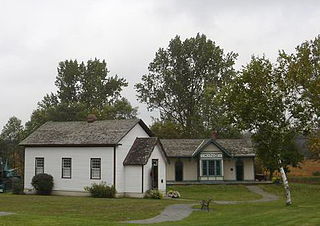The geography of Canada describes the geographic features of Canada, the world's second largest country in total area.

The Mississippi River is a tributary of the Ottawa River in Eastern Ontario, Canada. It is 200 kilometres (120 mi) in length from its source at Mackavoy Lake, has a drainage area of 4,450 square kilometres (1,720 sq mi), and has a mean discharge of 40 cubic metres per second (1,400 cu ft/s). There are more than 250 lakes in the watershed.

Southern Ontario is a primary region of the province of Ontario, Canada, the other primary region being Northern Ontario. It is the most densely populated and southernmost region in Canada. The exact northern boundary of Southern Ontario is disputed; however, the core region is situated south of Algonquin Park, the latter being in an area of transition between coniferous forest north of the French and Mattawa Rivers and southern deciduous forest. It covers between 14 and 15% of the province, depending on the inclusion of the Parry Sound and Muskoka districts which also lie in the transitional area between northern and southern forest regions. With more than 12.7 million people, the region is home to approximately one-third of Canada's population of 35.1 million.

Baden is a suburban community and unincorporated place in Township of Wilmot, Regional Municipality of Waterloo in Southwestern Ontario, Canada. It has a population of around 4500 and was named after Baden-Baden, Germany. The approximate population as of 2011, as per township statistics, is 4,553.
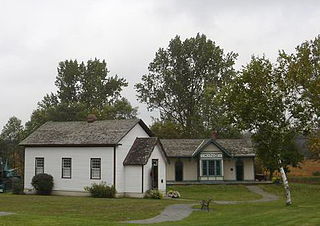
King City is an unincorporated Canadian community in King, Ontario located north of Toronto. It is the largest community in King Township, with 2,396 dwellings and a population of 6,970 as of the Canada 2016 Census.
King Creek is the old name for what is now known as the East Humber River. Originally a small community called "Humber Trails" nestled in the valley around the King Creek west of The Mill Road. After hurricane Hazel, in the fall of 1954, the Toronto Regional Park Authority expropriated the land creating the Humber Trails Conservation area. One street named Elmpine Trails, on the south side of the King Creek, was not expropriated as the homes were on high ground with no chance of a flood damaging the houses. Several properties on the Mill Road were also not expropriated for the same reason. For approximately fifteen years the Humber Trails Conservation Area was a manicured Park. However a decision was made to allow the park to become a nature preserve. Today there are few signs that streets and homes and later, a manicured park had existed in the valley, except for a few walking paths and a Humber Trails post office structure that was assimilated into the buildings of a private residence and working farm located on either side of Mill Road. King Township, Ontario, Canada.The area is located immediately east of Nobleton. To the east is King City.
Pottageville is an unincorporated community located in northeastern King Township, in Ontario, Canada. It is near Schomberg. It is named for one of its early settlers, Edward Pottage.

The Ministry of Natural Resources and Forestry (MNRF) is a government ministry of the Canadian province of Ontario that is responsible for Ontario’s provincial parks, forests, fisheries, wildlife, mineral aggregates and the Crown lands and waters that make up 87 per cent of the province. Its offices are divided into Northwestern, Northeastern and Southern Ontario regions with the main headquarters in Peterborough, Ontario.

Laurentian Valley is a township municipality in Renfrew County in eastern Ontario, Canada. It borders on the Ottawa River, the city of Pembroke and the town of Petawawa.

The Oak Ridges Moraine lies in Southern Ontario, Canada. It contains the headwaters of sixty-five rivers and streams. It has a wide diversity of woodlands, wetlands, watercourses, kettle lakes, kettle bogs, and significant flora and fauna. It is one of the few remaining continuous green corridors in southern Ontario: it remains thirty percent forested and is one of the last refuges for forest birds in all of southern Ontario.
Ontario Parks is the agency in Ontario, Canada, that protects significant natural and cultural resources in a system of parks and protected areas that is sustainable and provides opportunities for inspiration, enjoyment and education. The Ontario Parks system covers over 78,000 square kilometres (30,000 sq mi), about 10 percent of the province's surface area or the equivalent of an area approximately equal to Nova Scotia. It falls under the responsibility and mandate of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Forestry.

Val Rita-Harty is a township municipality in Cochrane District in Northeastern Ontario, Canada.

Cold Creek Conservation Area, usually Cold Creek, is an ecologically diverse protected Area of Natural and Scientific Interest in south-central Ontario, Canada. The 190-hectare (470-acre) conservation area was opened on 20 June 1962 by Wilf Spooner and the Toronto and Region Conservation Authority. It is located on the western end of King Township, overlapping the Oak Ridges Moraine. The Government of Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources classifies the area as a provincially significant Area of Natural and Scientific Interest for its "provincially or regionally significant representative ecological features". The area was also a site classified for the International Biological Program. The Life Science area, known as Cold Creek Swamp, is composed of a swamp and forest.
There are numerous natural areas in King, a township in Ontario, Canada. These areas are zones officially designated by the Government of Ontario that are within the township and exhibit provincially or regionally significant features representative of the region. The list of zones is defined and maintained by the provincial Ministry of Natural Resources Natural Heritage Information Centre.
Matchedash Bay is a bay and Ramsar wetland in Simcoe County in Central Ontario, Canada. It is the "final inland extension of Severn Sound" on Lake Huron's Georgian Bay, and is "situated at the interface between the Saint Lawrence Lowlands and the Canadian Shield ". It exhibits geologically unique features at the junction of the Canadian Shield and southern Ontario limestone. Wetland habitats in Matchedash Bay are varied, and include swamps, fens, cattail marshes, wet meadows and beaver ponds. Other features include "permanent freshwater lakes; upland hardwood forest, agricultural lands, native grass meadows and a unique, coniferous wetland forest".

Minesing Wetlands, previously known as Minesing Swamp, is a Ramsar boreal wetland in central Ontario, Canada stretching from the western periphery of Barrie to Georgian Bay. It was identified and classified through the International Biological Program. It is "the largest and best example of fen bog in southern Ontario", one of the "most diverse undisturbed wetland tracts in Canada" and is a provincially significant Area of Natural and Scientific Interest. The term minesing is of Ojibwe origin and means "island", referring to an island located within Lake Edenvale, which encompassed the present-day wetlands and surrounding areas.

Southern James Bay is a coastal wetland complex in northeastern Ontario, Canada bordering James Bay and Quebec. It was designated as a wetland of international importance via the Ramsar Convention on May 27, 1987. The shallow waters of the James Bay region represent an important late autumn staging area for migratory, Arctic-breeding waterbirds.

Batchawana Bay is an unincorporated place and Compact Rural Community in Algoma District in Northeastern Ontario, Canada. It is also the name of a local services board, consisting of parts of the geographic townships of Fisher, Herrick, Ryan and Tilley. It is located north of Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, on the shores of Batchawana Bay off Lake Superior.