
The Chauvet-Pont-d'Arc Cave in the Ardèche department of southeastern France is a cave that contains some of the best-preserved figurative cave paintings in the world, as well as other evidence of Upper Paleolithic life. It is located near the commune of Vallon-Pont-d'Arc on a limestone cliff above the former bed of the river Ardèche, in the Gorges de l'Ardèche.

Rhinoceros is a genus comprising one-horned rhinoceroses. This scientific name was proposed by Swedish taxonomist Carl Linnaeus in 1758. The genus contains two species, the Indian rhinoceros and the Javan rhinoceros. Although both members are threatened, the Javan rhinoceros is one of the most endangered large mammals in the world with only 60 individuals surviving in Java (Indonesia). The word 'rhinoceros' is of Greek origin meaning "nose-horn".

Hemitragus is a genus of bovids that currently contains a single living species, the Himalayan tahr. Two extinct species are also known from the Pleistocene.

Civettictis is a genus of viverrid that contains the extant African civet (Civettictis civetta) and a recently described extinct relative from the Plio-Pleistocene of South Africa known as Civettictis braini.

Vassacyon is an extinct genus of placental mammals from clade Carnivoraformes, that lived in North America and Europe from the late Paleocene to early Eocene. It is considered the largest of the early Eocene mammals.
Bohlinia is an extinct genus of the artiodactyl family Giraffidae that lived during the Late Miocene in Eurasia and Africa. It was first named by the paleontologist Dr. W. Matthew in 1929, and contains two species, B. adoumi and B. attica. The species B. attica has been reclassified several times since its description being first named Camelopardalis attica and then reclassified as Giraffa attica.

Stephanorhinus is an extinct genus of two-horned rhinoceros native to Eurasia and North Africa that lived during the Late Pliocene to Late Pleistocene. Species of Stephanorhinus were the predominant and often only species of rhinoceros in much of temperate Eurasia, especially Europe, for most of the Pleistocene. The last two species of Stephanorhinus – Merck's rhinoceros and the narrow-nosed rhinoceros – went extinct during the last glacial period.

Lartetotherium is an extinct genus of rhinocerotid that lived during the Miocene in Europe and possibly China.

Brachypotherium is an extinct genus of rhinocerotid that lived in Eurasia and Africa during the Miocene.

The narrow-nosed rhinoceros, also known as the steppe rhinoceros is an extinct species of rhinoceros belonging to the genus Stephanorhinus that lived in western Eurasia, including Europe, as well as North Africa during the Pleistocene. It first appeared in Europe around 500,000 years ago during the Middle Pleistocene and survived there until at least 34,000 years Before Present. It was native to temperate and Mediterranean environments, where it fed on low growing plants and to a lesser extent woody plants. Evidence has been found that it was exploited for food by archaic humans, including Neanderthals.

Hyaenotherium is an extinct genus of hyena.

Prototherium is a genus of extinct sirenian related to the dugong. It is known from middle (Bartonian) and upper Eocene deposits in Italy and Spain. Type species is P. veronenses
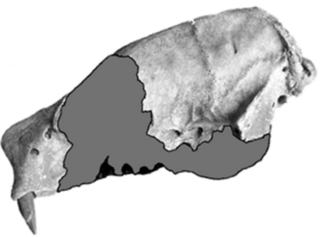
Australonyx is an extinct genus of ground sloths, endemic to South America during the Late Pleistocene. It was found in Brazil.
Orienspterodon is an extinct genus of hyainailourid hyaenodonts from paraphyletic subfamily Hyainailourinae that lived in China and Myanmar during the middle to late Eocene. Orienspterodon dahkoensis was originally assigned to genus Pterodon in 1975, but was eventually assigned to its own genus in 2007.

Arago cave is a prehistoric site in the community of Tautavel, in the department of Pyrénées-Orientales. It is a large cavity overlooking a perennial stream called the Verdouble. Human remains attributed to the Tautavel Man and the lithic remnants of the Lower Paleolithic were discovered in the cave.

Hemitragus bonali, the Bonal tahr, is an extinct species of bovid from the Pleistocene of Europe and the Caucasus Mountains region.
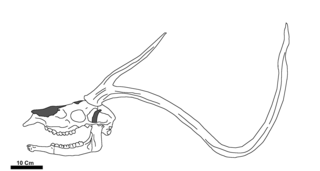
Haploidoceros is an extinct genus of deer that lived in Europe during the Pleistocene. It contains a single species, Haploidoceros mediterraneus. It had a distribution limited to southern France and the Iberian Peninsula.
Civettictis braini is an extinct species of civet that lived in South Africa during the Plio-Pleistocene.
Geinitzia is an extinct genus of conifers, with an uncertain position within the group. Species belonging to the genus lived in the late Cretaceous and have been found in Argentina and Europe.
Propachyrucos is an extinct genus of late Oligocene hegetotheriid notoungulate. It is known from a few mandibular fragments from the Sarmiento Formation, Chubut Province, Argentina.















