
Parasitology is the study of parasites, their hosts, and the relationship between them. As a biological discipline, the scope of parasitology is not determined by the organism or environment in question but by their way of life. This means it forms a synthesis of other disciplines, and draws on techniques from fields such as cell biology, bioinformatics, biochemistry, molecular biology, immunology, genetics, evolution and ecology.

Monogeneans are a group of ectoparasitic flatworms commonly found on the skin, gills, or fins of fish. They have a direct lifecycle and do not require an intermediate host. Adults are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive structures.

Numedalslågen is a river located in the counties of Vestfold and Telemark and Viken in southeastern Norway. It is one of the longest rivers in Norway.
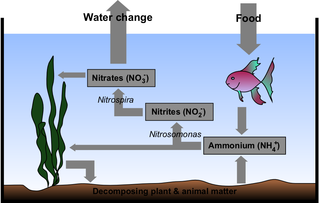
Ornamental fish kept in aquariums are susceptible to numerous diseases. Due to their generally small size and the low cost of replacing diseased or dead fish, the cost of testing and treating diseases is often seen as more trouble than the value of the fish.

Alcolapia grahami, the Lake Magadi tilapia or Graham's cichlid, is a vulnerable species of fish in the family Cichlidae. It is specialised to live in hot, alkaline waters in springs and lagoons around hypersaline lakes.
The Norwegian Black List (Fremmedartslista) is an overview of alien species in Norway, with ecological risk assessments for some of the species. The Norwegian Black List was first published in 2007 by the Norwegian Biodiversity Information Centre and developed in cooperation with 18 scientific experts from six research institutions.
Dactylogyrus is a genus of monogeneans in the Dactylogyridae family.

Abbottina rivularis is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Cyprinidae, the carps and minnows. It is native to China, Korea, and Japan. It has been introduced to the Mekong River Basin and it is also known from rivers in Turkmenistan.
Gyrodactylus gondae is a species of monogenean ectoparasites. It was found in Pomatoschistus minutus and Pomatoschistus lozanoi in European coastal waters.
Gyrodactylus arcuatoides is an ectoparasite. It was found on the sand goby in European coastal waters.
Gyrodactylus branchialis is a species of monogenean ectoparasites. It was found in Pomatoschistus microps in European coastal waters.

Gyrodactylidae is a family of flatworms in the order Gyrodactylidea.

The Monopisthocotylea are a subclass of parasitic flatworms in the class Monogenea.

Gyrodactylus is a genus of parasitic flatworms in the family Gyrodactylidae.
Alexandr Vladimirovich Gussev, sometimes spelled Gusev in the literature, was a Russian helminthologist specialist of monogeneans.
Gyrodactylus turnbulli is an ectoparasite from the class Monogenea, is part of the phylum Platyhelminthes, and from the genus Gyrodactylus. It only requires one host to transmit an infection; however, since this parasite lacks oncomiracidium, it must rely on either the adult or subadult for spread of infection. Found in freshwater, this flatworm is commonly found on the gills and fins of the guppy, Poecilia reticulata. G. turnbulli was said to be host specific, but an experiment where parasitologists artificially infected guppies suggests that the parasite can infect a wider range of species. This ability is achievable by host switching, which promotes speciation.

Gyrodactylus leptorhynchi is a small monogenean obligate ectoparasite which parasitizes freshwater Bay Pipefish. Gyrodactylus leptorhynchi is the seventh Gyrodactylus species known to infect Bay Pipefish and the first characterized along the Pacific coast of North America. The parasite can get into captive fish environments, such as fish farms and aquariums, where it may spread in as little as 10 days. Gyrodactylus species are known to centralize on the brood pouch in male fish, this may allow. for transmission to newly hatched young. However, in Gyrodactylus leptorhynchi the parasite was found mostly found attached to body surfaces such as the dorsal fins.
Gyrodactylus elegans is a species of monogenean parasitic flatworms in the family Gyrodactylidae.
Fundulotrema is a genus of monogeneans in the family Gyrodactylidae.








