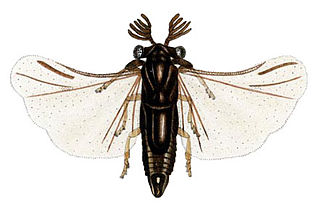
The Strepsiptera are an order of insects with eleven extant families that include about 600 described species. They are endoparasites of other insects, such as bees, wasps, leafhoppers, silverfish, and cockroaches. Females of most species never emerge from the host after entering its body, finally dying inside it. The early-stage larvae do emerge because they must find an unoccupied living host, and the short-lived males must emerge to seek a receptive female in her host. They are believed to be most closely related to beetles, from which they diverged 300–350 million years ago, but do not appear in the fossil record until the mid-Cretaceous around 100 million years ago.

Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- di- "two", and πτερόν pteron "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced mechanosensory organs known as halteres, which act as high-speed sensors of rotational movement and allow dipterans to perform advanced aerobatics. Diptera is a large order containing an estimated 1,000,000 species including horse-flies, crane flies, hoverflies, mosquitoes and others, although only about 125,000 species have been described.

Trophallaxis is the transfer of food or other fluids among members of a community through mouth-to-mouth (stomodeal) or anus-to-mouth (proctodeal) feeding. Along with nutrients, trophallaxis can involve the transfer of molecules such as pheromones, organisms such as symbionts, and information to serve as a form of communication. Trophallaxis is used by some birds, gray wolves, vampire bats, and is most highly developed in eusocial insects such as ants, wasps, bees, and termites.

In evolutionary ecology, a parasitoid is an organism that lives in close association with its host at the host's expense, eventually resulting in the death of the host. Parasitoidism is one of six major evolutionary strategies within parasitism, distinguished by the fatal prognosis for the host, which makes the strategy close to predation.

The Tachinidae are a large and variable family of true flies within the insect order Diptera, with more than 8,200 known species and many more to be discovered. Over 1,300 species have been described in North America alone. Insects in this family commonly are called tachinid flies or simply tachinids. As far as is known, they all are protelean parasitoids, or occasionally parasites, of arthropods, usually other insects. The family is known from many habitats in all zoogeographical regions and is especially diverse in South America.

Brood parasitism is a subclass of parasitism and phenomenon and behavioural pattern of certain animals, brood parasites, that rely on others to raise their young. The strategy appears among birds, insects and fish. The brood parasite manipulates a host, either of the same or of another species, to raise its young as if it were its own, usually using egg mimicry, with eggs that resemble the host's.

Pieris rapae is a small- to medium-sized butterfly species of the whites-and-yellows family Pieridae. It is known in Europe as the small white, in North America as the cabbage white or cabbage butterfly, on several continents as the small cabbage white, and in New Zealand as the white butterfly. The butterfly is recognizable by its white color with small black dots on its wings, and it can be distinguished from P. brassicae by its larger size and the black band at the tip of its forewings.
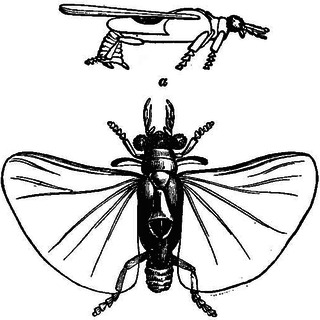
Stylopidae is a family of twisted-winged insects in the order Strepsiptera. There are about 15 genera and more than 330 described species in Stylopidae.

A planidium is a specialized form of insect larva seen in the first-instar of a few families of insects that have parasitoidal ways of life. They are usually flattened, highly sclerotized (hardened), and quite mobile. The function of the planidial stage is to find a host on which the later larval instars may feed, generally until the insect pupates.
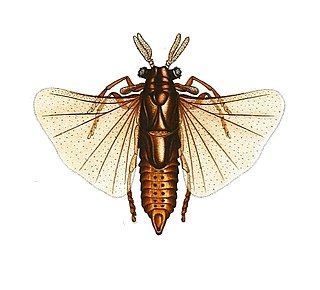
Xenos vesparum is a parasitic insect species of the order Strepsiptera that are endoparasites of paper wasps in the genus Polistes that was first described in 1793. Like other members of this family, X. vesparum displays a peculiar lifestyle, and demonstrates extensive sexual dimorphism.

Xenos is a genus of insects belonging to the family Xenidae. The word derives from the Greek word for strange. A species of the genus is Xenos vesparum, first described by Pietro Rossi in 1793. The females are permanent entomophagous endoparasites of Polistes paper wasps. They dwell their whole lives in the abdomens of wasps.

Apocephalus borealis is a species of North American parasitoid phorid fly that attacks bumblebees, honey bees, and paper wasps. This parasitoid's genus Apocephalus is best known for the "decapitating flies" that attack a variety of ant species, though A. borealis attacks and alters the behavior of bees and wasps. These flies are colloquially known as zombie flies and the bees they infect are colloquially known as zombees. Association with honey bees has so far only been documented from California, South Dakota, Oregon, Washington, British Columbia, and Vermont.

Ammophila sabulosa, the red-banded sand wasp, is a species of the subfamily Ammophilinae of the solitary hunting wasp family Sphecidae, also called digger wasps. Found across Eurasia, the parasitoid wasp is notable for the mass provisioning behaviour of the females, hunting caterpillars mainly on sunny days, paralysing them with a sting, and burying them in a burrow with a single egg. The species is also remarkable for the extent to which females parasitise their own species, either stealing prey from nests of other females to provision their own nests, or in brood parasitism, removing the other female's egg and laying one of her own instead.

Stylops is a genus of obligately endoparasitic insects in the family Stylopidae. Hosts are typically members of the order Hymenoptera.

Stylops melittae is a species of the order Strepsiptera of flying insects, that parasitize various species of sand bees (Andrena).

Bombylius canescens, commonly known as the western bee-fly, is a species of bee-fly belonging to the family Bombyliidae.

Andrena scotica, the chocolate mining bee or hawthorn bee, is a species of mining bee from the family Andrenidae. It occurs in western Europe and is one of the most frequently encountered mining bees found in Great Britain, where it had been previously misidentified as Andrena carantonica.

Physocephala tibialis is a species of thick-headed fly found throughout the eastern United States, often near flowering plants. The adult fly is primarily black with a yellow face and thin white stripes on the abdomen. It is commonly found along the east coast of the United States and is often found near flowering plants.

Caenocholax fenyesi is a species of twisted-winged parasitic insects in the order Strepsiptera and family Myrmecolacidae. It has a sporadic distribution throughout North America, Central America, and South America. Chaenochlax brasiliensis is the only other named species in the genus.

Mengenillidae is a family of insects belonging to the order Strepsiptera. It is the second most basal member of the order, after Bahiaxenidae. Unlike members of Stylopidia, which contains the vast majority of strepsipterans, the adult females of the family are free-living with legs. Members of the family with known hosts parasitise members of the family Lepismatidae.



















