
The obliquus capitis inferior muscle is the larger of the two oblique muscles of the neck. It arises from the apex of the spinous process of the axis and passes laterally and slightly upward, to be inserted into the lower and back part of the transverse process of the atlas.

The obliquus capitis superior muscle is a small muscle in the upper back part of the neck and is one of the suboccipital muscles and part of the suboccipital triangle. It arises from the lateral mass of the atlas bone. It passes superiorly and posteriorly to insert into the lateral half of the inferior nuchal line on the external surface of the occipital bone. The muscle is innervated by the suboccipital nerve, the dorsal ramus of the first spinal nerve.
Harpalus, son of Machatas, was a Macedonian aristocrat and childhood friend of Alexander the Great in the 4th century BC. Harpalus was repeatedly entrusted with official duties by Alexander and absconded with large sums of money on three occasions. Alexander appointed him treasurer of his empire in Babylon in 330 BC. In 324 BC he fled from Babylon to Athens with a large sum of money. The resulting political controversy in Athens was a contributing factor in the Lamian War.

The vastus medialis is an extensor muscle located medially in the thigh that extends the knee. The vastus medialis is part of the quadriceps muscle group.

In anatomy, the abdominal wall represents the boundaries of the abdominal cavity. The abdominal wall is split into the anterolateral and posterior walls.

Betulin is an abundant, naturally occurring triterpene. It is commonly isolated from the bark of birch trees. It forms up to 30% of the dry weight of silver birch bark. It is also found in birch sap. Inonotus obliquus contains betulin.

Otodus is an extinct, cosmopolitan genus of mackerel shark which lived from the Paleocene to the Pliocene epoch. The name Otodus comes from Ancient Greek ὠτ and ὀδούς – thus, "ear-shaped tooth".

The anterior divisions of the seventh, eighth, ninth, tenth, and eleventh thoracic intercostal nerves are continued anteriorly from the intercostal spaces into the abdominal wall; hence they are named thoraco-abdominal nerves.

Inonotus obliquus, commonly called chaga, is a fungus in the family Hymenochaetaceae. It is parasitic on birch and other trees. The sterile conk is irregularly formed and resembles burnt charcoal. It is not the fruiting body of the fungus, but a sclerotium or mass of mycelium, mostly black because of a great amount of melanin. Some people consider chaga medicinal.
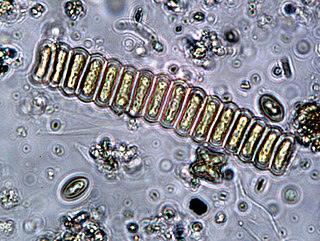
Scenedesmus is a genus of green algae, in the class Chlorophyceae. They are colonial and non-motile.

Harpalus is a genus of ground beetle first described by Pierre André Latreille in 1802.
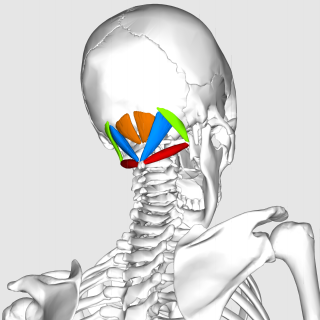
The suboccipital muscles are a group of muscles defined by their location to the occiput. Suboccipital muscles are located below the occipital bone. These are four paired muscles on the underside of the occipital bone; the two straight muscles (rectus) and the two oblique muscles (obliquus).

Scaphinotus is a genus of beetles in the family Carabidae. There are at least 60 species, all native to North America. They eat snails and are generally limited to the moist environments where snails live. These beetles are flightless.

Pterostichinae is a subfamily of ground beetles. It belongs to the advanced harpaline assemblage, and if these are circumscribed sensu lato as a single subfamily, Pterostichinae are downranked to a tribe Pterostichini. However, as the former Pterostichitae supertribe of the Harpalinae as loosely circumscribed does seem to constitute a lineage rather distinct from Harpalus, its core group is here considered to be the present subfamily and the Harpalinae are defined more narrowly.
Anisancylus obliquus is a species of small, freshwater, air-breathing limpet, an aquatic pulmonate gastropod mollusc in the family Planorbidae, the ram's horn snails and their allies.

Adetus is a genus of beetles in the family Cerambycidae.
The scenedesmus obliquus mitochondrial code is a genetic code found in the mitochondria of Scenedesmus obliquus, a species of green algae.

Scenedesmus obliquus is a green algae species of the genus Scenedesmus.

Stenolophina is a subtribe of ground beetles in the family Carabidae. There are about 9 genera and at least 50 described species in Stenolophina.















