
Halmahera Arc is the volcanic arc of the Halmahera region of eastern Indonesia. It is considered to belong to the Halmahera plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone.

Halmahera Arc is the volcanic arc of the Halmahera region of eastern Indonesia. It is considered to belong to the Halmahera plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone.
Potassium-argon ages of Neogene to Recent igneous rocks from the Halmahera region record a history of intra-oceanic arc development since the late Middle Miocene following an earlier phase of collisional plutonism. Arc formation from the Middle Miocene onwards was due to the east-directed subduction of the Molucca Sea plate beneath the Philippine Sea plate as it arrived at the Eurasian margin. The distribution of ages within the Neogene arc indicates a northward migration of volcanic activity during the Late Miocene to Pliocene. Results of the dating work show that after collision with the Australian margin at c. 22 Ma there was a period of volcanic quiescence and limestone deposition before a new arc formed. This arc began erupting at around 11 Ma on Obi as a result of subduction of the Molucca Sea plate. Initiation of subduction is thought to have occurred around 15–17 Ma and may have been responsible for disturbing potassium-argon ages of pre-Neogene rocks. Dates from fresh rocks show that the volcanic front migrated northwards through Bacan and Halmahera throughout the Late Miocene to Early Pliocene. Limestone deposition was curtailed as arc activity migrated north while volcanism died out from the south. No Neogene volcanism younger than 8 Ma is observed in the Obi area while on Bacan subduction-related volcanism ceased at c. 2 Ma.
Late Pliocene crustal deformation caused a 30–40 km westward shift of the volcanic front. Quaternary volcanic rocks exposed in Bacan and the extreme south of Halmahera are not direct products of subduction but, rather, display geochemical characteristics of both subduction and fault-related magmatism. These volcanic rocks are distributed along splays of the Sorong Fault system. The formation and propagation of the Halmahera arc is a consequence of the clockwise rotation of the Philippine Sea plate as the southern edge moved across the northern Australian margin and impinged on the east Eurasian margin. The ages of initiation of volcanism and subduction track the developing plate boundary as subduction propagated northwards. [1]

The Paleogene Period is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period 66 Ma to the beginning of the Neogene Period 23.03 Ma. It is the first period of the Cenozoic Era, the tenth period of the Phanerozoic and is divided into the Paleocene, Eocene, and Oligocene epochs. The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the time now covered by the Paleogene Period and subsequent Neogene Period; despite no longer being recognized as a formal stratigraphic term, "Tertiary" still sometimes remains in informal use. Paleogene is often abbreviated "Pg", although the United States Geological Survey uses the abbreviation "Pe" for the Paleogene on the Survey's geologic maps.

A convergent boundary is an area on Earth where two or more lithospheric plates collide. One plate eventually slides beneath the other, a process known as subduction. The subduction zone can be defined by a plane where many earthquakes occur, called the Wadati–Benioff zone. These collisions happen on scales of millions to tens of millions of years and can lead to volcanism, earthquakes, orogenesis, destruction of lithosphere, and deformation. Convergent boundaries occur between oceanic-oceanic lithosphere, oceanic-continental lithosphere, and continental-continental lithosphere. The geologic features related to convergent boundaries vary depending on crust types.

The Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt, also known as the Transvolcanic Belt and locally as the Sierra Nevada, is an active volcanic belt that covers central-southern Mexico. Several of its highest peaks have snow all year long, and during clear weather, they are visible to a large percentage of those who live on the many high plateaus from which these volcanoes rise.

The Central American Volcanic Arc is a chain of volcanoes which extends parallel to the Pacific coastline of the Central American Isthmus, from Mexico to Panama. This volcanic arc, which has a length of 1,100 kilometers (680 mi) is formed by an active subduction zone, with the Cocos plate subducting underneath the Caribbean plate, the North American plate and the Panama plate. Volcanic activity is recorded in the Central American region since the Permian. Numerous volcanoes are spread throughout various Central American countries; many have been active in the geologic past, varying in intensity of their activity according to different factors.

Located in the western Pacific Ocean near Indonesia, the Molucca Sea Plate has been classified by scientists as a fully subducted microplate that is part of the Molucca Sea Collision Complex. The Molucca Sea Plate represents the only known example of divergent double subduction (DDS), which describes the subduction on both sides of a single oceanic plate.
Sorong fault also is an active, broad zone of inferred left lateral shear at the triple junction of the Australian Plate, Eurasian Plate, and Pacific Plate, where many plate fragments exist, such as the Philippine Sea Plate, Bird's Head Plate, Halmahera Plate and the Molucca Sea Plate. It has been implicated in numerous large earthquakes. It is one of the two major faults created by the Australian and Pacific plate convergence, the other being the Ramu-Markham Fault zone. The fault triggered the destructive 1998 North Maluku earthquake which killed 41 people.
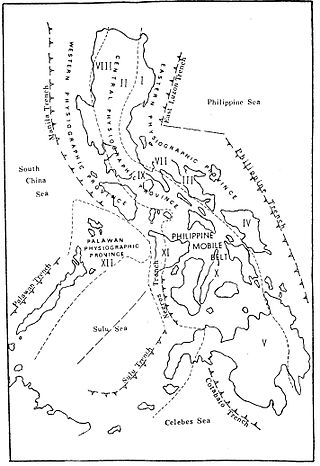
In the geology of the Philippines, the Philippine Mobile Belt is a complex portion of the tectonic boundary between the Eurasian Plate and the Philippine Sea Plate, comprising most of the country of the Philippines. It includes two subduction zones, the Manila Trench to the west and the Philippine Trench to the east, as well as the Philippine Fault System. Within the Belt, a number of crustal blocks or microplates which have been shorn off the adjoining major plates are undergoing massive deformation.
The Molucca Sea Collision Zone is postulated by paleogeologists to explain the tectonics of the area based on the Molucca Sea in Indonesia, and adjacent involved areas.
Halmahera plate has recently (1990s) been postulated to be a microplate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone of eastern Indonesia.
Sangihe Plate has recently (1990s) been postulated to be a microplate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone of eastern Indonesia.

The island of Taiwan was formed approximately 4 to 5 million years ago at a convergent boundary between the Philippine Sea Plate and the Eurasian Plate. In a boundary running the length of the island and continuing southwards, the Eurasian Plate is sliding under the Philippine Sea Plate. In the northeast of the island, the Philippine Sea Plate slides under the Eurasian Plate. Most of the island comprises a huge fault block tilted to the west.

The Pacific Ocean evolved in the Mesozoic from the Panthalassic Ocean, which had formed when Rodinia rifted apart around 750 Ma. The first ocean floor which is part of the current Pacific Plate began 160 Ma to the west of the central Pacific and subsequently developed into the largest oceanic plate on Earth.
The South China Sea Basin is one of the largest marginal basins in Asia. South China Sea is located to the east of Vietnam, west of Philippines and the Luzon Strait, and north of Borneo. Tectonically, it is surrounded by the Indochina Block on the west, Philippine Sea Plate on the east, Yangtze Block to the north. A subduction boundary exists between the Philippine Sea Plate and the Asian Plate. The formation of the South China Sea Basin was closely related with the collision between the Indian Plate and Eurasian Plates. The collision thickened the continental crust and changed the elevation of the topography from the Himalayan orogenic zone to the South China Sea, especially around the Tibetan Plateau. The location of the South China Sea makes it a product of several tectonic events. All the plates around the South China Sea Basin underwent clockwise rotation, subduction and experienced an extrusion process from the early Cenozoic to the Late Miocene.
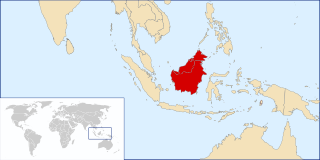
The Kutai sedimentary basin extends from the central highlands of Borneo, across the eastern coast of the island and into the Makassar Strait. With an area of 60,000 km2, and depths up to 15 km, the Kutai is the largest and deepest Tertiary age basin in Indonesia. Plate tectonic evolution in the Indonesian region of SE Asia has produced a diverse array of basins in the Cenozoic. The Kutai is an extensional basin in a general foreland setting. Its geologic evolution begins in the mid Eocene and involves phases of extension and rifting, thermal sag, and isostatic subsidence. Rapid, high volume, sedimentation related to uplift and inversion began in the Early Miocene. The different stages of Kutai basin evolution can be roughly correlated to regional and local tectonic events. It is also likely that regional climate, namely the onset of the equatorial ever wet monsoon in early Miocene, has affected the geologic evolution of Borneo and the Kutai basin through the present day. Basin fill is ongoing in the lower Kutai basin, as the modern Mahakam River delta progrades east across the continental shelf of Borneo.

The Tengchong Volcanic Field (TVF) is a Cenozoic volcanic field located in the Southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau around 40 km from the Chinese border with Myanmar. The TVF is uniquely the only region affected by Quaternary volcanism that is part of the Himalayan Geothermal Belt caused by the Indo-Asian continent-continent collision. The TVF is characterized by hydrothermal activity and large-scale eruptions last recorded in 1609CE. Although the volcanoes themselves are considered extinct, several geothermal fields geographically linked to the TVF are still highly active. Evidence for geothermal activity can be linked to several prevalent active hot-springs located predominantly within the vicinity of the volcanoes in the TVF. Holocene eruptions occurred predominantly in the three largest volcanoes in the TVF named the Dayingshan, Maa'nshan and Heikongshan, the highest of which (Dayingshan) reaches 2865 meters above sea level. The volcanoes are distributed in a string-like pattern clustered from North to South in the middle on the Tengchong basin and are characterized by post-collisional high-Potassium (K) calc-alkaline series eruptions. The TVF provides unique geographical and geological knowledge as understanding the geological processes of creation provides insight into aspects such as the history of volcanism during the Quaternary Era in the region and as well as compositional information of its source and crustal assimilants. The TVF can be visited in the Tengchong Volcanic Geothermal National Geological Park.`

The base of rocks that underlie Borneo, an island in Southeast Asia, was formed by the arc-continent collisions, continent–continent collisions and subduction–accretion due to convergence between the Asian, India–Australia, and Philippine Sea-Pacific plates over the last 400 million years. The active geological processes of Borneo are mild as all of the volcanoes are extinct. The geological forces shaping SE Asia today are from three plate boundaries: the collisional zone in Sulawesi southeast of Borneo, the Java-Sumatra subduction boundary and the India-Eurasia continental collision.

Divergent double subduction, also called outward dipping double-sided subduction, is a special type of subduction process in which two parallel subduction zones with different directions are developed on the same oceanic plate. In conventional plate tectonics theory, an oceanic plate subducts under another plate and new oceanic crust is generated somewhere else, commonly along the other side of the same plates However, in divergent double subduction, the oceanic plate subducts on two sides. This results in the closure of ocean and arc–arc collision.
The geology of Sicily records the collision of the Eurasian and the African plates during westward-dipping subduction of the African slab since late Oligocene. Major tectonic units are the Hyblean foreland, the Gela foredeep, the Apenninic-Maghrebian orogen, and the Calabrian Arc. The orogen represents a fold-thrust belt that folds Mesozoic carbonates, while a major volcanic unit is found in an eastern portion of the island. The collision of Africa and Eurasia is a retreating subduction system, such that the descending Africa is falling away from Eurasia, and Eurasia extends and fills the space as the African plate falls into the mantle, resulting in volcanic activity in Sicily and the formation of Tyrrhenian slab to the north.

The subduction tectonics of the Philippines is the control of geology over the Philippine archipelago. The Philippine region is seismically active and has been progressively constructed by plates converging towards each other in multiple directions. The region is also known as the Philippine Mobile Belt due to its complex tectonic setting.
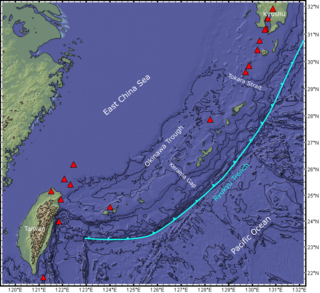
The Ryukyu Arc is an island arc which extends from the south of Kyushu along the Ryukyu Islands to the northeast of Taiwan, spanning about 1,200 kilometres (750 mi). It is located along a section of the convergent plate boundary where the Philippine Sea Plate is subducting northwestward beneath the Eurasian Plate along the Ryukyu Trench. The arc has an overall northeast to southwest trend and is located northwest of the Pacific Ocean and southeast of the East China Sea. It runs parallel to the Okinawa Trough, an active volcanic arc, and the Ryukyu Trench. The Ryukyu Arc, based on its geomorphology, can be segmented from north to south into Northern Ryukyu, Central Ryukyu, and Southern Ryukyu; the Tokara Strait separates Northern Ryukyu and Central Ryukyu at about 130˚E while the Kerama Gap separates Central Ryukyu and Southern Ryukyu at about 127 ˚E. The geological units of the arc include igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, ranging from the Paleozoic to Cenozoic in age.