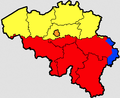
| Hainaut | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Province of Belgium | |||
| |||
 | |||
| Coordinates: 50°30′N3°55′E / 50.5°N 3.92°E Coordinates: 50°30′N3°55′E / 50.5°N 3.92°E | |||
| Country | |||
| Region | |||
| Capital | Mons | ||
| Government | |||
| • Governor | Tommy Leclercq | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 3,800 km2 (1,500 sq mi) | ||
| Population (1 January 2017) [1] | |||
| • Total | 1,339,562 | ||
| • Density | 350/km2 (910/sq mi) | ||
| Website | www | ||
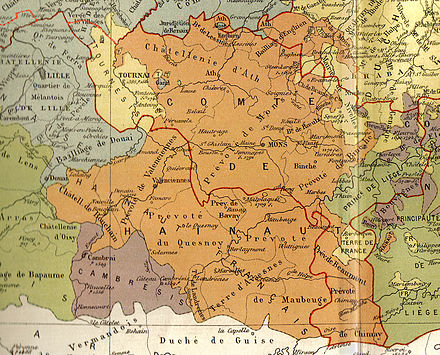
Hainaut (French : Hainaut, French pronunciation: [ɛno] ; Dutch : Heinaut, IPA: [ˈɦeːnəɣʌuə(n)] (![]()

French is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the spoken Latin in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) has largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the (Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French.

Dutch(
Walloon is a Romance language that is spoken in much of Wallonia in Belgium, in some villages of Northern France and in the northeast part of Wisconsin until the mid 20th century and in some parts of Canada. It belongs to the langue d'oïl language family, whose most prominent member is the French language. The historical background of its formation was the territorial extension since 980 of the Principality of Liège to the south and west.
Contents
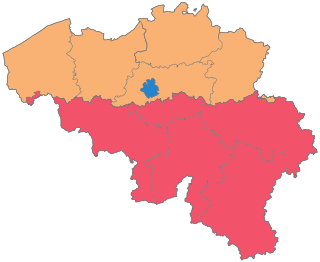
To its south lies the French department of Nord, while within Belgium it borders (clockwise from the North) on the Flemish provinces of West Flanders, East Flanders, Flemish Brabant and the Walloon provinces of Walloon Brabant and Namur.

France, officially the French Republic, is a country whose territory consists of metropolitan France in Western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. The metropolitan area of France extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. It is bordered by Belgium, Luxembourg and Germany to the northeast, Switzerland and Italy to the east, and Andorra and Spain to the south. The overseas territories include French Guiana in South America and several islands in the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian oceans. The country's 18 integral regions span a combined area of 643,801 square kilometres (248,573 sq mi) and a total population of 67.3 million. France, a sovereign state, is a unitary semi-presidential republic with its capital in Paris, the country's largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. Other major urban areas include Lyon, Marseille, Toulouse, Bordeaux, Lille and Nice.

Nord is a department in the far north of France. It was created from the western halves of the historical counties of Flanders and Hainaut, and the Bishopric of Cambrai. The modern coat of arms was inherited from the County of Flanders.

The Flemish Region is one of the three regions of the Kingdom of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and the Brussels-Capital Region. Colloquially, it is usually simply referred to as Flanders. It occupies the northern part of Belgium and covers an area of 13,522 km2. It is one of the most densely populated regions of Europe with around 480 inhabitants per square kilometer.
Its capital is Mons (Dutch Bergen) and the most populous city is Charleroi, the province's urban, economic and cultural hub, the financial capital of Hainaut and the fifth largest city in the country by population.

Mons is a Walloon city and municipality, and the capital of the Belgian province of Hainaut. The Mons municipality includes the former communes of Cuesmes, Flénu, Ghlin, Hyon, Nimy, Obourg, Jemappes, Ciply, Harmignies, Harveng, Havré, Maisières, Mesvin, Nouvelles, Saint-Denis, Saint-Symphorien, Spiennes and Villers-Saint-Ghislain. Together with the Czech city of Plzeň, Mons was the European Capital of Culture in 2015.

Charleroi is a city and a municipality of Wallonia, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. By January 1, 2008, the total population of Charleroi was 201,593. The metropolitan area, including the outer commuter zone, covers an area of 1,462 square kilometres (564 sq mi) with a total population of 522,522 by January 1, 2008, ranking it as the 5th most populous in Belgium after Brussels, Antwerp, Liège, and Ghent. The inhabitants are called Carolorégiens or simply Carolos.