
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula NO−
3. Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are soluble in water. An example of an insoluble nitrate is bismuth oxynitrate.

The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmosphere, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through both biological and physical processes. Important processes in the nitrogen cycle include fixation, ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification. The majority of Earth's atmosphere (78%) is atmospheric nitrogen, making it the largest source of nitrogen. However, atmospheric nitrogen has limited availability for biological use, leading to a scarcity of usable nitrogen in many types of ecosystems.

Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula KNO
3. It is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ and nitrate ions NO3−, and is therefore an alkali metal nitrate. It occurs in nature as a mineral, niter (or nitre in the UK). It is a source of nitrogen, and nitrogen was named after niter. Potassium nitrate is one of several nitrogen-containing compounds collectively referred to as saltpetre (or saltpeter in North America).

Sodium nitrate is the chemical compound with the formula NaNO
3. This alkali metal nitrate salt is also known as Chile saltpeter to distinguish it from ordinary saltpeter, potassium nitrate. The mineral form is also known as nitratine, nitratite or soda niter.
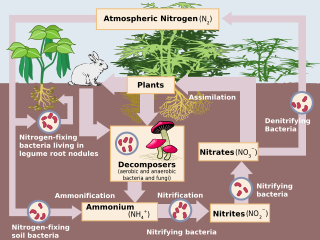
Nitrification is the biological oxidation of ammonia to nitrite followed by the oxidation of the nitrite to nitrate occurring through separate organisms or direct ammonia oxidation to nitrate in comammox bacteria. The transformation of ammonia to nitrite is usually the rate limiting step of nitrification. Nitrification is an important step in the nitrogen cycle in soil. Nitrification is an aerobic process performed by small groups of autotrophic bacteria and archaea.

The nitrite ion has the chemical formula NO−
2. Nitrite is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite can also refer to organic compounds with the – ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid.

Sodium nitrite is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaNO2. It is a white to slightly yellowish crystalline powder that is very soluble in water and is hygroscopic. From an industrial perspective, it is the most important nitrite salt. It is a precursor to a variety of organic compounds, such as pharmaceuticals, dyes, and pesticides, but it is probably best known as a food additive used in processed meats and (in some countries) in fish products.

Halomonadaceae is a family of halophilic Pseudomonadota.
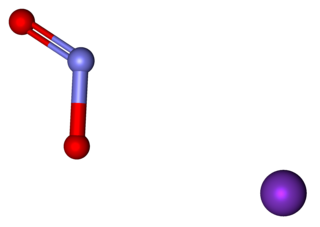
Potassium nitrite (distinct from potassium nitrate) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula KNO2. It is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ and nitrite ions NO2−, which forms a white or slightly yellow, hygroscopic crystalline powder that is soluble in water.
Nitrobacter is a genus comprising rod-shaped, gram-negative, and chemoautotrophic bacteria. The name Nitrobacter derives from the Latin neuter gender noun nitrum, nitri, alkalis; the Ancient Greek noun βακτηρία, βακτηρίᾱς, rod. They are non-motile and reproduce via budding or binary fission. Nitrobacter cells are obligate aerobes and have a doubling time of about 13 hours.
Curing is any of various food preservation and flavoring processes of foods such as meat, fish and vegetables, by the addition of salt, with the aim of drawing moisture out of the food by the process of osmosis. Because curing increases the solute concentration in the food and hence decreases its water potential, the food becomes inhospitable for the microbe growth that causes food spoilage. Curing can be traced back to antiquity, and was the primary method of preserving meat and fish until the late-19th century. Dehydration was the earliest form of food curing. Many curing processes also involve smoking, spicing, cooking, or the addition of combinations of sugar, nitrate, and nitrite.
Nitrifying bacteria are chemolithotrophic organisms that include species of genera such as Nitrosomonas, Nitrosococcus, Nitrobacter, Nitrospina, Nitrospira and Nitrococcus. These bacteria get their energy from the oxidation of inorganic nitrogen compounds. Types include ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB). Many species of nitrifying bacteria have complex internal membrane systems that are the location for key enzymes in nitrification: ammonia monooxygenase, hydroxylamine oxidoreductase, and nitrite oxidoreductase.
Paracoccus denitrificans, is a coccoid bacterium known for its nitrate reducing properties, its ability to replicate under conditions of hypergravity and for being a relative of the eukaryotic mitochondrion.

Cured fish is fish which has been cured by subjecting it to fermentation, pickling, smoking, or some combination of these before it is eaten. These food preservation processes can include adding salt, nitrates, nitrite or sugar, can involve smoking and flavoring the fish, and may include cooking it. The earliest form of curing fish was dehydration. Other methods, such as smoking fish or salt-curing also go back for thousands of years. The term "cure" is derived from the Latin curare, meaning to take care of. It was first recorded in reference to fish in 1743.

GFAJ-1 is a strain of rod-shaped bacteria in the family Halomonadaceae. It is an extremophile that was isolated from the hypersaline and alkaline Mono Lake in eastern California by geobiologist Felisa Wolfe-Simon, a NASA research fellow in residence at the US Geological Survey. In a 2010 Science journal publication, the authors claimed that the microbe, when starved of phosphorus, is capable of substituting arsenic for a small percentage of its phosphorus to sustain its growth. Immediately after publication, other microbiologists and biochemists expressed doubt about this claim, which was robustly criticized in the scientific community. Subsequent independent studies published in 2012 found no detectable arsenate in the DNA of GFAJ-1, refuted the claim, and demonstrated that GFAJ-1 is simply an arsenate-resistant, phosphate-dependent organism.
Calcium nitrite is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca(NO
2)
2. In this compound, as in all nitrites, nitrogen is in a +3 oxidation state. It has many applications such as antifreeze, rust inhibitor of steel and wash heavy oil.
Nitrospira moscoviensis was the second bacterium classified under the most diverse nitrite-oxidizing bacteria phylum, Nitrospirae. It is a gram-negative, non-motile, facultative lithoauthotropic bacterium that was discovered in Moscow, Russia in 1995. The genus name, Nitrospira, originates from the prefix “nitro” derived from nitrite, the microbe’s electron donor and “spira” meaning coil or spiral derived from the microbe’s shape. The species name, moscoviensis, is derived from Moscow, where the species was first discovered. N. moscoviensis could potentially be used in the production of bio-degradable polymers.
Halomonas desiderata is an alkaliphilic, halotolerant and denitrifying bacterium first isolated from a municipal sewage works.
Halomonas anticariensis is a bacterium. It is strictly aerobic and because of its production of exopolysaccharides forms cream-coloured, mucoid colonies. FP35T is the type strain. Its genome has been sequenced.
Celery powder is a dried, ground concentrate prepared from fresh celery that is used as a seasoning and as a food preservative in organic meat products. Several commercial preparations exist, and it can also be made using a food dehydrator. Some celery powders are prepared from celery juice.











