Related Research Articles

HD 209458 is a star with an orbiting exoplanet in the constellation Pegasus. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 7.65 and an absolute magnitude of 4.28. Because it is located at a distance of 157 light-years from the Sun as measured via parallax, it is not visible to the unaided eye. With good binoculars or a small telescope it should be easily detectable. The system is drifting closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −14.8 km/s.
14 Herculis or 14 Her is a K-type main-sequence star 58.4 light-years away in the constellation Hercules. It is also known as HD 145675. Because of its apparent magnitude, of 6.61 the star can be very faintly seen with the naked eye. As of 2021, 14 Herculis is known to host two exoplanets in orbit around the star.
HD 37124 is a star in the equatorial constellation of Taurus, positioned about a half degree to the SSW of the bright star Zeta Tauri. The apparent visual magnitude of this star is 7.68, which is too dim to be visible to the naked eye. It is located at a distance of 103 light years from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −23 km/s. Three extrasolar planets have been found to orbit the star.
HD 168443 is an ordinary yellow-hued star in the Serpens Cauda segment of the equatorial constellation of Serpens. It is known to have two substellar companions. With an apparent visual magnitude of 6.92, the star lies just below the nominal lower brightness limit of visibility to the normal human eye. This system is located at a distance of 127 light years from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −48.7 km/s.
79 Ceti, also known as HD 16141, is a binary star system located 123 light-years from the Sun in the southern constellation of Cetus. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +6.83, which puts it below the normal limit for visibility with the average naked eye. The star is drifting closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −51 km/s.
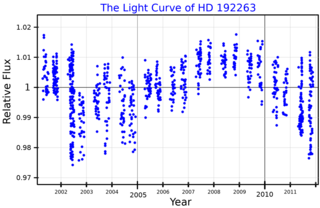
HD 192263 is a star with an orbiting exoplanet in the equatorial constellation of Aquila. The system is located at a distance of 64 light years from the Sun based on parallax measurements, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of −10.7 km/s. It has an absolute magnitude of 6.36, but at that distance the apparent visual magnitude is 7.79. It is too faint to be viewed with the naked eye, but with good binoculars or small telescope it should be easy to spot.
HD 177830 is a 7th magnitude binary star system located approximately 205 light-years away in the constellation of Lyra. The primary star is slightly more massive than the Sun, but cooler being a type K star. Therefore, it is a subgiant clearly more evolved than the Sun. In visual light it is four times brighter than the Sun, but because of its distance, about 204 light years, it is not visible to the unaided eye. With binoculars it should be easily visible.
HD 210277 is a single star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 6.54, which makes it a challenge to view with the naked eye, but it is easily visible in binoculars. The star is located at a distance of 69.6 light years from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −20.9 km/s.
109 Piscium is a yellow hued G-type main-sequence star located about 108 light-years away in the zodiac constellation of Pisces. It is near the lower limit of visibility to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 6.27. The star is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −45.5 km/s. It has one known exoplanet.
23 Librae b, also known as HD 134987 b, is an extrasolar Jovian planet discovered in November 1999 orbiting the star 23 Librae. It orbits in its star's habitable zone.

79 Ceti b is an extrasolar planet orbiting 79 Ceti every 75 days. Discovered along with HD 46375 b on March 29, 2000, it was the joint first known extrasolar planet to have minimum mass less than the mass of Saturn.

109 Piscium b is a long-period extrasolar planet discovered in orbit around 109 Piscium. It is about 5.74 times the mass of Jupiter and is likely to be a gas giant. As is common for long-period planets discovered around other stars, it has an orbital eccentricity greater than that of Jupiter.
HD 222582 is a multiple star system in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. It is invisible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 7.7, but can be viewed with binoculars or a small telescope. The system is located at a distance of 137 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +12 km/s. It is located close enough to the ecliptic that it is subject to lunar occultations.
HD 37124 c is an extrasolar planet approximately 103 light-years away in the constellation of Taurus. The planet was discovered in 2002 orbiting the star HD 37124. The planet is most likely to be a gas giant.
HD 37124 d is an extrasolar planet approximately 103 light-years away in the constellation of Taurus. The planet was discovered in 2005 orbiting the star HD 37124 in a long-period orbit. Based on its mass, it is considered to be a gas giant. An alternative solution to the radial velocities gives a period of 29.92 days and a minimum mass 17% that of Jupiter.
HD 222582 b is an extrasolar planet that is 8.37 times the mass of Jupiter orbiting the star HD 222582. The orbital period is 572 days and orbits at a semimajor axis of 1.35 AU in one of the most eccentric orbits of the known planets.
HD 210277 b is an extrasolar planet orbiting the star HD 210277. It was discovered in September 1998 by the California and Carnegie Planet Search team using the highly successful radial velocity method. The planet is at least 24% more massive than Jupiter. The mean distance of the planet from the star is slightly more than Earth's distance from the Sun. However, the orbit is very eccentric, so at periastron this distance is almost halved, and at apastron it is as distant as Mars is from the Sun.
HD 40979 b is an extrasolar planet orbiting the star HD 40979, was detected from the Lick and Keck observatories and photometric observations at Fairborn Observatory reveal low-amplitude brightness variations in HD 40979. It is thought to be a large gas giant planet. It was discovered in 2002 by Debra Fischer.
HD 46375 b is an extrasolar planet located approximately 109 light-years away in the constellation of Monoceros, orbiting the star HD 46375. With 79 Ceti b on March 29, 2000, it was joint first known extrasolar planet less massive than Saturn orbiting a normal star. The planet is a "hot Jupiter", a type of planet that orbits very close to its parent star. In this case the orbital distance is only a tenth that of the planet Mercury. No transit of the planet has been detected, so its inclination must be less than 83°. Because the inclination is unknown, the true mass of the planet is not known.
HD 192263 b, also named Beirut, is a gas giant planet with a mass about three quarters that of Jupiter mass. It orbits the star in a circular orbit completing one revolution in 24 days or so. It was discovered in 2000 by the Geneva Extrasolar Planet Search team. The planet was independently detected by the California and Carnegie Planet Search team.
References
- ↑ "Astronomers discover six new planets orbiting nearby stars" (Press release). Kamuela, Hawaii: W. M. Keck Observatory. November 1, 1999. Archived from the original on December 2, 2018. Retrieved December 19, 2017.
- 1 2 Vogt, Steven S.; Marcy, Geoffrey W.; Butler, R. Paul; Apps, Kevin (20 June 2000). "Six New Planets from the Keck Precision Velocity Survey". The Astrophysical Journal. 536 (2): 902–914. arXiv: astro-ph/9911506 . Bibcode:2000ApJ...536..902V. doi:10.1086/308981. S2CID 119375519.