
In polymer chemistry and materials science, resin is a solid or highly viscous substance of plant or synthetic origin that is typically convertible into polymers. Resins are usually mixtures of organic compounds. This article focuses on naturally occurring resins.

Gum arabic, also known as gum sudani, acacia gum, Arabic gum, gum acacia, acacia, Senegal gum, Indian gum, and by other names, is a natural gum originally consisting of the hardened sap of two species of the Acacia tree, Senegalia senegal and Vachellia seyal. The term "gum arabic" does not legally indicate a particular botanical source, however. The gum is harvested commercially from wild trees, mostly in Sudan (80%) and throughout the Sahel, from Senegal to Somalia. The name "gum Arabic" was used in the Middle East at least as early as the 9th century. Gum arabic first found its way to Europe via Arabic ports, so retained its name.

Chewing gum is a soft, cohesive substance designed to be chewed without being swallowed. Modern chewing gum is composed of gum base, sweeteners, softeners/plasticizers, flavors, colors, and, typically, a hard or powdered polyol coating. Its texture is reminiscent of rubber because of the physical-chemical properties of its polymer, plasticizer, and resin components, which contribute to its elastic-plastic, sticky, chewy characteristics.

Frankincense is an aromatic resin used in incense and perfumes, obtained from trees of the genus Boswellia in the family Burseraceae. The word is from Old French franc encens. There are several species of Boswellia that produce true frankincense: Boswellia sacra, B. frereana, B. serrata, and B. papyrifera. Resin from each is available in various grades, which depends on the time of harvesting. The resin is hand-sorted for quality.

A thickening agent or thickener is a substance which can increase the viscosity of a liquid without substantially changing its other properties. Edible thickeners are commonly used to thicken sauces, soups, and puddings without altering their taste; thickeners are also used in paints, inks, explosives, and cosmetics.

Sterculia is a genus of flowering plants in the mallow family, Malvaceae: subfamily Sterculioideae. Members of the genus are colloquially known as tropical chestnuts. Sterculia may be monoecious or dioecious, and its flowers unisexual or bisexual.

Tragacanth is a natural gum obtained from the dried sap of several species of Middle Eastern legumes of the genus Astragalus, including A. adscendens, A. gummifer, A. brachycalyx, and A. tragacantha. Some of these species are known collectively under the common names "goat's thorn" and "locoweed". The gum is sometimes called Shiraz gum, shiraz, gum elect or gum dragon. The name derives from the Greek words tragos and akantha ("thorn"). Iran is the biggest producer of this gum.

Tara spinosa, commonly known as tara (Quechua), also known as Peruvian carob or spiny holdback, is a small leguminous tree or thorny shrub native to Peru. T. spinosa is cultivated as a source of tannins based on a galloylated quinic acid structure. This chemical structure has been confirmed also by LC-MS. It is also grown as an ornamental plant because of its large colorful flowers and pods.
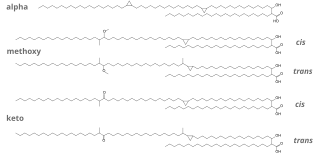
Cyclopropane fatty acids (CPA) are a subgroup of fatty acids that contain a cyclopropane group. Although they are usually rare, the seed oil from lychee contains nearly 40% CPAs in the form of triglycerides.

Locust bean gum is a galactomannan vegetable gum extracted from the seeds of the carob tree and used as a thickening agent in food technology.

Kino is a botanical gum produced by various trees and other plants, particularly bloodwood species of eucalypts and Pterocarpus, in reaction to mechanical damage, and which can be tapped by incisions made in the trunk or stalk. Many Eucalyptus, Angophora and Corymbia species are commonly referred to as 'bloodwoods', as the kino usually oozes out a very dark red colour. Kino flow in angiosperms contrasts with resin flow in conifers. The word kino is of Indian origin. In Australia, "red gum" is a term for kino from bloodwood trees and red acaroid resin from Xanthorrhoea spp.

Sterculia apetala, commonly known as the Panama tree, camoruco, manduvi tree or anacagüita, is a species of flowering plants in the family Malvaceae. It is found in Central and South America, as well as the Caribbean islands. Sterculia apetala is recognized as the national tree of the Republic of Panama.

Sterculia foetida is a soft wooded tree that can grow up to 35 metres tall. Common names for the plant are the bastard poon tree, java olive tree, hazel sterculia, wild almond tree, and skunk tree.

Astragalus gummifer, is a small woody evergreen shrub, with a typical height and spread of 30 cm at maturity, indigenous to western Asia, specifically Iraq and Turkey. This nitrogen fixing plant bears hermaphroditic flowers, which are bee-pollinated. It has many medical, culinary, and material uses.

The Indian Institute of Natural Resins and Gums, formerly known as the Indian Lac Research Institute, is an autonomous institute, established under the umbrella of Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) by the Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India for advanced research on lac and other natural resins and gums. The Institute is located at Namkum, Ranchi in Jharkhand, India.

Sterculia urens is a species of plant in the family Malvaceae. It is native to India and has been introduced into Burma. A small to medium-sized tree with a pale-coloured trunk, it is commonly known as the bhutyā in Marathi, kulu, Indian tragacanth, gum karaya, katira, sterculia gum or kateera gum. The specific name urens refers to the stinging hairs present on the flowers.

Sterculia setigera is a deciduous tree species within the Malvaceae family. It commonly occurs in the Sahelo-Sudan and Guinea savannah zones of Tropical Africa. Among the Hausa people it is known as Kukkuki. It is an important tree crop in Senegal as Gum karaya obtained from the woody species is exported from the country.

















