
The Rauma is a river that runs through Romsdalen, a valley in Møre og Romsdal and Innlandet counties in Norway. It runs for 68 kilometres (42 mi) from Lesjaskogsvatnet, a lake in the municipality of Lesja, to the town of Åndalsnes in the municipality of Rauma. The river was once famous for its salmon-fishing, but since an infection with Gyrodactylus salaris only 5 to 10% of the original stock survives. The salmon runs up to the Slettafossen, a 16-metre (52 ft) high combination of waterfalls and rapids more than 42 kilometres (26 mi) upriver from the estuary.

Monogeneans are a group of ectoparasitic flatworms commonly found on the skin, gills, or fins of fish. They have a direct lifecycle and do not require an intermediate host. Adults are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive structures.

Åndalsnes (help·info) is a town in Rauma Municipality in Møre og Romsdal county, Norway. Åndalsnes is in the administrative center of Rauma Municipality. It is located along the Isfjorden, at the mouth of the river Rauma, at the north end of the Romsdalen valley. The village of Isfjorden lies about 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) to the east, Veblungsnes lies just to the west across the Rauma, and Innfjorden lies about 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) to the southwest via the European Route E136 highway.

Numedalslågen is a river located in the counties of Vestfold and Telemark and Viken in southeastern Norway. It is one of the longest rivers in Norway.

The Vefsnfjord or Vefsnfjorden is a fjord in the Helgeland traditional district of Nordland county, Norway. It is about 51 kilometres (32 mi) long, reaching a maximum depth of about 440 metres (1,440 ft) below sea level. The fjord flows through the municipalities of Alstahaug, Leirfjord, and Vefsn.

Gyrodactylus salaris, commonly known as salmon fluke, is a tiny monogenean ectoparasite which lives on the body surface of freshwater fish. This leech-like parasite has been implicated in the reduction of Atlantic salmon populations in the Norwegian fjords. It also parasitises other species, including rainbow trout. G. salaris requires fresh water, but can survive in brackish water for up to 18 hours.

Vefsna (Norwegian), also known as Vaapstenjeanoe (Southern Sami) or Vapstälven (Swedish), is the largest river in Nordland county, Norway. It is 163 kilometres (101 mi) long and drains a watershed of 4,122 square kilometres (1,592 sq mi). Its headwaters lie in the mountains of Børgefjell National Park at the lake Simskardvatnet. The river runs through the municipalities of Hattfjelldal, Grane, and Vefsn. The southern parts of the river are sometimes called the river Susna. The river flows north, not far from the Swedish border, and some of the minor tributaries come from Sweden. At the town of Mosjøen, the river discharges into the Vefsnfjord. The Laksforsen waterfall lies along its course.
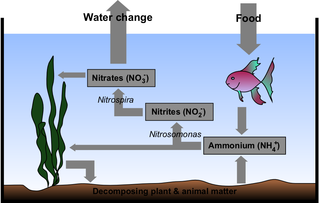
Ornamental fish kept in aquariums are susceptible to numerous diseases. Due to their generally small size and the low cost of replacing diseased or dead fish, the cost of testing and treating diseases is often seen as more trouble than the value of the fish.
Dactylogyrus is a genus of monogeneans in the Dactylogyridae family.

Abbottina rivularis is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Cyprinidae, the carps and minnows. It is native to China, Korea, and Japan. It has been introduced to the Mekong River Basin and it is also known from rivers in Turkmenistan.
Gyrodactylus gondae is a species of monogenean ectoparasites. It was found in Pomatoschistus minutus and Pomatoschistus lozanoi in European coastal waters.
Gyrodactylus flavescensis is a species of monogenean ectoparasites. It was found in Gobiusculus flavescens in European coastal waters.
Gyrodactylus branchialis is a species of monogenean ectoparasites. It was found in Pomatoschistus microps in European coastal waters.

The Monopisthocotylea are a subclass of parasitic flatworms in the class Monogenea.

Gyrodactylus is a genus of parasitic flatworms in the family Gyrodactylidae.
Gyrodactylus turnbulli is an ectoparasite from the class Monogenea, is part of the phylum Platyhelminthes, and from the genus Gyrodactylus. It only requires one host to transmit an infection; however, since this parasite lacks oncomiracidium, it must rely on either the adult or subadult for spread of infection. Found in freshwater, this flatworm is commonly found on the gills and fins of the guppy, Poecilia reticulata. G. turnbulli was said to be host specific, but an experiment where parasitologists artificially infected guppies suggests that the parasite can infect a wider range of species. This ability is achievable by host switching, which promotes speciation.

Gyrodactylus leptorhynchi is a small monogenean obligate ectoparasite which parasitizes freshwater Bay Pipefish. Gyrodactylus leptorhynchi is the seventh Gyrodactylus species known to infect Bay Pipefish and the first characterized along the Pacific coast of North America. The parasite can get into captive fish environments, such as fish farms and aquariums, where it may spread in as little as 10 days. Gyrodactylus species are known to centralize on the brood pouch in male fish, this may allow. for transmission to newly hatched young. However, in Gyrodactylus leptorhynchi the parasite was found mostly found attached to body surfaces such as the dorsal fins.
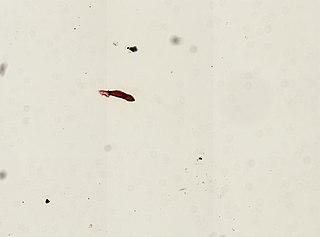
Gyrodactylus elegans is a species of monogenean parasitic flatworms in the family Gyrodactylidae.
Fundulotrema is a genus of monogeneans in the family Gyrodactylidae.











