
The Sharpless epoxidation reaction is an enantioselective chemical reaction to prepare 2,3-epoxyalcohols from primary and secondary allylic alcohols. The oxidizing agent is tert-butyl hydroperoxide. The method relies on a catalyst formed from titanium tetra(isopropoxide) and diethyl tartrate.

Lysergic acid, also known as D-lysergic acid and (+)-lysergic acid, is a precursor for a wide range of ergoline alkaloids that are produced by the ergot fungus and found in the seeds of Turbina corymbosa (ololiuhqui), Argyreia nervosa, and Ipomoea tricolor.
The Fischer indole synthesis is a chemical reaction that produces the aromatic heterocycle indole from a (substituted) phenylhydrazine and an aldehyde or ketone under acidic conditions. The reaction was discovered in 1883 by Emil Fischer. Today antimigraine drugs of the triptan class are often synthesized by this method.

The Aza-Diels–Alder reaction is a modification of the Diels–Alder reaction wherein a nitrogen replaces sp2 carbon. The nitrogen atom can be part of the diene or the dienophile.

The Corey–Itsuno reduction, also known as the Corey–Bakshi–Shibata (CBS) reduction, is a chemical reaction in which a prochiral ketone is enantioselectively reduced to produce the corresponding chiral, non-racemic alcohol. The oxazaborolidine reagent which mediates the enantioselective reduction of ketones was previously developed by the laboratory of Itsuno and thus this transformation may more properly be called the Itsuno-Corey oxazaborolidine reduction.

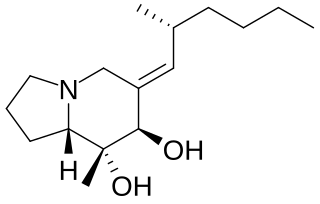
Lupinine is a quinolizidine alkaloid present in the genus Lupinus of the flowering plant family Fabaceae. The scientific literature contains many reports on the isolation and synthesis of this compound as well as a vast number of studies on its biosynthesis from its natural precursor, lysine. Studies have shown that lupinine hydrochloride is a mildly toxic acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and that lupinine has an inhibitory effect on acetylcholine receptors. The characteristically bitter taste of lupin beans, which come from the seeds of Lupinus plants, is attributable to the quinolizidine alkaloids which they contain, rendering them unsuitable for human and animal consumption unless handled properly. However, because lupin beans have potential nutritional value due to their high protein content, efforts have been made to reduce their alkaloid content through the development of "sweet" varieties of Lupinus.

In organic chemistry, organocatalysis is a form of catalysis in which the rate of a chemical reaction is increased by an organic catalyst. This "organocatalyst" consists of carbon, hydrogen, sulfur and other nonmetal elements found in organic compounds. Because of their similarity in composition and description, they are often mistaken as a misnomer for enzymes due to their comparable effects on reaction rates and forms of catalysis involved.
Allopumiliotoxin 267A is a toxin found in the skin of several poison frogs of the family Dendrobates. It is a member of the class of compounds known as allopumiliotoxins. The frogs produce the toxin by modifying the original version, pumiliotoxin 251D. It has been tested on mice and found to be five times more potent than the former version. It has been produced synthetically through a variety of different routes.

Larry E. Overman is Distinguished Professor of Chemistry at the University of California, Irvine. He was born in Chicago in 1943. Overman obtained a B.A. degree from Earlham College in 1965, and he completed his Ph.D. in chemistry from the University of Wisconsin–Madison in 1969, under Howard Whitlock Jr. Professor Overman is a member of the United States National Academy of Sciences and the American Academy of Arts and Sciences. He was the recipient of the Arthur C. Cope Award in 2003, and he was awarded the Tetrahedron Prize for Creativity in Organic Chemistry for 2008.
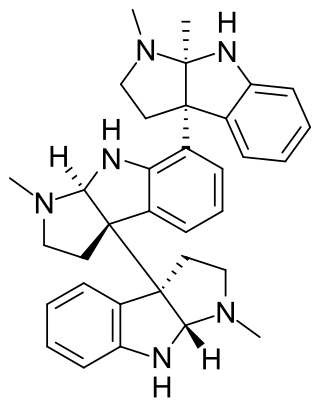
Hodgkinsine is an alkaloid found in plants of the genus Psychotria, particularly Psychotria colorata, although it is also found in Psychotria lyciiflora and probably other species in this family,

(−)-Magellanine is a member of the Lycopodium alkaloid class of natural products. It was isolated from the club moss Lycopodium magellanicum in 1976. It has been synthesized five times, with the first synthesis having been completed by the Larry E. Overman group at the University of California, Irvine in 1993. It has also been synthesized by the Leo Paquette group in 1993 at Ohio State University, the Chun-Chen Liao group in 2002 at National Tsing Hua University, the Miyuki Ishikazi and Tamiko Takahashi groups in 2005 at the Josai International University and Tokyo University of Science, and the Chisato Mukai group in 2007 at the Kanazawa University. One partial synthesis was completed by the A. I. Meyers group in 1995 at Colorado State University.

The 10-hydroxy Lycopodium alkaloids, which include 10-hydroxylycopodine, deacetylpaniculine, and paniculine, are a series of natural products isolated from a Chilean club moss Lycopodium confertum. Deacetylpaniculine and paniculine were also isolated from Lycopodium paniculatum.

Akuammicine is a monoterpene indole alkaloid of the Vinca sub-group. It is found in the Apocynaceae family of plants including Picralima nitida, Vinca minor and the Aspidosperma.

Dendrobine is an alkaloid found in Dendrobium nobile at an average of 0.5% by weight. It is a colorless solid at room temperature. It is related to the picrotoxin family of natural products. When given a fatal dose, death is usually caused by convulsions. It possesses a molecular structure that attracted interest in its total synthesis by organic chemists.

Stephacidin A and B are antitumor alkaloids isolated from the fungus Aspergillus ochraceus that belong to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines. This unusual family of fungal metabolites are complex bridged 2,5-diketopiperazine alkaloids that possess a unique bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane core ring system and are constituted mainly from tryptophan, proline, and substituted proline derivatives where the olefinic unit of the isoprene moiety has been formally oxidatively cyclized across the α-carbon atoms of a 2,5-diketopiperazine ring. The molecular architecture of stephacidin B, formally a dimer of avrainvillamide, reveals a complex dimeric prenylated N-hydroxyindole alkaloid that contains 15 rings and 9 stereogenic centers and is one of the most complex indole alkaloids isolated from fungi. Stephacidin B rapidly converts into the electrophilic monomer avrainvillamide in cell culture, and there is evidence that the monomer avrainvillamide interacts with intracellular thiol-containing proteins, most likely by covalent modification.
Biomimetic synthesis is an area of organic chemical synthesis that is specifically biologically inspired. The term encompasses both the testing of a "biogenetic hypothesis" through execution of a series of reactions designed to parallel the proposed biosynthesis, as well as programs of study where a synthetic reaction or reactions aimed at a desired synthetic goal are designed to mimic one or more known enzymic transformations of an established biosynthetic pathway. The earliest generally cited example of a biomimetic synthesis is Sir Robert Robinson's organic synthesis of the alkaloid tropinone.
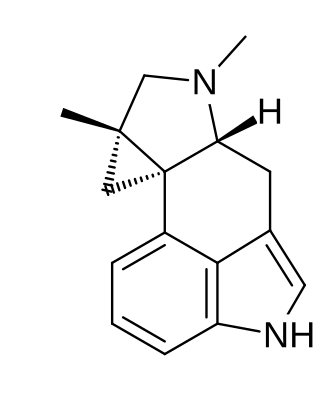
Cycloclavine is an ergot alkaloid. It was first isolated in 1969 from seeds of Ipomoea hildebrandtii vatke. The first total synthesis of (±)-cycloclavine was published in 2008 by Szántay. Further reports came from Wipf and Petronijevic, Cao and Brewer. In 2016, Wipf and McCabe completed an 8-step asymmetric synthesis of (–)-cycloclavine, and in 2018, they expanded this approach toward (+)-cycloclavine and a biological characterization of the binding profile of both enantiomers on 16 brain receptors. Natural (+)- and unnatural (–)-cycloclavine demonstrated significant stereospecificity and unique binding profiles in comparison to LSD, psilocin, and DMT. Differential 5-HT receptor affinities, as well as novel sigma-1 receptor properties, suggest potential future therapeutic opportunities of clavine alkaloid scaffolds.

Dideoxyverticillin A, also known as (+)-11,11′-dideoxyverticillin A, is a complex epipolythiodioxopiperazine initially isolated from the marine fungus Penicillium sp. in 1999. It has also been found in the marine fungus Bionectriaceae, and belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines.
Sarah Elizabeth Reisman is the Bren Professor of Chemistry and the Chair of Division of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering at California Institute of Technology. She received the (2013) Arthur C. Cope Scholar Award and the (2014) Tetrahedron Young Investigator Award for Organic Synthesis. Her research focuses on the total synthesis of complex natural products and data-driven developments of asymmetric catalysis.

The nitro-Mannich reaction is the nucleophilic addition of a nitroalkane to an imine, resulting in the formation of a beta-nitroamine. With the reaction involving the addition of an acidic carbon nucleophile to a carbon-heteroatom double bond, the nitro-Mannich reaction is related to some of the most fundamental carbon-carbon bond forming reactions in organic chemistry, including the aldol reaction, Henry reaction and Mannich reaction.

















