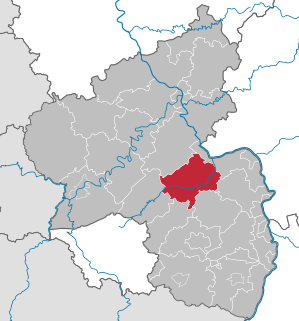
Bad Kreuznach is a district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Rhein-Hunsrück, Mainz-Bingen, Alzey-Worms, Donnersbergkreis, Kusel and Birkenfeld.

Berglangenbach is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Birkenfeld district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde of Baumholder, whose seat is in the like-named town.

Bingen (Rhein) Hauptbahnhof is a railway station in the German city of Bingen am Rhein on the West Rhine Railway. It is located in the borough of Bingerbrück. The station that serves central Bingen is called Bingen Stadt.

Berschweiler bei Kirn is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Birkenfeld district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde of Herrstein, whose seat is in the like-named municipality. Berschweiler bei Kirn is one of two municipalities in the district with the name Berschweiler. The two are distinguished from each other by their geographical “tags”; the other one is called Berschweiler bei Baumholder.

Mettweiler is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Birkenfeld district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde of Baumholder, whose seat is in the like-named town.
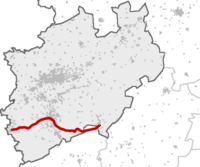
The Rhein-Sieg-Express is a Regional-Express service in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate running from Aachen via Düren, Cologne, Troisdorf, Siegburg and Betzdorf to Siegen. It is operated by DB Regio NRW.
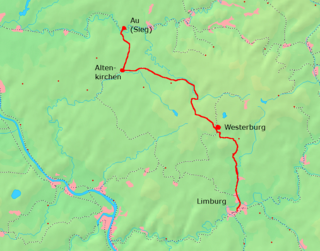
The Limburg–Altenkirchen railway is a 65.1 km long branch line from Limburg via Westerburg to Altenkirchen and connecting via the Engers–Au railway to Au through the Westerwald. The line is also known in German as the Oberwesterwaldbahn. It runs through the German states of Hesse and Rhineland-Palatinate.
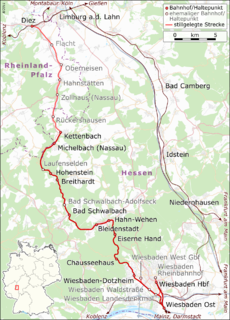
The Aar Valley Railway is a 53.7 km long line between Wiesbaden, the capital of the German state of Hesse, and Diez in Rhineland-Palatinate. From 1985 to 2007, the southern end was operated as a heritage railway with historic trains. The Hessian part of the line is heritage-listed. Currently, two bridges are unusable and several sets of points are defective and need to be repaired. Its northern end is operated with draisines.

The Hunsrück Railway is a partially disused railway branch line in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate, which branches from the West Rhine Railway in Boppard and used to run as far as Simmern. The 38 kilometre section south of Emmelshausen has been dismantled and has been since replaced by the Schinderhannes-Radweg cycle path. In Simmern it connected with the now partially closed Hunsrückquerbahn between Langenlonsheim and Hermeskeil.

The Worms–Bingen Stadt railway or Rheinhessenbahn is a non-electrified line that links Worms via Alzey to Bingen Stadt in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate.

Alzey station is, along with the stations Alzey Süd and Alzey West, one of three stations in the urban area of the Rhenish Hesse town of Alzey in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 3 station.
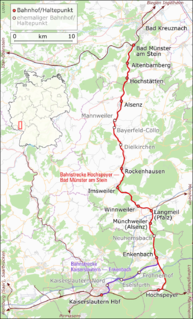
The Alsenz Valley Railway is a line that runs from Hochspeyer via Winnweiler and Alsenz to Bad Munster am Stein in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. The line follows the Alsenz river from the Enkenbach district and crossed it several times. It was originally built primarily as a long-distance route, but it has lost this function since 1990 and is now exclusively used for local transport.

Kusel station is the station of the town of Kusel in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. It was opened on 22 September 1868 as the terminus of the Landstuhl–Kusel railway. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 6 station. The station is located in the network area of the Verkehrsverbund Rhein-Neckar and it is in fare zone 770. The address of the station is Bahnhofstraße 65.

The Düren–Neuss railway is a line in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The non-electrified main line originally ran from Düren to Neuss, but the Düren–Bedburg section has been closed and dismantled.
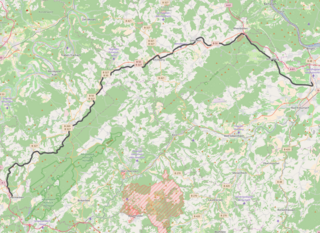
The Hunsrückquerbahn is a deactivated railway located in the Hunsrück region of Rheinland-Pfalz, Germany. The line connects with the Nahe Valley Railway (Nahetalbahn) in Langenlonsheim to the east with the partially abandoned Hochwaldbahn in Hermeskeil to the west. It was the primary railway through the Hunsrück, having both passenger and freight services.

The Cross Eifel Railway is a non-electrified railway line between Andernach and Gerolstein in the Eifel in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. From Andernach to Mayen Ost (East), it is classified as main line and it has two tracks as far as Mendig.

























