Related Research Articles

Monroe County is a county located in the U.S. state of Illinois. According to the 2010 census, it had a population of 32,957. Its county seat and largest city is Waterloo.

Jefferson County is a county located in the southern part of the U.S. state of Illinois. According to the 2010 census, it has a population of 38,827. The county seat is Mount Vernon.

Gallatin County is a county located in the U.S. state of Illinois. According to the 2010 census, it has a population of 5,589, making it the fifth-least populous county in Illinois. Its county seat is Shawneetown. It is located in the southern portion of Illinois known locally as "Little Egypt".

Mount Vernon is a city in and the county seat of Jefferson County, Illinois, United States. The population was 15,277 at the 2010 census.

Walnut Hill is a village in Marion County, Illinois, United States. The population was 109 at the 2000 census.

U.S. Route 40 or U.S. Highway 40 (US 40), also known as the Main Street of America, is a major east–west United States Highway traveling across the United States from the Mountain States to the Mid-Atlantic States. As with most routes whose numbers end in a zero, US 40 once traversed the entire United States. It is one of the first U.S. Highways created in 1926 and its original termini were in San Francisco, California and Atlantic City, New Jersey. In the western United States, US 40 was functionally replaced by Interstate 80 (I-80), resulting in the route being truncated multiple times. US 40 currently ends at a junction with I-80 in Silver Summit, Utah, just outside Salt Lake City.

The South Yamhill River is a tributary of the Yamhill River, approximately 60 miles (97 km) long, in northwest Oregon in the United States. It drains an area of the Northern Oregon Coast Range, as well as part of the Willamette Valley west of the Willamette River.

Opdyke is a census-designated place in the southeastern part of Jefferson County, Illinois, United States. As of the 2010 census, its population was 254. Opdyke was laid out in 1871, following construction of the St. Louis & Southeastern Railroad. The nearby, earlier town of Lynchburg was largely abandoned and moved to Opdyke.
The Goshen Settlement was an early American pioneer settlement in what is now Illinois, USA, located to the east of St. Louis, Missouri. The settlement was located about one mile (1.6 km) southwest of modern Glen Carbon, Illinois, at the point where Judy's Creek emerges from the bluffs into the American Bottoms, on its way to the Mississippi River.
Lusk's Ferry Road was an early road in Illinois that provided an overland connection between the main settlement, Fort Kaskaskia, on the Mississippi River, and Lusk's Ferry, an important crossing point on the Ohio River. The overland route afforded an alternative to the river route, which required a difficult trip upstream on the Mississippi.
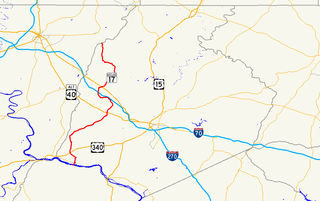
Maryland Route 17 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. The state highway begins at the Virginia state line at the Potomac River in Brunswick, where the highway continues south as Virginia State Route 287. MD 17 runs 29.49 miles (47.46 km) north from the Brunswick Bridge to the Frederick–Washington county line near Wolfsville. The state highway serves as the main north–south highway of the Middletown Valley of western Frederick County. MD 17 connects Brunswick and Wolfsville with Rosemont, Burkittsville, Middletown, and Myersville. The state highway also connects those communities with the valley's main east–west highways, which include U.S. Route 340, US 40 Alternate, Interstate 70 (I-70), and US 40.
Salt Creek is a tributary of the Little Wabash River, which it joins near Edgewood, Illinois, near the boundary between Effingham and Clay counties. There are at least two other "Salt Creeks" in Illinois: Salt Creek and Salt Creek.
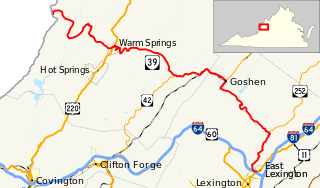
State Route 39 is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of Virginia. The state highway runs 59.17 miles (95.22 km) from the West Virginia state line near Mountain Grove, where the highway continues as West Virginia Route 39, east to U.S. Route 11 in East Lexington. SR 39 connects Lexington with several communities formed around hot springs in Bath County. In Rockbridge County, the state highway passes through the town of Goshen and Goshen Pass, a gorge formed by the Maury River.

Red Hills State Park is an Illinois state park on 967 acres (391 ha) in Lawrence County, Illinois, United States. The park sits at an elevation of 515 feet (157 m). Red Hills State Park is open for year-round recreation including boating, fishing, hunting, hiking and various winter sports. The park includes a restaurant which is open year-round and has banquet facilities.
Stockton–Los Angeles Road, also known as the Millerton Road, Stockton–Mariposa Road, Stockton–Fort Miller Road or the Stockton–Visalia Road, was established about 1853 following the discovery of gold on the Kern River in Old Tulare County. This route between Stockton and Los Angeles followed by the Stockton–Los Angeles Road is described in "ITINERARY XXI. From Fort Yuma to Benicia, California", in The Prairie Traveler: A Hand-book for Overland Expeditions by Randolph Barnes Marcy. The Itinerary was derived from the report of Lieutenant R. S. Williamson on his topographical survey party in 1853, that was in search of a railroad route through the interior of California.

The Juab Valley is a 40-mile (64 km) long valley located on the eastern edge of Juab County, Utah, United States.

Salt Creek is a tributary, 30 miles (48 km) long, of the Middle Fork Willamette River in Lane County in the U.S. state of Oregon. It is named for salt springs along its banks that are used as licks by deer. The stream originates as an outflow of Lower Betty Lake in the forested Cascade Range just southeast of Waldo Lake. From its source, Salt Creek flows generally south, through Gold Lake, to Route 58, which it then follows mainly northwest for about 26 miles (42 km) to its mouth at the Middle Fork Willamette River just below Hills Creek Dam. At Salt Creek Falls—roughly 4 miles (6.4 km) west of Willamette Pass and a little more than 22 miles (35 km) upstream from the mouth—the stream plunges 286 feet (87 m), discharging an average of 50,000 U.S. gallons (190,000 L) of water per minute, or 111 cubic feet per second (3.1 m3/s). Below the falls, the creek enters a narrow canyon shaped by glaciation and basalt lava flows from higher in the Cascades. McCredie Hot Springs, at the former community of McCredie Springs, are natural hot springs along the lower half of Salt Creek beside Route 58.
Mormon Road, also known to the 49ers as the Southern Route, of the California Trail, was a seasonal wagon road first pioneered by a Mormon party from Salt Lake City, Utah led by Jefferson Hunt, that followed the route of Spanish explorers and the Old Spanish Trail across southwestern Utah, northwestern Arizona, southern Nevada and the Mojave Desert of California to Los Angeles in 1847. From 1855, it became a military and commercial wagon route between California and Utah, called the Los Angeles - Salt Lake Road. In later decades this route was variously called the "Old Mormon Road", the "Old Southern Road", or the "Immigrant Road" in California. In Utah, Arizona and Nevada it was known as the "California Road".

The Canajoharie Creek is a river that flows into the Mohawk River in the Village of Canajoharie in the U.S. State of New York. The name "Canajoharie" is a Mohawk language term meaning "the pot that washes itself", referring to the "Canajoharie Boiling Pot", a 20-foot (6.1 m) wide and 10-foot (3.0 m) deep pothole in the Canajoharie Creek, just south of the village of Canajoharie. Bowmans Creek is one main tributary that enters the creek east of the Hamlet of Sprout Brook. The other main tributary is Brimstone Creek which enters the creek north-northwest of the Village of Ames.

Currant Creek is a stream in eastern Juab County and southern Utah County in northern Utah, United States.