
Puget Sound is a sound on the northwestern coast of the U.S. state of Washington. It is a complex estuarine system of interconnected marine waterways and basins. A part of the Salish Sea, Puget Sound has one major and two minor connections to the Strait of Juan de Fuca, which in turn connects to the open Pacific Ocean. The major connection is Admiralty Inlet; the minor connections are Deception Pass and the Swinomish Channel.

The San Juan Islands is an archipelago in the Pacific Northwest of the United States between the U.S. state of Washington and Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. The San Juan Islands are part of Washington state, and form the core of San Juan County.

The Strait of Juan de Fuca is a body of water about 96 miles long that is the Salish Sea's main outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre of the Strait.

Bainbridge Island is a city and island in Kitsap County, Washington, United States. It is located in Puget Sound. The population was 24,825 at the 2020 census, making Bainbridge Island the second largest city in Kitsap County.

Poulsbo is a city on Liberty Bay in Kitsap County, Washington, United States. It is the smallest of the four cities in Kitsap County. The population was 11,970 at the 2020 census and an estimated 10,927 in 2018.

Seattle was a leader of the Duwamish and Suquamish peoples. A leading figure among his people, he pursued a path of accommodation to white settlers, forming a personal relationship with Doc Maynard. The city of Seattle, in the U.S. state of Washington, was named after him. A widely publicized speech arguing in favor of ecological responsibility and respect of Native Americans' land rights had been attributed to him.

A petroglyph is an image created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other descriptions of the technique to refer to such images. Petroglyphs, estimated to be 20,000 years old are classified as protected monuments and have been added to the tentative list of UNESCO's World Heritage Sites. Petroglyphs are found worldwide, and are often associated with prehistoric peoples. The word comes from the Greek prefix petro-, from πέτρα petra meaning "stone", and γλύφω glýphō meaning "carve", and was originally coined in French as pétroglyphe.

The Suquamish are a Lushootseed-speaking Native American people, located in present-day Washington in the United States. They are a southern Coast Salish people.
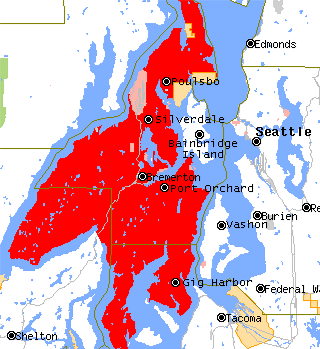
The Kitsap Peninsula lies west of Seattle across Puget Sound, in Washington state in the Pacific Northwest. Hood Canal separates the peninsula from the Olympic Peninsula on its west side. The peninsula, a.k.a. "Kitsap", encompasses all of Kitsap County except Bainbridge and Blake Islands, as well as the northeastern part of Mason County and the northwestern part of Pierce County. The highest point on the Kitsap Peninsula is Gold Mountain. The U.S. Navy's Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, and Naval Base Kitsap are on the peninsula. Its main city is Bremerton.

Blake Island is a Puget Sound island in Kitsap County, Washington, United States, that is preserved as Blake Island Marine State Park. The island lies north of Vashon Island, south of Bainbridge Island, and east of Manchester. On the northeast end of the island is Tillicum Village, a tourist attraction based on Northwest Coast Indian arts, culture, and food. The park is managed by the Washington State Parks and Recreation Commission.

The Suquamish Indian Tribe of the Port Madison Reservation is a federally recognized tribe and Indian reservation in the U.S. state of Washington.

Agate Pass or Agate Passage is a high-current tidal strait in Puget Sound connecting Port Madison and mainland Kitsap County in the US state of Washington. It lies between Bainbridge Island and the mainland of the Kitsap Peninsula near Suquamish. It leads south towards Bremerton, extending about one mile (1.6 km) in a straight, southwesterly direction. The depth is about 20 feet (6.1 m). The shores are wooded and fairly steep. The shoreline is mostly rocky and fringed with kelp to Point Bolin. The tidal currents have velocities up to six knots; the flood tide sets southwesterly, and the ebb tide northeasterly.

Pacific Creosoting Company was a company founded on Bainbridge Island that treated logs with creosote as a preservative.
The Sammamish people are a Lushootseed-speaking Southern Coast Salish people. They are indigenous to the Sammamish River Valley in central King County, Washington. The Sammamish speak Lushootseed, a Coast Salish language which was historically spoken across most of Puget Sound, although its usage today is mostly reserved for cultural and ceremonial practices.

The Salish Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean located in the Canadian province of British Columbia and the U.S. state of Washington. It includes the Strait of Georgia, the Strait of Juan de Fuca, Puget Sound, and an intricate network of connecting channels and adjoining waterways.
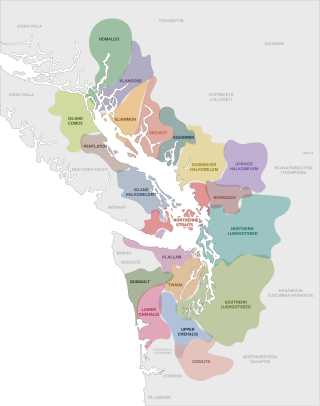
The Coast Salish are a group of ethnically and linguistically related Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast, living in the Canadian province of British Columbia and the U.S. states of Washington and Oregon. They speak one of the Coast Salish languages. The Nuxalk nation are usually included in the group, although their language is more closely related to Interior Salish languages.

State Route 305 (SR 305) is a 13.50-mile-long (21.73 km) state highway in the U.S. state of Washington, primarily serving Bainbridge Island in Kitsap County and connecting it to Seattle in King County via the Seattle–Bainbridge Island ferry. The highway travels north through Bainbridge Island and leaves the island on the Agate Pass Bridge into the Kitsap Peninsula. SR 305 continues northwest through Poulsbo, intersecting SR 307 and ending at the SR 3 freeway. The highway was created during the 1964 highway renumbering and was preceded by Secondary State Highway 21A (SSH 21A), established in 1937. The ferry, part of the highway since 1994, is served by the Jumbo Mark-II-classMV Tacoma and MV Wenatchee and operates on a 35-minute crossing time.
The Suquamish Museum preserves and displays relics and records related to the Suquamish Tribe, including artifacts from the Old Man House and the Baba'kwob site. It is located on the Port Madison Indian Reservation in Washington state and was founded in 1983. The museum currently occupies a facility opened in 2012.

The Deer Valley Petroglyph Preserve, formerly known as the Deer Valley Rock Art Center, is a 47-acre nature preserve featuring over 1500 Hohokam, Patayan, and Archaic petroglyphs visible on 500 basalt boulders in the Deer Valley area of Phoenix, Arizona. In 1980, the US Army Corps of Engineers contracted J. Simon Bruder to conduct an archaeological investigation prior to the construction of the Adobe Dam at the Hedgpeth Hills. The petroglyphs are between 500 and 5,000 years old. The site was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984, and it was also listed with the Phoenix Points of Pride. The preserve and museum are operated by the ASU College of Liberal Arts and Sciences's School of Human Evolution and Social Change.

Frog Rock is a glacial erratic on Bainbridge Island, Washington. The frog shape is made of two stacked granite boulders, painted by a pair of local residents to resemble a frog on June 6, 1971, The pair of boulders were reportedly once a single boulder which was dynamited in the 1950s or earlier, in order to remove it from a road right-of-way. After the dynamiting, the rock was known as "Split Rock".




















