
Digital enhanced cordless telecommunications (Digital European cordless telecommunications), usually known by the acronym DECT, is a standard primarily used for creating cordless telephone systems. It originated in Europe, where it is the common standard, replacing earlier cordless phone standards, such as 900 MHz CT1 and CT2.

Wireless communication is the transfer of information (telecommunication) between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most common wireless technologies use radio waves. With radio waves, intended distances can be short, such as a few meters for Bluetooth or as far as millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications. It encompasses various types of fixed, mobile, and portable applications, including two-way radios, cellular telephones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and wireless networking. Other examples of applications of radio wireless technology include GPS units, garage door openers, wireless computer mouse, keyboards and headsets, headphones, radio receivers, satellite television, broadcast television and cordless telephones. Somewhat less common methods of achieving wireless communications involve other electromagnetic phenomena, such as light and magnetic or electric fields, or the use of sound.

Headphones are a pair of small loudspeaker drivers worn on or around the head over a user's ears. They are electroacoustic transducers, which convert an electrical signal to a corresponding sound. Headphones let a single user listen to an audio source privately, in contrast to a loudspeaker, which emits sound into the open air for anyone nearby to hear. Headphones are also known as earphones or, colloquially, cans. Circumaural and supra-aural headphones use a band over the top of the head to hold the speakers in place. Another type, known as earbuds or earpieces consist of individual units that plug into the user's ear canal. A third type are bone conduction headphones, which typically wrap around the back of the head and rest in front of the ear canal, leaving the ear canal open. In the context of telecommunication, a headset is a combination of headphone and microphone.

A phone connector, also known as phone jack, audio jack, headphone jack or jack plug, is a family of electrical connectors typically used for analog audio signals. A plug, the "male" connector, is inserted into the jack, the "female" connector.

A hearing aid is a device designed to improve hearing by making sound audible to a person with hearing loss. Hearing aids are classified as medical devices in most countries, and regulated by the respective regulations. Small audio amplifiers such as personal sound amplification products (PSAPs) or other plain sound reinforcing systems cannot be sold as "hearing aids".

A cordless telephone or portable telephone has a portable telephone handset that connects by radio to a base station connected to the public telephone network. The operational range is limited, usually to the same building or within some short distance from the base station.

An intercom, also called an intercommunication device, intercommunicator, or interphone, is a stand-alone voice communications system for use within a building, small collection of buildings or portably within a small coverage area, which functions independently of the public telephone network. Intercoms are generally mounted permanently in buildings and vehicles, but can also be detachable and portable. Intercoms can incorporate connections to public address loudspeaker systems, walkie talkies, telephones, and other intercom systems. Some intercom systems incorporate control of devices such as signal lights and door latches.
Plantronics, Inc. is an American electronics company — branded Poly to reflect its dual Plantronics and Polycom heritage — producing audio communications equipment for business and consumers. Its products support unified communications, mobile use, gaming and music. Plantronics is headquartered in Santa Cruz, California, and most of its products are produced in China and Mexico.
Mobile VoIP or simply mVoIP is an extension of mobility to a voice over IP network. Two types of communication are generally supported: cordless telephones using DECT or PCS protocols for short range or campus communications where all base stations are linked into the same LAN, and wider area communications using 3G or 4G protocols.
Various accessories for the PlayStation 3 video game console have been produced by Sony and third-party companies. These include controllers, audio and video input devices like microphones, video cameras, and cables for better sound and picture quality.

The Xbox 360 Wireless Headset is a wireless headset designed for the Xbox 360 and Xbox Live; it is manufactured by Microsoft. It can be used for in game voice chat, private chat, audio for video chat and in game voice recognition. Up to four wireless headsets can be used simultaneously on a single Xbox 360. The headset fits over either ear and comes with two sizes of removable earloops for a better fit. It uses the same 2.4 GHz wireless technology as the Xbox 360 Wireless Controller, so it will work within 30 feet of the console. It can achieve up to eight hours of battery life per charge, with an AC wall adapter or a USB DC charger for recharging. USB chargers are readily available from mobile phone accessory shops. The headset can be used with or without a controller. The headset also produces various beeps to signal different actions and give messages to the user. The headset is also compatible for use with a PC via the Microsoft Wireless Receiver. Up to 4 wireless headsets and wireless controllers can be used in conjunction at any one time. The number lit up on the headset will correspond to the quadrant lit up on the controller..
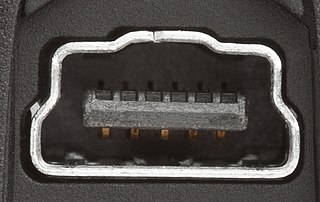
An enhanced mini-USB (EMU) connector is a type of hybrid electrical connector which carries Universal Serial Bus data and power as well as other connections such as bidirectional audio. It was invented for and is mainly used on mobile phones. Motorola, HTC Corporation, and other mobile phone manufacturers use EMU connectors. There is more than one standard for EMU connectors, which are incompatible between manufacturers, but all are physically and electrically compatible with standard mini-USB connectors. The EMU connector has five pins for USB on one side. While regular USB connectors are empty on the other side, EMU has more pins intended for headsets. In HTC's version, two pins are for the microphone, three are for stereo sound, and one is for the push-to-talk switch.

Wireless speakers are loudspeakers that receive audio signals using radio frequency (RF) waves rather than over audio cables. The two most popular RF frequencies that support audio transmission to wireless loudspeakers include a variation of WiFi IEEE 802.11, while others depend on Bluetooth to transmit audio data to the receiving speaker.
Gigaset AG, formerly known as Siemens Home and Office Communication Devices, is a German multinational corporation based in Bocholt, Germany. The company is most active in the area of communications technology. Gigaset manufactures DECT telephones. In 2017, it had 930 employees, revenue of 293 million Euro and sales activities in approximately 70 countries.

Apple Inc. has produced and sold headphones since 2001, available for standalone purchase and bundled with iPhone and iPod products. Apple's current product line consists of EarPods, AirPods and AirPods Pro, and AirPods Max.

The Xbox Wireless Controller is the primary game controller for the Xbox One and Xbox Series X/S home video game consoles, also commercialized for its use in Windows-based PCs, and compatible with other operating systems such as macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android. The controller maintains the overall layout found in the Xbox 360 controller, but with various tweaks to its design, such as a revised shape, redesigned analog sticks, shoulder buttons, and triggers, along with new rumble motors within the triggers to allow for directional haptic feedback.
The charts below compare hardware and firmware features in the FRITZ!Box device range.
A microphone blocker is a phone microphone connector used to trick feature phones that have a physical microphone switch to disconnect the microphone. Microphone blockers won't operate on smartphones or laptops because the microphone is controlled with software rather than a physical switch.




















