Related Research Articles

60 Sagittarii is a suspected binary star system in the southern constellation of Sagittarius. It has the Bayer designation A Sagittarii, while 60 Sagittarii is the Flamsteed designation. This naked eye object forms the northwest corner of the asterism called the Terebellum and, with an apparent magnitude of approximately 4.84, it is the dimmest of the four stars in the Terebellum. It is located 379 light years from the Sun, based on parallax, but is moving closer with a radial velocity of −51 km/s.
Epsilon Telescopii, Latinized from ε Telescopii, is a solitary, orange-hued star in the southern constellation of Telescopium. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.53. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 7.80 mas as seen from Earth, it is located roughly 420 light years from the Sun, give or take 30 light years.
Iota Tucanae is a solitary star in the southern constellation of Tucana. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 10.72 mas as seen from Earth, it is located around 304 light years from the Sun. With an apparent visual magnitude of +5.33, it is faintly visible to the naked eye.

Zeta Volantis is a binary star system in the southern constellation of Volans. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 3.93, which is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. Based upon parallax measurements, it is approximately 141 light years from the Sun. The companion is a magnitude 9.7 star at an angular separation of 16.7″. Based upon their motion through space, this system made its perihelion passage some 858,000 years ago when it came within 22 ly (6.6 pc) of the Sun. It is currently moving away with a radial velocity of 48 km/s.

66 Aquarii is a single star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. 66 Aquarii is the Flamsteed designation though the star also bears the Bayer designation of g1 Aquarii. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, orange-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.673. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 7.53 milliarcseconds, the distance to this star is about 430 light-years.
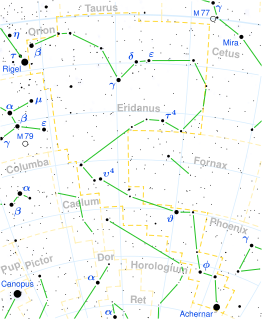
Upsilon² Eridani, officially named Theemin, is a star in the constellation of Eridanus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.8. Based upon parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 66 parsecs from the Sun.
Zeta Caeli, Latinized from ζ Caeli, is an orange-hued star in the constellation Caelum with a visual magnitude of +6.36. It is an evolved K-type giant star and a member of the Milky Way's thick disk population. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 7.59 mas as seen from Earth, this star is located about 430 light years from the Sun.
HD 94510 is a single star in the southern constellation of Carina, positioned near the northern constellation border with Vela. It has the Bayer designation u Carinae; HD 94520 is the identifier from the Henry Draper Catalogue. This object has an orange hue and is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around +3.78. The star is located at a distance of 95 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +8 km/s.
HR 3159 is a single star in the southern constellation of Carina, positioned near the southern constellation border with Volans. It has the Bayer designation D Carinae; HR 3159 is the Bright Star Catalogue designation. This object has a blue-white hue and is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.81. It is located at a distance of approximately 499 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of 22 km/s.
HD 96566 is a single star in the southern constellation of Carina. It has the Bayer designation z1 Carinae; HD 96566 is the identifier from the Henry Draper Catalogue. This object has a yellow hue and is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.62. The star is located at a distance of approximately 376 light years from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −1 km/s. It has an absolute magnitude of −0.81.
V448 Carinae is a single star in the constellation Carina. It has the Bayer designation O Carinae, while V448 Carinae is the variable star designation. This object has an orange hue and is dimly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 5.60. It is located at a distance of approximately 680 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of around +26 km/s.
Beta Mensae, Latinized from β Mensae, is the third-brightest star in the constellation of Mensa. Despite this, it is only faintly visible to the naked eye, appearing as a dim, yellow-hued point of light with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.31. The star is positioned near the southwest edge of the Large Magellanic Cloud, but it does not form part of this much more distant satellite galaxy. Based upon an annual parallax shift of just 4.11 mas as seen from the Earth, the star is located at a distance of roughly 790 light years from the Sun. It is moving closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −11 km/s.
Eta Circini, Latinized from η Circini, is the Bayer designation for a solitary star located in the southern constellation of Circinus. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.17. The distance to this star, as determined from an annual parallax shift of 11.82 mas, is around 276 light years.

Eta Reticuli is a solitary star in the southern constellation of Reticulum. With an apparent visual magnitude of 5.22, it is faintly visible to the naked eye on a dark night. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 8.48 mas, it is located at a distance of roughly 385 light years from the Sun. It may be a member of the high-velocity Zeta Herculis Moving Group of stars that share a common motion through space.

Zeta Pyxidis (ζ Pyxidis) is a wide binary star system in the southern constellation of Pyxis. It is visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of +4.88. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 13.35 mas as seen from Earth, it is located around 244 light years from the Sun.
Iota Eridani is a solitary star in the constellation Eridanus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent magnitude of 4.11. With an annual parallax shift of 0.02165 arcseconds, it lies at an estimated distance of about 151 light years.
Delta1 Gruis, Latinized from δ1 Gruis, is a candidate binary star system in the constellation Grus. With a peak apparent visual magnitude of 3.97, it is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye at night. The distance to this system, as determined using an annual parallax shift of 10.54 mas as seen from the Earth, is around 309 light years. It is gradually moving away from the Sun with a radial velocity of +4.9 km/s.
ν Gruis, Latinised as Nu Gruis, is a solitary, yellow-hued star in the southern constellation of Grus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.47. The distance to this star, as determined using an annual parallax shift of 11.6 mas as seen from the Earth, is 280 light years. It is drifting further away with a heliocentric radial velocity of +11 km/s.
λ Pictoris, Latinised as Lambda Pictoris, is a solitary, orange-hued star in the southern constellation of Pictor. It is visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of +5.29. With an annual parallax shift of 8.71 mas as seen from the Earth, it is located around 374 light years from the Sun. At the estimated age of 2.24 billion years old, it is an evolved K-type giant star with a stellar classification of K0/1 III. Lambda Pictoris has 2.2 times the mass of the Sun and is radiating 112 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 4,581 K.
ξ Mensae, Latinized as Xi Mensae, is a single star in the southern circumpolar constellation of Mensa. It has a yellow-orange hue and is just barely visible to the naked eye as a dim point of light with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.84. This object is located about 366 light years away from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −5 km/s.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 van Leeuwen, F. (2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv: 0708.1752 , Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters, 38 (5): 331, arXiv: 1108.4971 , Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015.
- ↑ Houk, Nancy (1979), Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars, 3, Ann Arbor, Michigan: Dept. of Astronomy, University of Michigan, Bibcode:1982mcts.book.....H.
- 1 2 3 Alves, S.; et al. (April 2015), "Determination of the spectroscopic stellar parameters for 257 field giant stars", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 448 (3): 2749–2765, arXiv: 1503.02556 , Bibcode:2015MNRAS.448.2749A, doi:10.1093/mnras/stv189.
- 1 2 "HD 83380". SIMBAD . Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg . Retrieved 2018-05-09.