
Grewia villosa is a shrub, often scrambling and hardly exceeding 4 m in height. Leaves are fairly large, serrated and heart-shaped. It grows naturally, mainly in dry habitats. It is common in most of the semi-arid parts of Eastern Africa but may now be rare in parts of its natural distribution. Seen in Ein Gedi oasis in Israel, common in South Africa. Its ripe copper-coloured fruits are eaten in East Africa.

Grewioideae is a subfamily of the family Malvaceae and was first described by Hochreutiner. The group is named after its type genus, Grewia, which is named for the English scientist Nehemiah Grew (1641-1712). It contains a number of genera that were previously placed in the defunct family Tiliaceae.

The large flowering plant genus Grewia is today placed by most authors in the mallow family Malvaceae, in the expanded sense as proposed by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group. Formerly, Grewia was placed in either the family Tiliaceae or the Sparrmanniaceae. However, these were both not monophyletic with respect to other Malvales - as already indicated by the uncertainties surrounding placement of Grewia and similar genera - and have thus been merged into the Malvaceae. Together with the bulk of the former Sparrmanniaceae, Grewia is in the subfamily Grewioideae and therein the tribe Grewieae, of which it is the type genus.

Basidiolichens are lichenized members of the Basidiomycota, a much smaller group of lichens than the far more common ascolichens in the Ascomycota. In arctic, alpine, and temperate forests, the most common basidiolichens are in the agaric genus Lichenomphalia and the clavarioid genus Multiclavula. Several lichenized genera occur in tropical regions, the most common being the foliose Dictyonema. Previously basidiolichens had been classified in their own subclass, Basidiolichenes. Molecular based phylogeny does not support classification of the genera together.

Grewia asiatica is a species of Grewia. It was first found in Varanasi India and was taken by Buddhist scholars to other Asian countries and the rest of the world. Grewia celtidifolia was initially considered a mere variety of Phalsa, but is now recognized as a distinct species.
Grewia turbinata is a species of flowering plant in the family Malvaceae sensu lato or Tiliaceae or Sparrmanniaceae. It is found only in Yemen. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry forests.

Lichenomphalia is both a basidiolichen and an agaric genus. Most of the species have inconspicuous lichenized thalli that consist of scattered, small, loose, nearly microscopic green balls or foliose small flakes containing single-celled green algae in the genus Coccomyxa, all interconnected by a loose network of hyphae. The agaric fruit bodies themselves are nonlichenized and resemble other types of omphalinoid mushrooms. These agarics lack clamp connections and do not form hymenial cystidia. The basidiospores are hyaline, smooth, thin-walled, and nonamyloid. Most of the species were originally classified in the genera Omphalina or Gerronema. Historically the species were classified with those other genera in the family, the Tricholomataceae together with the nonlichenized species. Lichenomphalia species can be grouped into brightly colored taxa, with vivid yellow and orange colors, versus the grey brown group, depending upon the microscopic pigmentation deposits. Molecular research comparing DNA sequences now place Lichenomphalia close to the redefined genus Arrhenia, which together with several other genera not traditionally considered to be related, fall within the newly redefined Hygrophoraceae.

Pisonia umbellifera, commonly known as the birdlime tree or bird catcher tree, is a species of plant in the Nyctaginaceae family. It grows throughout the tropical Indo-Pacific. It is native to the Andaman Islands, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Thailand, Vietnam, China, Taiwan, Hawaii and Madagascar and the states of New South Wales and Queensland in Australia. A variegated form is widely cultivated in frost-free climates.

Grevillea sarissa, the wheel grevillea, is a shrub which is native to South Australia and Western Australia. It grows to between 0.6 and 3.5 metres in height and produces yellow, red or pink flowers between August and December in its native range.
Pseudohandelia is a genus of flowering plants in the chamomile tribe within the daisy family.

Netrobalane canopus, the buff-tipped skipper, is a butterfly of the family Hesperiidae. It is found in savannah in Africa, from South Africa to Kenya to Nigeria and southern Sudan.
Caprona pillaana, the ragged skipper, is a butterfly of the family Hesperiidae. It is found in South Africa, Zimbabwe, Botswana, from Mozambique to eastern Africa, Ethiopia and south-western Arabia.
Abantis tettensis, the spotted velvet skipper, is a butterfly of the family Hesperiidae. It is found in South-West Africa, Botswana, Transvaal, northern Cape, from Zimbabwe to Zaire and in Kenya.

Grewia occidentalis, the crossberry, is a small, hardy, attractive tree indigenous to Southern Africa.

Charaxes tiridates, the common blue charaxes, is a butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is found in Senegal, Guinea, Burkina Faso, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Togo, Benin, Nigeria, Equatorial Guinea, Cameroon, Gabon, the Republic of the Congo, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Central African Republic, Sudan, Ethiopia, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Kenya, Tanzania, Angola and Zambia. The habitat consists of lowland evergreen forests and dense savanna.
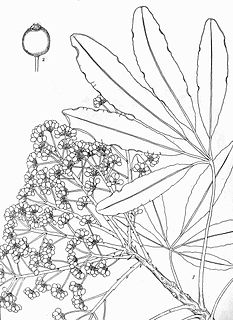
Schefflera umbellifera is an evergreen to semi-deciduous Southern African tree of 15-20m growing in escarpment and coastal forest in Malawi, through eastern Zimbabwe and Mozambique along the east coast to South Africa, as far south as the Garden Route. It belongs to the Araliaceae or Cabbage Tree family and is one of some 600 species in the genus Schefflera, created by J.R.Forst. & G.Forst. in 1776 to honour the 18th century German physician and botanist Johann Peter Ernst von Scheffler of Danzig, and not to be confused with writer and physician Jacob Christoph Scheffler (1698-1745) of Altdorf bei Nürnberg.

Grewia robusta is a multi-stemmed shrub or small tree, up to 3 m high, endemic to the semi-desert Karoo of South Africa, and very similar to Grewia occidentalis. It is one of some 325 species of Grewia in the family Malvaceae, and having a tropical African, Asian and Australian distribution. It is found in the arid regions of the Karoo and Eastern Cape, and generally prefers growing among dry scrub on rocky hillsides.










