Related Research Articles

Grant County is a county located on the northern border of the U.S. state of Oklahoma. As of the 2010 census, the population was 4,527. Its county seat is Medford. Originally designated as part of the Cherokee Outlet, it was named County L in Oklahoma Territory at the time of its opening to non-Indian settlement. A county election renamed it for U.S. President Ulysses S. Grant.
Deer Creek is a town in Grant County, Oklahoma, United States. The population was 130 at the 2010 census, an 11.6 percent decrease from the figure of 147 in 2000. It was named for a nearby stream, which is a tributary of the Salt Fork of the Arkansas River.
The DeQueen and Eastern Railroad , also referred to as the De Queen and Eastern Railroad, is a Class III short-line railroad located in southwest Arkansas and owned by Patriot Rail Company of Jacksonville, Florida. It is operated along with its affiliate, the Texas, Oklahoma and Eastern Railroad in southeast Oklahoma as a single combined railroad with 91 miles of track. Specifically, the DQE continues west from a railway connection at Perkins, Arkansas through Dierks, Lockesburg and De Queen to the Oklahoma border, while the TOE runs from the border through Broken Bow and Wright City to Valliant, Oklahoma.
The Oklahoma City – Ada – Atoka Railway (OCAA) was formed from trackage from Oklahoma City to Atoka via Shawnee, Ada, and Coalgate, Oklahoma. Atoka to Coalgate had been built between 1882 and 1886 as feeder to the old Missouri–Kansas–Texas Railroad (Katy) main line, and Coalgate-Shawnee-Oklahoma City had been constructed by Katy affiliates, and specifically the first 40 miles northwest out of Coalgate having been built by the Texas and Oklahoma Railroad in 1902, and the remaining 78 miles into Oklahoma City having been built in the 1903-1904 timeframe by that line’s successor, the Missouri, Kansas and Oklahoma Railroad Company. However, these properties were not included in the 1923 reorganization of the Katy, and were put in the OCAA instead. The OCAA ended up being sold to the Muskogee Company in 1929, becoming one of the Muskogee Roads.
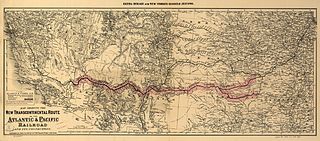
The Atlantic and Pacific Railroad was a U.S. railroad that owned or operated two disjointed segments, one connecting St. Louis, Missouri with Tulsa, Oklahoma, and the other connecting Albuquerque, New Mexico with Needles in Southern California. It was incorporated by the U.S. Congress in 1866 as a transcontinental railroad connecting Springfield, Missouri and Van Buren, Arkansas with California. The central portion was never constructed, and the two halves later became parts of the St. Louis-San Francisco Railway and Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway systems, now both merged into the BNSF Railway.
K-99 is a state highway in the U.S. state of Kansas. The highway runs 234.473 miles (377.348 km) from Oklahoma State Highway 99 (SH-99) at the Oklahoma state line near Chautauqua north to Nebraska Highway 99 (N-99) at the Nebraska state line in Summerfield. K-99 connects Emporia with several smaller county seats to the south and north, including Sedan, Howard, Eureka, Alma, and Westmoreland while passing through the Flint Hills of eastern Kansas.

The Panhandle and Santa Fe Railway (P&SF) is a now-defunct railroad company that was a subsidiary of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (AT&SF), operating primarily in the Texas Panhandle.

The Oregon Railroad and Navigation Company (OR&N) was a railroad that operated a rail network of 1,143 miles (1,839 km) running east from Portland, Oregon, United States, to northeastern Oregon, northeastern Washington, and northern Idaho. It operated from 1896 as a consolidation of several smaller railroads.
K-2 is a 61.516-mile-long (99.000 km) state highway in the south-central portion of the U.S. state of Kansas. Its southern terminus is at an intersection with U.S. Route 281 (US-281) east of Hardtner and its northern terminus is at an intersection with K-42 west of the town of Viola. Along the way K-2 passes through the cities of Kiowa, Hazelton, Anthony and Harper. Between the latter two, it has an overlap with US-160.
K-14 is a 219.3-mile-long (352.9 km) north–south state highway which runs through the central part of the U.S. state of Kansas. K-14's southern terminus is at U.S. Highway 160 (US-160) and K-2 in the city of Harper, and the northern terminus is a continuation as Nebraska Highway 14 (N-14) at the Nebraska border by Superior, Nebraska. Along the way it intersects several major east–west highways in the larger cities it passes through, including US-54 and US-400 by Kingman; US-50, K-61 and K-96 by South Hutchinson; K-156 and K-140 by South Ellsworth; Interstate 70 (I-70) and US-40 north of Ellsworth; K-18 in Lincoln; US-24 and K-9 in Beloit; and US-36 east of Mankato. The northern and southern halves of the highway differ fairly significantly in terms of terrain and landscape. The southern half of K-14 travels over fairly flat terrain in the valley of the Arkansas River. Just north of the intersection with K-4 in southern Ellsworth County, K-14 passes into the Smoky Hills region, traveling over a series of broad, rolling hills, providing several scenic vistas of the surrounding countryside. The portion of the highway between Lincoln and Beloit is particularly hilly.
K-33 is an approximately 10.4-mile-long (16.7 km) north–south state highway in the U.S. state of Kansas. K-33's southern terminus is at K-68 in rural Franklin County east of Ottawa and the northern terminus is at U.S. Route 56 (US-56) in Douglas County, east of Baldwin City and southwest of Kansas City. K-33 provides an important link between US-56 and K-68 to Interstate 35 (I-35) and US-50 in Wellsville. K-33 is a two-lane rural highway for most of its length, except for the section within Wellsville.
K-42 is a 75.061-mile-long (120.799 km) east–west state highway in the U.S. state of Kansas. K-42's western terminus is at U.S. Route 281 (US-281) in Sawyer and the eastern terminus is at Interstate 235 (I-235) in Wichita. Along the way it intersects K-14, a major north–south highway, in Rago and K-2 east of Norwich. The highway is a two-lane highway for most of its length with the exception of the section within Wichita, which is a four-lane divided highway.
K-23 is a 199.117-mile-long (320.448 km) south–north state highway in the U.S. State of Kansas. It starts as a continuation of Oklahoma State Highway 23 (SH-23) and it runs northward to U.S. Route 83 (US-83) and K-383 near Selden. Along the way it intersects several major east–west highways, including US-54 and US-160 in Meade, US-50 and US-400 in Cimarron, US-56 near Montezuma, K-4 near Healy, and Interstate 70 (I-70) and US-40 south of Grainfield. All but about 1.5 miles (2.4 km) of K-23's alignment is maintained by the Kansas Department of Transportation. The entire section within Cimarron is maintained by the city and a section in Hoxie from Utah Street to Queen Street is maintained by the city.
K-47 is an approximately 61.6-mile-long (99.1 km) state highway in the U.S. state of Kansas. It is an east-west route, and connects small towns and cities in southeast Kansas. K-47's western terminus is at the Fredonia city limits, just west of the intersection with U.S. Route 400 (US-400). The eastern terminus is US-69 in Franklin. Along the way, it intersects several major highways including US-75 in Altoona, US-59 south of Erie, and K-7 in Girard. With the exception of the cities K-47 passes through, the highway travels through rural farmland.
K-49 is a 35.354-mile-long (56.897 km) north–south state highway in the U.S. state of Kansas. K-49 begins at U.S. Route 81 (US-81) in Caldwell, and runs north to K-42 in Viola. Along the way, K-49 has a brief overlap with US-160 south of Conway Springs. The majority of the route exists in Sumner County, with only a mile existing in Sedgwick County.
The Kingston and Choctaw Valley Railroad (K&CV) was a short-lived industrial railway serving the lumber industry in the later days of Indian Territory, in what is now Le Flore County in the State of Oklahoma. Twelve miles in length, it ran from Thomasville to rail connections at Howe.
The Texas and Oklahoma Railroad (T&O) existed briefly from its incorporation in mid-1902 to its consolidation with another line at the end of 1903. Its main accomplishment was to construct 40 miles of track northwest out of Coalgate, Oklahoma.
The Texas and Oklahoma Railroad (TXOR), created in 1991, ran between Oklahoma and Texas on rail purchased from the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (AT&SF). Much of the trackage has since been sold or abandoned; however, the railway continues to exist as a shortline carrier operating between Sweetwater, Texas and Maryneal, Texas.
The Hutchinson and Southern Railroad was formed through articles of consolidation dated October 5, 1889 and filed in Kansas two days later. It combined The McPherson, Texas and Gulf Railroad Company, which had been incorporated in Kansas on May 31, 1887, with The Hutchison, Oklahoma and Gulf Railway Company, which had been incorporated in Kansas on March 7, 1889. The railroad originally built 32 miles of standard-gauge line from Hutchinson, Kansas south to Kingman, Kansas, plus 1.1 miles of siding, in 1889. At that point it had two locomotives and two passenger cars, and was headquartered in Hutchinson. In 1890 it gained approval for a scheme to construct track through Anthony, Kansas to the state line, then through Indian Territory and specifically through the towns of Pond Creek and Guthrie, and terminating at a point in Grayson County, Texas, possibly Denison. It finished trackage to the state line in 1890, giving it 82.2 miles of rails. But the Indian Territory portion of the line ended up terminating in Wakita, Oklahoma in February of 1897, just 8.5 miles south of the Kansas-Oklahoma state line.
The Hutchinson and Southern Railway was incorporated under the general laws of the State of Kansas on December 21, 1897. On January 21, 1898 it acquired at foreclosure the assets of the Hutchinson and Southern Railroad Company, which had built 90.7 miles of trackage from Hutchinson, Kansas south through Kingman, Kansas and Anthony, Kansas to terminate at Wakita, Oklahoma. In the 1898-1899 timeframe, it also acquired all the assets of the Gulf Railroad Company, which had built 36.7 miles of track from Wakita to Blackwell, Oklahoma.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Railroads of Oklahoma, June 6, 1870 to April 1, 1978. State of Oklahoma Department of Transportation, Survey Division. April 1, 1978. pp. 29–38.
- ↑ "Deer Creek". Linda D. Wilson, Oklahoma Historical Society. Retrieved May 21, 2022.
- ↑ "Kansas Railroad Map Historic" (PDF). Kansas Department of Transportation. Retrieved May 23, 2022.
- ↑ "Oklahoma 2018-2020 State Railroad Map" (PDF). Oklahoma Department of Transportation. Retrieved December 13, 2021.