
Pseudomonas is a genus of Gram-negative, Gammaproteobacteria, belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae and containing 191 validly described species. The members of the genus demonstrate a great deal of metabolic diversity and consequently are able to colonize a wide range of niches. Their ease of culture in vitro and availability of an increasing number of Pseudomonas strain genome sequences has made the genus an excellent focus for scientific research; the best studied species include P. aeruginosa in its role as an opportunistic human pathogen, the plant pathogen P. syringae, the soil bacterium P. putida, and the plant growth-promoting P. fluorescens, P. lini, P. migulae, and P. graminis.

Pseudomonas fluorescens is a common Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium. It belongs to the Pseudomonas genus; 16S rRNA analysis as well as phylogenomic analysis has placed P. fluorescens in the P. fluorescens group within the genus, to which it lends its name.
Pseudomonas putida is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, saprotrophic soil bacterium.

Burkholderia is a genus of Proteobacteria whose pathogenic members include the Burkholderia cepacia complex, which attacks humans and Burkholderia mallei, responsible for glanders, a disease that occurs mostly in horses and related animals; Burkholderia pseudomallei, causative agent of melioidosis; and Burkholderia cepacia, an important pathogen of pulmonary infections in people with cystic fibrosis (CF). Burkholderia species is also found marine environment. S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated and characterized Burkholderia cepacia from marine sponges of the Saint Martin's Island of the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh.

Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a common encapsulated, Gram-negative, strict aerobic, Rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, P. aeruginosa is a multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes.

Burkholderia cepacia complex (BCC), or simply Burkholderia cepacia, is a group of catalase-producing, lactose-nonfermenting, Gram-negative bacteria composed of at least 20 different species, including B. cepacia, B. multivorans, B. cenocepacia, B. vietnamiensis, B. stabilis, B. ambifaria, B. dolosa, B. anthina, B. pyrrocinia and B. ubonensis. B. cepacia is an opportunistic human pathogen that most often causes pneumonia in immunocompromised individuals with underlying lung disease. Patients with sickle-cell haemoglobinopathies are also at risk. The species complex also attacks young onion and tobacco plants, and displays a remarkable ability to digest oil. Burkholderia cepacia is also found in marine environment and some strain of Burkholderia cepacia can tolerate high salinity. S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated and biochemically characterized salt tolerant strains of Burkholderia cepacia from marine sponges of the Saint Martin's Island of the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh.

Pseudomonas syringae is a rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacterium with polar flagella. As a plant pathogen, it can infect a wide range of species, and exists as over 50 different pathovars, all of which are available to researchers from international culture collections such as the NCPPB, ICMP, and others.
Pseudomonas argentinensis is a yellow-pigmented, Gram-negative, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming, strictly aerobic organism bacterium that infects the rhizospheres of Chloris ciliata and Pappophorum caespitosum, both grasses native to the Chaco region (Cordoba) of Argentina.
Pseudomonas palleroniana is a Gram-negative bacterium that infects rice. The type strain is CFBP 4389.
Pseudomonas trivialis is a fluorescent, Gram-negative bacterium isolated from the phyllosphere of grasses. The type strain is DSM 14937.
Pseudomonas poae is a fluorescent, Gram-negative bacterium isolated from the phyllosphere of grasses. The type strain is DSM 14936.
Pseudomonas amygdali is a Gram-negative plant pathogenic bacterium. It is named after its ability to cause disease on almond trees. Different analyses, including 16S rRNA analysis, DNA-DNA hybridization, and MLST clearly placed P. amygdali in the P. syringae group together with the species Pseudomonas ficuserectae and Pseudomonas meliae, and 27 pathovars of Pseudomonas syringae/Pseudomonas savastanoi, constituting a single, well-defined phylogenetic group which should be considered as a single species. This phylogenetic group has not been formally named because of the lack of reliable means to differentiate it phenotipically from closely related species, and it is currently known as either genomospecies 2 or phylogroup 3. When it is formally named, the correct name for this new species should be Pseudomonas amygdali, which takes precedence over all the other names of taxa from this group, including Pseudomonas savastanoi, which is and inadequate and confusing name whose use is not recommended.
Pseudomonas kilonensis is a Gram-negative soil bacterium isolated from agricultural soil in Germany. The type strain is DSM 13647.
Pseudomonas luteola is an opportunistic pathogen, found ubiquitously in damp environments. Originally designated in the genus Chryseomonas, the species has since been reassigned to the genus Pseudomonas.
Pseudomonas oryzihabitans, also known as Flavimonas oryzihabitans, is a nonfermenting yellow-pigmented, gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause sepsis, peritonitis, endophthalmitis, and bacteremia. It is an opportunistic pathogen of humans and warm-blooded animals that is commonly found in several environmental sources, from soil to rice paddies. They can be distinguished from other nonfermenters by their negative oxidase reaction and aerobic character. This organism can infect individuals that have major illnesses, including those undergoing surgery or with catheters in their body. Based on the 16S RNA analysis, these bacteria have been placed in the Pseudomonas putida group.
Pseudomonas panacis is a Gram-negative, aerobic, motile with one or more polar flagella, rod-shaped bacterium. It derives its name from the fact that it causes rusty root lesions on Korean ginseng, as the ginseng genus is Panax.
Pseudomonas azotifigens is a Gram-negative, nitrogen-fixing bacterium isolated from a compost pile in Japan.
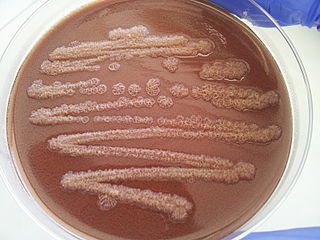
Pseudomonas stutzeri is a Gram-negative soil bacterium that is motile, has a single polar flagellum, and is classified as bacillus, or rod-shaped. While this bacterium was first isolated from human spinal fluid, it has since been found in many different environments due to its various characteristics and metabolic capabilities. P. stutzeri is an opportunistic pathogen in clinical settings, although infections are rare. Based on 16S rRNA analysis, this bacterium has been placed in the P. stutzeri group, to which it lends its name.
Pelomonas saccharophila is a Gram-negative soil bacterium. It was originally named Pseudomonas saccharophila in 1940, but was reclassified in 2005 to the newly created genus, Pelomonas. The original strain was isolated from mud.

Cefsulodin is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic that is active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and was discovered by Takeda Pharmaceutical Company in 1977.







