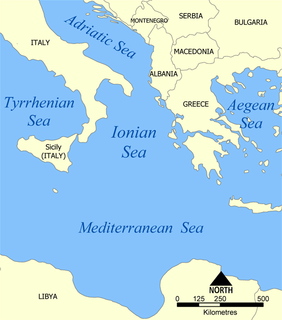
The Ionian Sea is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea, south of the Adriatic Sea. It is bounded by Southern Italy including Calabria, Sicily, and the Salento peninsula to the west, southern Albania to the north, and the west coast of Greece.

Baikonur Cosmodrome is a spaceport located in an area of southern Kazakhstan leased to Russia.
The alpha process, also known as the alpha ladder, is one of two classes of nuclear fusion reactions by which stars convert helium into heavier elements, the other being the triple-alpha process. The triple-alpha process consumes only helium, and produces carbon. After enough carbon has accumulated, the reactions below take place, all consuming only helium and the product of the previous reaction.

In geology, the places known as hotspots or hot spots are volcanic regions thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. Their position on the Earth's surface is independent of tectonic plate boundaries. There are two hypotheses that attempt to explain their origins. One suggests that hotspots are due to mantle plumes that rise as thermal diapirs from the core–mantle boundary. The other hypothesis is that lithospheric extension permits the passive rising of melt from shallow depths. This hypothesis considers the term "hotspot" to be a misnomer, asserting that the mantle source beneath them is, in fact, not anomalously hot at all. Well-known examples include the Hawaii, Iceland and Yellowstone hotspots.

CD36, also known as platelet glycoprotein 4, fatty acid translocase (FAT), scavenger receptor class B member 3 (SCARB3), and glycoproteins 88 (GP88), IIIb (GPIIIB), or IV (GPIV) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD36 gene. The CD36 antigen is an integral membrane protein found on the surface of many cell types in vertebrate animals. It imports fatty acids inside cells and is a member of the class B scavenger receptor family of cell surface proteins. CD36 binds many ligands including collagen, thrombospondin, erythrocytes parasitized with Plasmodium falciparum, oxidized low density lipoprotein, native lipoproteins, oxidized phospholipids, and long-chain fatty acids.

The European route E 22 is one of the longest European routes. It has a length of about 5,320 km (3,310 mi). Many of the E-roads have been extended into Asia since the year 2000; the E 22 was extended on 24 June 2002.

Baingoin County is a county within Nagqu of the Tibet Autonomous Region.
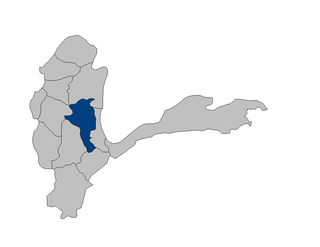
Warduj District is one of the 28 districts of Badakhshan Province in eastern Afghanistan. It was created in 2005 from part of Baharak District and is home to approximately 17,000 residents. Total area of the district is 929 square kilometers. 45 villages are located within its borders. Ethnic composition: 90% Tajik and 10% Uzbek.
Kepoi or Cepoi was an ancient Greek colony situated on the Taman peninsula, three kilometres to the east of Phanagoria, in the present-day Krasnodar Krai of Russia. The colony was established by the Milesians in the 6th century BC. In the Hellenistic period, it was controlled by the kings of the Cimmerian Bosporus, who made a present of a place called "the Gardens" to Gylon, the grandfather of Demosthenes. The town reached its peak in the 1st centuries AD, but the Huns and Goths put an end to its prosperity in the 4th century. Soviet excavations, started in 1957, yielded rich finds, including a marble statue of a Greek goddess. More than 400 burials were explored at Kepoi in the 1960s and 1970s; the rest of the site has been submerged by the Sea of Azov.

Kimmerikón was an ancient Greek city in Crimea, on the southern shore of the Kerch Peninsula, at the western slope of Mount Opuk, roughly 40 kilometres southwest of modern Kerch. It was situated with its acropolis on the hills on the west side of the mountain. The town was founded by the Milesian colonists in the 5th century BC and flourished at the beginning of the Christian era. Its name may refer to an earlier Cimmerian settlement on the site.

Edward F. Ricketts State Marine Conservation Area is one of four small marine protected areas located near the cities of Monterey and Pacific Grove, at the southern end of Monterey Bay on California’s central coast. The four areas together encompass 2.96 square miles (7.7 km2). Within SMCAs fishing and take of all living marine resources is prohibited except the recreational take of finfish by hook-and-line and the commercial take of giant and bull kelp under certain conditions.

Cennet and Cehennem are the names of two large sinkholes in the Taurus Mountains, in Mersin Province, Turkey. The sinkholes are among the tourist attractions of the province.

Ancient road at is the unearthed section of an ancient road in the historical city of Tarsus, Turkey.

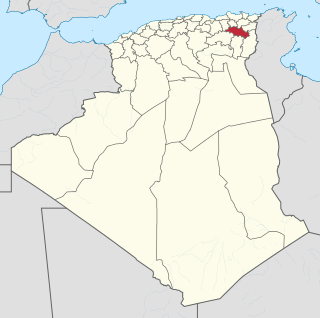
The Université Constantine 1, formerly the University of Mentouri, is a university located in Constantine, Algeria. The university was designed by Brazilian architect Oscar Niemeyer and built from 1969–1972.
Chah-e Dasht Mohammad Khan 6 is a village in Sahra Rural District, Anabad District, Bardaskan County, Razavi Khorasan Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 17, in 5 families.
German submarine U-595 was a Type VIIC U-boat built for Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine for service during World War II. She was laid down on 4 January 1941 by Blohm & Voss, Hamburg as yard number 571, launched on 17 September 1941 and commissioned on 6 November 1941 under Oberleutnant zur See Jürgen Quaet-Faslem.
Pashbard is a village in Melkari Rural District, Vazineh District, Sardasht County, West Azerbaijan Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 49, in 6 families.

Shirgaon Fort / Shirgao Fort is a fort located 6.5km from Palghar, in Palghar district, of Maharashtra. This fort is in very good condition. The outer walls, steps, parapets, bastions etc. in solid masonry are in excellent order and worth seeing. The fort is located in the Shirgaon village.

Frederick Barbarossa Memorial is a monument dedicated to Holy Roman Emperor Frederick I located in Mersin Province, southern Turkey.