
The Constitution of Haiti was modeled after the constitutions of the United States and France. The document was approved by Parliament in March 2011 and came into effect on June 20, 2012.
This electoral calendar 2005 lists the national/federal direct elections held in 2005 in the de jure and de facto sovereign states and their dependent territories. Referendums are included, although they are not elections. By-elections are not included.
This electoral calendar 2006 lists the national/federal direct elections held in 2006 in the de jure and de facto sovereign states and their dependent territories. Referendums are included, although they are not elections. By-elections are not included.
This electoral calendar 2009 lists the national/federal direct elections held in 2009 in the de jure and de facto sovereign states and their dependent territories. Referendums are included, although they are not elections. By-elections are not included.
This national electoral calendar for the year 2010 lists the national/federal direct elections held in 2010 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. Referendums are included, even though they are not elections. By-elections are not included.

A constitutional referendum was held in Haiti on 22 July 1985. The amendments to the new constitution would restore multi-party politics, although only on the condition that all parties swore allegiance to President Jean-Claude Duvalier, as well as re-confirming Duvalier as President for Life and allowing him to single-handedly appoint the Prime Minister and his successor. The changes were reportedly approved by 99.98% of voters, although it was widely considered a sham and led to Duvalier being overthrown the following year.
This national electoral calendar for the year 2011 lists the national/federal direct elections held in 2011 in the de jure and de facto sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.

This national electoral calendar for the year 2012 lists the national/federal direct elections held in 2012 in the de jure and de facto sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.

A constitutional referendum was held in Haiti on 10 and 11 January 1928. Voters were asked to approve or reject thirteen amendments to the constitution. Each amendment was voted on separately, with all approved by at least 97% of voters.

A referendum on annexation by the United States was held in the Dominican Republic on 19 February 1870. The proposal was approved by 99.93% of voters, although turnout was just 30%. However, the United States Senate rejected the annexation on 30 June 1870 with a 28–28 vote.
The Anti-Duvalier protest movement was a series of demonstrations in Haiti from 23 May 1984 – 7 February 1986, that led to the overthrow of President Jean-Claude Duvalier and the Duvalier dynasty regime.

This national electoral calendar for the year 2015 lists the national/federal direct elections held in 2015 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.

This national electoral calendar for the year 2016 lists the national/federal direct elections held in 2016 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.

This national electoral calendar for the year 2017 lists the national/federal direct elections held in 2017 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included.

A four-part referendum on arbitration over a border dispute with Haiti was held in the Dominican Republic on 2 June 1895. Voters were asked whether an arbitration tribunal should be established, whether the Pope would be an appropriate arbitrator, what compensation Haiti should receive if the outcome was favourable to the Dominican Republic, and whether the government should comply with the tribunal outcome if it was unfavourable to the Dominican Republic. All four proposals were approved by voters.
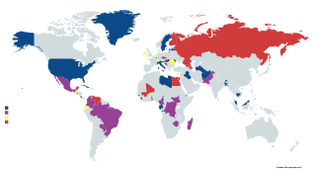
This national electoral calendar for the year 2018 lists the national/federal direct elections to be held in 2018 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included. Specific dates are given where they have been known.

The period of 1859 to 1957 in Haitian history covers an era of political struggles, the period of American occupation and multiple coups and elections until the Duvalier dynasty seized control of the country in 1957.

This national electoral calendar for the year 2019 lists the national/federal direct elections to be held in 2019 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referendums are included. Specific dates are given where they have been known.












