
Gastropods, commonly known as slugs and snails, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda.
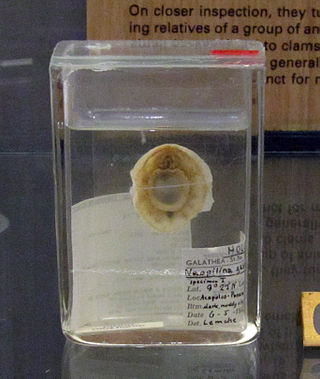
Monoplacophora, meaning "bearing one plate", is a polyphyletic superclass of molluscs with a cap-like shell, inhabiting deep sea environments. Extant representatives were not recognized as such until 1952; previously they were known only from the fossil record, and were thought to have become extinct 375 million years ago.

Bellerophon is a genus of extinct paleozoic marine molluscs of uncertain position in the family Bellerophontidae.
Strepsodiscus is an extinct genus of very primitive fossil snail-like molluscs from the early part of the Late Cambrian of North America. The coiled, slightly asymmetrical shells are about 3 cm in height. It is not known whether these are shells of gastropods or monoplacophorans, which are more primitive mollusks.

The Bellerophontida is a taxonomic order of extinct marine mollusks that are found in the fossil record from the Lower Cambrian to the Lower Triassic. They are considered by some experts to be primitive sea snails with primarily symmetrically coiled shells, marine gastropod mollusks.

The Bellerophontidae are an extinct family of specialized globose bellerophontids, Paleozoic and early Triassic mollusks of the class Gastropoda.

The Euomphalina comprise a major suborder of mainly Paleozoic archaeogastropods, shells of which are hyperstophic to depressed orthstrophic, commonly with an angulation at the outer upper whorl surface thought to be coincident with the exhalent channel; shell wall thick, outer layer calcitic, inner layers aragonitic but not nacreous; operculum calcareous and heavy. Their range is from the Upper Cambrian to the Triassic, and possibly as high as the Upper Cretaceous.

Yochelcionella is an extinct genus of basal molluscs which lived during the Tommotian epoch, the first epoch of the Cambrian period. This genus is often reconstructed to resemble snails.
Adrianitinae is a subfamily of the Adrianitidae which is part of the goniatitid superfamily Adrianitaceae. The Adrianitinae which comprise the more advanced genera in the Adrianitidae have sutures that form 14 to 30 lobes. Shells may be discoidal or globular or in between.

Trochoidea is a superfamily of small to very large vetigastropod sea snails with gills and an operculum. Species within this superfamily have nacre as the inner shell layer. The families within this superfamily include the Trochidae, the top snails. This superfamily is the largest vetigastropodan superfamily, containing more than 2,000 species.

The molluscshell is typically a calcareous exoskeleton which encloses, supports and protects the soft parts of an animal in the phylum Mollusca, which includes snails, clams, tusk shells, and several other classes. Not all shelled molluscs live in the sea; many live on the land and in freshwater.

Helcionelloida is an extinct group of ancient molluscs. These are the oldest known conchiferan molluscs, that is, they had a mineralised shell. Some members of this class were mistaken for Monoplacophorans. The class was erected by Peel in 1991.

Euomphalus is a genus of fossil marine gastropods known to have lived from the Silurian to the Middle Permian.

Pleurotomariacea is one of two names that are used for a taxonomic superfamily of sea snails that are an ancient lineage and are well represented in the fossil record. The name Pleurotomariacea is used by paleontologists, who, because they usually have only the hard parts of mollusks to study, often use a slightly different scheme of classification from that used by scientists who study living mollusks.

Bellerophontoidea, common name "bellerophonts", is a superfamily of extinct planospirally-coiled globose molluscs. This superfamily is generally included within the Gastropoda, but may instead be a group of monoplacophorans. The taxon first appeared late in the Cambrian and continued until late in the Triassic.
Bucanellidae is an extinct family of Paleozoic molluscs of uncertain position, belonging either to Gastropoda (snails) or Monoplacophora. The family lived from the upper Cambrian to middle Permian and the shells are characterized by a relatively small median sinus in the upper margin of the aperture, and collabral (transverse) or spiral (longitudinal) threads covering the shell. The shells are planispirally coiled rather than trochospirally with a spire as is the case with most shelled gastropods.
Bucaniidae is an extinct family of Paleozoic molluscs of uncertain position possibly being either gastropods or monoplacophorans in the superfamily Bellerophontoidea. The family lived from the Lower Ordovician to the Devonian and have shells in which the apertural margins tend to flare. Most genera have a slit and selenizone, others some modification of this feature.

Macluritidae is an extinct family of relatively large, Lower Ordovician to Devonian, macluritacean gastropods(?), hypserstrophically coiled, that is dextral while appearing sinistral, of which the genus Maclurites is arch-typical. The base of their shells is flat or gently protruding while the upper side is generally concave.

Euomphaloidea, originally Euomphalacea, is an extinct superfamily of marine molluscs that lived from the Early Ordovician to the Late Cretaceous, included in the Gastropoda but speculated as instead perhaps Monoplacophora.
The Trochina is a taxon that is used by paleontologists. It is a suborder of primitive sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks.









