Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes.
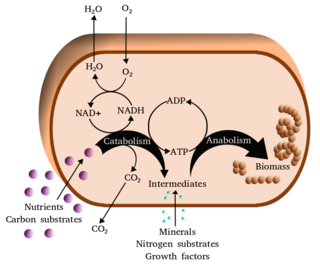
Metabolism is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism.

Mannose is a sugar monomer of the aldohexose series of carbohydrates. It is a C-2 epimer of glucose. Mannose is important in human metabolism, especially in the glycosylation of certain proteins. Several congenital disorders of glycosylation are associated with mutations in enzymes involved in mannose metabolism.

The enzyme fructose bisphosphatase (EC 3.1.3.11; systematic name D-fructose-1,6-bisphosphate 1-phosphohydrolase) catalyses the conversion of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to fructose 6-phosphate in gluconeogenesis and the Calvin cycle, which are both anabolic pathways:
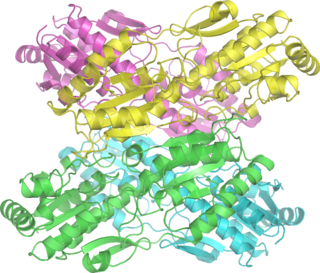
Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) is one of the most important regulatory enzymes of glycolysis. It is an allosteric enzyme made of 4 subunits and controlled by many activators and inhibitors. PFK-1 catalyzes the important "committed" step of glycolysis, the conversion of fructose 6-phosphate and ATP to fructose 1,6-bisphosphate and ADP. Glycolysis is the foundation for respiration, both anaerobic and aerobic. Because phosphofructokinase (PFK) catalyzes the ATP-dependent phosphorylation to convert fructose-6-phosphate into fructose 1,6-bisphosphate and ADP, it is one of the key regulatory steps of glycolysis. PFK is able to regulate glycolysis through allosteric inhibition, and in this way, the cell can increase or decrease the rate of glycolysis in response to the cell's energy requirements. For example, a high ratio of ATP to ADP will inhibit PFK and glycolysis. The key difference between the regulation of PFK in eukaryotes and prokaryotes is that in eukaryotes PFK is activated by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. The purpose of fructose 2,6-bisphosphate is to supersede ATP inhibition, thus allowing eukaryotes to have greater sensitivity to regulation by hormones like glucagon and insulin.

Pyruvate kinase is the enzyme involved in the last step of glycolysis. It catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to adenosine diphosphate (ADP), yielding one molecule of pyruvate and one molecule of ATP. Pyruvate kinase was inappropriately named before it was recognized that it did not directly catalyze phosphorylation of pyruvate, which does not occur under physiological conditions. Pyruvate kinase is present in four distinct, tissue-specific isozymes in animals, each consisting of particular kinetic properties necessary to accommodate the variations in metabolic requirements of diverse tissues.
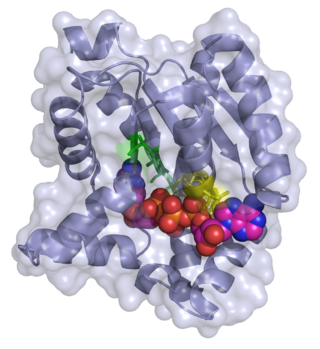
Adenylate kinase is a phosphotransferase enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of the various adenosine phosphates. By constantly monitoring phosphate nucleotide levels inside the cell, ADK plays an important role in cellular energy homeostasis.

Henrik Kacser FRSE was a Austro-Hungarian-born biochemist and geneticist who worked in Britain in the 20th century. Kacser's achievements have been recognised by his election to the Royal Society of Edinburgh in 1990, by an honorary doctorate of the University of Bordeaux II in 1993.
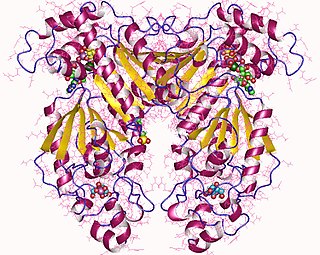
Phosphofructokinase-2 (6-phosphofructo-2-kinase, PFK-2) or fructose bisphosphatase-2 (FBPase-2), is an enzyme indirectly responsible for regulating the rates of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in cells. It catalyzes formation and degradation of a significant allosteric regulator, fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (Fru-2,6-P2) from substrate fructose-6-phosphate. Fru-2,6-P2 contributes to the rate-determining step of glycolysis as it activates enzyme phosphofructokinase 1 in the glycolysis pathway, and inhibits fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 in gluconeogenesis. Since Fru-2,6-P2 differentially regulates glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, it can act as a key signal to switch between the opposing pathways. Because PFK-2 produces Fru-2,6-P2 in response to hormonal signaling, metabolism can be more sensitively and efficiently controlled to align with the organism's glycolytic needs. This enzyme participates in fructose and mannose metabolism. The enzyme is important in the regulation of hepatic carbohydrate metabolism and is found in greatest quantities in the liver, kidney and heart. In mammals, several genes often encode different isoforms, each of which differs in its tissue distribution and enzymatic activity. The family described here bears a resemblance to the ATP-driven phospho-fructokinases; however, they share little sequence similarity, although a few residues seem key to their interaction with fructose 6-phosphate.
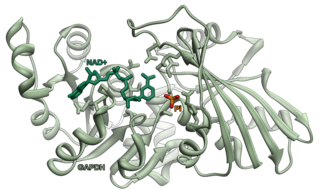
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase is an enzyme of about 37kDa that catalyzes the sixth step of glycolysis and thus serves to break down glucose for energy and carbon molecules. In addition to this long established metabolic function, GAPDH has recently been implicated in several non-metabolic processes, including transcription activation, initiation of apoptosis, ER-to-Golgi vesicle shuttling, and fast axonal, or axoplasmic transport. In sperm, a testis-specific isoenzyme GAPDHS is expressed.
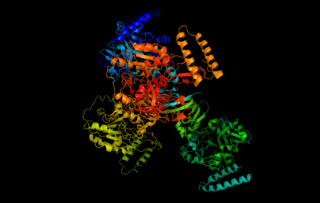
UTP—glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase also known as glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase is an enzyme involved in carbohydrate metabolism. It synthesizes UDP-glucose from glucose-1-phosphate and UTP; i.e.,

Phosphofructokinase (PFK) is a kinase enzyme that phosphorylates fructose 6-phosphate in glycolysis.

Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 1 (MAP3K1) is a signal transduction enzyme that in humans is encoded by the autosomal MAP3K1 gene.

Pyruvate kinase isozymes M1/M2 (PKM1/M2), also known as pyruvate kinase muscle isozyme (PKM), pyruvate kinase type K, cytosolic thyroid hormone-binding protein (CTHBP), thyroid hormone-binding protein 1 (THBP1), or opa-interacting protein 3 (OIP3), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PKM2 gene.

ADP/ATP translocase 4 (ANT4) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SLC25A31 gene on chromosome 4. This enzyme inhibits apoptosis by catalyzing ADP/ATP exchange across the mitochondrial membranes and regulating membrane potential. In particular, ANT4 is essential to spermatogenesis, as it imports ATP into sperm mitochondria to support their development and survival. Outside this role, the SLC25AC31 gene has not been implicated in any human disease.
Metabolite channeling is the passing of the intermediary metabolic product of one enzyme directly to another enzyme or active site without its release into solution. When several consecutive enzymes of a metabolic pathway channel substrates between themselves, this is called a metabolon. Channeling can make a metabolic pathway more rapid and efficient than it would be if the enzymes were randomly distributed in the cytosol, or prevent the release of unstable intermediates. It can also protect an intermediate from being consumed by competing reactions catalyzed by other enzymes.

Douglas Bruce Kell is a British biochemist and Research Professor of Systems Biology in the Institute of Systems, Molecular and Integrative Biology at the University of Liverpool. He was previously at the School of Chemistry at the University of Manchester, based in the Manchester Institute of Biotechnology (MIB). He founded and led the Manchester Centre for Integrative Systems Biology. He served as chief executive officer (CEO) of the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) from 2008 to 2013.
Stephen George Oliver is an Emeritus Professor in the Department of Biochemistry at the University of Cambridge, and a Fellow of Wolfson College, Cambridge.
David S. Broomhead was a British mathematician specialising in dynamical systems and was professor of applied mathematics at the School of Mathematics, University of Manchester.
Jan-Hendrik HofmeyrFRSSAf is one of the leaders in the field of metabolic control analysis and the quantitative analysis of metabolic regulation.