The HACEK organisms are a group of fastidious Gram-negative bacteria that are an unusual cause of infective endocarditis, which is an inflammation of the heart due to bacterial infection. HACEK is an abbreviation of the initials of the genera of this group of bacteria: Haemophilus, Aggregatibacter, Cardiobacterium, Eikenella, Kingella. The HACEK organisms are a normal part of the human microbiota, living in the oral-pharyngeal region.
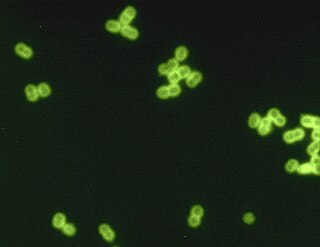
Streptococcus pneumoniae, or pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, spherical bacteria, alpha-hemolytic member of the genus Streptococcus. They are usually found in pairs (diplococci) and do not form spores and are non motile. As a significant human pathogenic bacterium S. pneumoniae was recognized as a major cause of pneumonia in the late 19th century, and is the subject of many humoral immunity studies.

Haemophilus influenzae is a Gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillary, facultatively anaerobic, capnophilic pathogenic bacterium of the family Pasteurellaceae. The bacteria are mesophilic and grow best at temperatures between 35 and 37 °C.

Lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI) is a term often used as a synonym for pneumonia but can also be applied to other types of infection including lung abscess and acute bronchitis. Symptoms include shortness of breath, weakness, fever, coughing and fatigue. A routine chest X-ray is not always necessary for people who have symptoms of a lower respiratory tract infection.

The bacterial capsule is a large structure common to many bacteria. It is a polysaccharide layer that lies outside the cell envelope, and is thus deemed part of the outer envelope of a bacterial cell. It is a well-organized layer, not easily washed off, and it can be the cause of various diseases.

Staphylococcus haemolyticus is a member of the coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS). It is part of the skin flora of humans, and its largest populations are usually found at the axillae, perineum, and inguinal areas. S. haemolyticus also colonizes primates and domestic animals. It is a well-known opportunistic pathogen, and is the second-most frequently isolated CoNS. Infections can be localized or systemic, and are often associated with the insertion of medical devices. The highly antibiotic-resistant phenotype and ability to form biofilms make S. haemolyticus a difficult pathogen to treat. Its most closely related species is Staphylococcus borealis.

Haemophilus is a genus of Gram-negative, pleomorphic, coccobacilli bacteria belonging to the family Pasteurellaceae. While Haemophilus bacteria are typically small coccobacilli, they are categorized as pleomorphic bacteria because of the wide range of shapes they occasionally assume. These organisms inhabit the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, mouth, vagina, and intestinal tract. The genus includes commensal organisms along with some significant pathogenic species such as H. influenzae—a cause of sepsis and bacterial meningitis in young children—and H. ducreyi, the causative agent of chancroid. All members are either aerobic or facultatively anaerobic. This genus has been found to be part of the salivary microbiome.
Brazilian purpuric fever (BPF) is an illness of children caused by the bacterium Haemophilus influenzae biogroup aegyptius which is ultimately fatal due to sepsis. BPF was first recognized in the São Paulo state of Brazil in 1984. At this time, young children between the ages of 3 months and 10 years were contracting a strange illness which was characterized by high fever and purpuric lesions on the body. These cases were all fatal, and originally thought to be due to meningitis. It was not until the autopsies were conducted that the cause of these deaths was confirmed to be infection by H. influenzae aegyptius. Although BPF was thought to be confined to Brazil, other cases occurred in Australia and the United States during 1984–1990.

N-Acetylneuraminic acid is the predominant sialic acid found in human cells, and many mammalian cells. Other forms, such as N-Glycolylneuraminic acid, may also occur in cells.
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobe, nonmotile bacterium that is often found in association with localized aggressive periodontitis, a severe infection of the periodontium. It is also suspected to be involved in chronic periodontitis. Less frequently, A. actinomycetemcomitans is associated with nonoral infections such as endocarditis. Its role in aggressive periodontitis was first discovered by Danish-born periodontist Jørgen Slots, a professor of dentistry and microbiology at the University of Southern California School of Dentistry.

The Haemophilus influenzae type B vaccine, also known as Hib vaccine, is a vaccine used to prevent Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) infection. In countries that include it as a routine vaccine, rates of severe Hib infections have decreased more than 90%. It has therefore resulted in a decrease in the rate of meningitis, pneumonia, and epiglottitis.

Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of these pathogenic species in humans is estimated to be fewer than a hundred. By contrast, several thousand species are part of the gut flora present in the digestive tract.
Haemophilus meningitis is a form of bacterial meningitis caused by the Haemophilus influenzae bacteria. It is usually associated with Haemophilus influenzae type b. Meningitis involves the inflammation of the protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. Haemophilus meningitis is characterized by symptoms including fever, nausea, sensitivity to light, headaches, stiff neck, anorexia, and seizures. Haemophilus meningitis can be deadly, but antibiotics are effective in treating the infection, especially when cases are caught early enough that the inflammation has not done a great deal of damage. Before the introduction of the Hib vaccine in 1985, Haemophilus meningitis was the leading cause of bacterial meningitis in children under the age of five. However, since the creation of the Hib vaccine, only two in every 100,000 children contract this type of meningitis. Five to ten percent of cases can be fatal, although the average mortality rate in developing nations is seventeen percent, mostly due to lack of access to vaccination as well as lack of access to medical care needed to combat the meningitis.

Staphylococcus capitis is a coagulase-negative species (CoNS) of Staphylococcus. It is part of the normal flora of the skin of the human scalp, face, neck, scrotum, and ears and has been associated with prosthetic valve endocarditis, but is rarely associated with native valve infection.

An acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis (AECB), is a sudden worsening of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) symptoms including shortness of breath, quantity and color of phlegm that typically lasts for several days.

In molecular biology, trimeric autotransporter adhesins (TAAs), are proteins found on the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Bacteria use TAAs in order to infect their host cells via a process called cell adhesion. TAAs also go by another name, oligomeric coiled-coil adhesins, which is shortened to OCAs. In essence, they are virulence factors, factors that make the bacteria harmful and infective to the host organism.

In bacteria, phasevarions mediate a coordinated change in the expression of multiple genes or proteins. This occurs via phase variation of a single DNA methyltransferase. Phase variation of methyltransferase expression results in differential methylation throughout the bacterial genome, leading to variable expression of multiple genes through epigenetic mechanisms.
N-glycosyltransferase is an enzyme in prokaryotes which transfers individual hexoses onto asparagine sidechains in substrate proteins, using a nucleotide-bound intermediary, within the cytoplasm. They are distinct from regular N-glycosylating enzymes, which are oligosaccharyltransferases that transfer pre-assembled oligosaccharides. Both enzyme families however target a shared amino acid sequence asparagine—-any amino acid except proline—serine or threonine (N–x–S/T), with some variations.
Actinobacillus equuli is a gram-negative, non-motile rod bacteria from the family Pasteurellaceae.
Janet Gilsdorf is an American pediatric infectious diseases physician, scientist, and writer at the University of Michigan. Her research has focused on the pathogenic, molecular, and epidemiologic features of the bacterium Haemophilus influenzae. She served as the Director of the Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases in the University of Michigan Health System from 1989 to 2012 and Co-Director of the Center for Molecular and Clinical Epidemiology of Infectious Diseases at the School of Public Health at the University of Michigan from 2000 – 2015. In addition to her scientific publications, she is also the author of two novels, one memoir, one non-fiction book, and a number of medically-oriented essays.











