naval vessel still in commission. She was ordered for the Royal Navy in 1758, during the Seven Years' War and laid down in 1759. That year saw British victories at Quebec, Minden, Lagos and Quiberon Bay and these may have influenced the choice of name when it was selected in October the following year. In particular, the action in Quiberon Bay had a profound affect on the course of the war; severely weakening the French Navy and shifting its focus away from the sea. There was therefore no urgency to complete the ship and the signing of the Treaty of Paris in February 1763, meant that when Victory was finally floated out in 1765, she was placed in ordinary. Her construction had taken 6,000 trees, 90% of them oak.
Peter Goodwin is a British maritime historian and author, and the former Keeper and Curator of HMS Victory.
William Lechmere was an officer of the Royal Navy who served during the American War of Independence and the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars.