
The Qutb Minar complex are monuments and buildings from the Delhi Sultanate at Mehrauli in Delhi, India. Construction of the Qutub Minar "victory tower" in the complex, named after the religious figure Sufi Saint Khwaja Qutbuddin Bakhtiar Kaki, was begun by Qutb-ud-din Aibak, who later became the first Sultan of Delhi of the Mamluk dynasty. It was continued by his successor Iltutmish, and finally completed much later by Firoz Shah Tughlaq, a Sultan of Delhi from the Tughlaq dynasty (1320–1412) in 1368 AD. The Qubbat-ul-Islam Mosque, later corrupted into Quwwat-ul Islam, stands next to the Qutb Minar.

Mirza Abu'l Fayaz Qutb-ud-Din Mohammad Azam, commonly known as Azam Shah, was briefly the seventh Mughal emperor from 14 March to 20 June 1707. He was the third son of the sixth Mughal emperor Aurangzeb and his chief consort Dilras Banu Begum.

Humayun's tomb is the tomb of Mughal emperor, Mirza Nasir al-Din Muhammad commonly known as Humayun situated in Delhi, India. The tomb was commissioned by Humayun's first wife and chief consort, Empress Bega Begum under her patronage in 1558, and designed by Mirak Mirza Ghiyas and his son, Sayyid Muhammad, Persian architects chosen by her. It was the first garden-tomb on the Indian subcontinent, and is located in Nizamuddin East, Delhi, close to the Dina-panah Citadel, also known as Purana Qila, that Humayun found in 1538. It was also the first structure to use red sandstone at such a scale. The tomb was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1993, and since then has undergone extensive restoration work, which is complete. Besides the main tomb enclosure of Humayun, several smaller monuments dot the pathway leading up to it, from the main entrance in the West, including one that even pre-dates the main tomb itself, by twenty years; it is the tomb complex of Isa Khan Niazi, an Afghan noble in Sher Shah Suri's court of the Suri dynasty, who fought against the Mughals, constructed in 1547 CE.

Lodi Gardens is a city park situated in New Delhi, India. Spread over 90 acres (360,000 m2), it contains Mohammed Shah's Tomb, the Tomb of Sikandar Lodi, the Shisha Gumbad and the Bara Gumbad, architectural works of the 15th century by Lodis - who ruled parts of northern India and Punjab and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of modern-day Pakistan, from 1451 to 1526 are present here. The site is now protected by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).

Mughal architecture is the type of Indo-Islamic architecture developed by the Mughals in the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries throughout the ever-changing extent of their empire in the Indian subcontinent. It developed from the architectural styles of earlier Muslim dynasties in India and from Iranian and Central Asian architectural traditions, particularly Timurid architecture. It also further incorporated and syncretized influences from wider Indian architecture, especially during the reign of Akbar. Mughal buildings have a uniform pattern of structure and character, including large bulbous domes, slender minarets at the corners, massive halls, large vaulted gateways, and delicate ornamentation; examples of the style can be found in modern-day Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India and Pakistan.

Tomb of I'timād-ud-Daulah is a Mughal mausoleum in the city of Agra in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. Often described as a "jewel box", sometimes called the "Bachcha Taj" or the "Baby Taj", the tomb of I'timād-ud-Daulah is often regarded as a draft of the Taj Mahal.

Adham Khan's Tomb is the 16th-century tomb of Adham Khan, a general of the Mughal Emperor Akbar. He was the younger son of Maham Anga, Akbar's wet nurse thus also his foster brother. However, when Adham Khan murdered Akbar’s favourite general Ataga Khan in May 1562, Akbar immediately ordered his execution by defenestration from the ramparts of the Agra Fort.

Indo-Islamic architecture is the architecture of the Indian subcontinent produced by and for Islamic patrons and purposes. Despite an initial Arab presence in Sindh, the development of Indo-Islamic architecture began in earnest with the establishment of Delhi as the capital of the Ghurid dynasty in 1193. Succeeding the Ghurids was the Delhi Sultanate, a series of Central Asian dynasties that consolidated much of North, East, and Central India, and later by the Mughal Empire during the early 16th century. Both of these dynasties introduced Islamic architecture and art styles from West Asia into the Indian subcontinent.

The Bibi Ka Maqbara is a tomb located in the city of Aurangabad in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It was commissioned in 1660 by the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb's son, Prince Azam Shah in the memory of his loving mother Dilras Banu Begum. It bears a striking resemblance to the Taj Mahal, the mausoleum of Aurangzeb's mother, Mumtaz Mahal and that is why it is also called the Taj of the Deccan. Aurangzeb was not much interested in architecture though he had commissioned the small, but elegant, Moti Masjid at Delhi. Bibi Ka Maqbara is the second largest structure that Aurangzeb has built, the largest being the Badshahi Mosque.

Khuldabad is a city and a Taluka of Aurangabad district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is known as the Valley of Saints, or the Abode of Eternity, because in the 14th century, several Sufi saints chose to reside here. The Bhadra Maruti Temple and Dargah of Zar Zari Zar Baksh, Shaikh Burhan ud-din Gharib Chisti and Shaikh Zain-ud-din Shirazi, along with the tomb of the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb and his trusted General Asif Jah I, the first Nizam of Hyderabad, are located in this town. It is a holy and spiritual city of Islamic saints.

The Tomb of Jahangir is a 17th-century mausoleum built for the Mughal emperor Jahangir. The mausoleum dates from 1637, and is located in Shahdara Bagh near city of Lahore, along the banks of River Ravi, in Punjab, Pakistan. The site is famous for its interiors that are extensively embellished with frescoes and marble, and its exterior that is richly decorated with pietra dura. The tomb, along with the adjacent Akbari Sarai and the Tomb of Asif Khan, are part of an ensemble currently on the tentative list for UNESCO World Heritage status.

The Qutub Shahi Tombs are located in the Ibrahim Bagh, close to the famous Golconda Fort in Hyderabad, India. They contain the tombs and mosques built by the various kings of the Qutub Shahi dynasty. The galleries of the smaller tombs are of a single storey while the larger ones are two-storied. In the centre of each tomb is a sarcophagus which overlies the actual burial vault in a crypt below. The domes were originally overlaid with blue and green tiles, of which only a few pieces now remain.

The Taj Mahal represents the finest and most sophisticated example of Indo-Islamic architecture. Its origins lie in the moving circumstances of its commission and the culture and history of an Islamic Mughal empire's rule of large parts of India. The distraught Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan commissioned the project upon the death of one of his favorite wives Mumtaz Mahal.

The Tomb of Mariam-uz-Zamani or Mariam's tomb is the mausoleum of Mariam-uz-Zamani, commonly known as Jodha Bai, the favorite wife of the Mughal Emperor Akbar. The tomb was built by her son Jahangir, in her memory between years 1623–1627 and is located in Sikandra, next to the Akbar's tomb, in the direction of Mathura. She stands as the only wife of Akbar buried closed to him.

The Tomb of Nur Jahan is a 17th-century mausoleum in Lahore, Pakistan, that was built for the Mughal empress Nur Jahan. The tomb's marble was plundered during the Sikh era in 18th century for use at the Golden Temple in Amritsar. The red sandstone mausoleum, along with the nearby tomb of Jahangir, tomb of Asif Khan, and Akbari Sarai, forms part of an ensemble of Mughal monuments in Lahore's Shahdara Bagh.

Persian Inscriptions on Indian Monuments is a book written in Persian by Dr Ali Asghar Hekmat E Shirazi and published in 1956 and 1958 and 2013. New edition contains the Persian texts of more than 200 epigraphical inscriptions found on historical monuments in India, many of which are currently listed as national heritage sites or registered as UNESCO world heritage, published in Persian; an English edition is also being printed.
Tughlaq Tombs in the Indian subcontinent are mostly simple, monotonous and heavy structures in Indo-Islamic architecture built during the Tughlaq dynasty (1320–1413). They look more like fortresses with walls surrounding them and have restrained decoration and embellishment compared to both earlier and later Indian Islamic tombs. Their architecture lacks the influence from Dravidian architecture and craftsmanship which was later found in Lodi and Mughal architecture. But Dravidian architecture influence on Tughlaq buildings was not totally absent. Features of Hindu influences on Tughlaq architecture include the flat lintel instead of pointed arch, pillars, windows with balconies and eaves and railings.
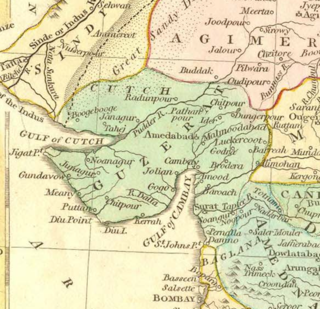
The Gujarat Subah was a province (subah) of the Mughal Empire, encompassing the Gujarat region. The region first fell under Mughal control in 1573, when the Mughal emperor Akbar defeated the Gujarat Sultanate under Muzaffar Shah III.

The tomb of the noble Isa Khan Niazi is located in the Humayun's Tomb complex in Delhi, India. The mausoleum, octagonal in shape and built mainly of red sandstone, was built in 1547–1548 during the reign of Sher Shah Suri. The mosque of Isa Khan is located west of the mausoleum, which along with other buildings form the UNESCO World Heritage Site of Humayun's tomb complex.

Nila Gumbad is a tomb located within the Humayun's Tomb complex at Delhi, India. Historians are unsure about the identity of the person who has been buried. Some claim that it houses the tomb of an attendant of a Mughal noble and was buried during the reign of Jahangir. According to others, the tomb existed much before the Humayun's Tomb was constructed. At the time of construction, it was covered with glazed tiles most of which have been destroyed. This building along with other buildings form the UNESCO World Heritage Site of Humayun's Tomb complex.























