
Mahdia is a Tunisian coastal city with 76,513 inhabitants, south of Monastir and southeast of Sousse.

Byzacena was a Late Roman province in the central part of Roman North Africa, which is now roughly Tunisia, split off from Africa Proconsularis.

Sfax is a city in Tunisia, located 270 km (170 mi) southeast of Tunis. The city, founded in AD 849 on the ruins of Taparura, is the capital of the Sfax Governorate, and a Mediterranean port. Sfax has a population of 341,999. Its main industries include phosphate, olive and nut processing, fishing and international trade. The city is the second-most populous in the country after the capital, Tunis.

The name early African church is given to the Christian communities inhabiting the region known politically as Roman Africa, and comprised geographically somewhat around the area of the Roman Diocese of Africa, namely: the Mediterranean littoral between Cyrenaica on the east and the river Ampsaga on the west; that part of it that faces the Atlantic Ocean being called Mauretania, in addition to Byzacena. Thus corresponding somewhat to contemporary Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia and Libya. The evangelization of Africa followed much the same lines as those traced by Roman civilization. From the late fifth and early sixth century, the region included several Christian Berber kingdoms.
Ruspe or Ruspae was a town in the Roman province of Byzacena, in Africa propria. It served as the episcopal see of Saint Fulgentius of Ruspe. It is now a Roman Catholic titular bishopric.
The 1977 FIFA World Youth Championship was the inaugural staging of the FIFA World Youth Championship, hosted by Tunisia from 27 June to 10 July 1977, in three venues — Tunis, Sousse and Sfax. The 28 matches played were the smallest number in tournament history. The USSR U20s defeated Mexico U20s in a penalty shootout, in the final held at Tunis's Stade El Menzah.
El Aïn is a town located in the Sfax Governorate, 7 kilometers north of Sfax, Tunisia. Its population in 2004 was 38,250.
Jebiniana is a town and commune in the Sfax Governorate, Tunisia.

Thyna, formerly Henchir-Tina, is a town and commune in the Sfax Governorate, Tunisia. As of 2004 it had a population of 26,635. It is located on the coast about 12 km (7 mi) south of Sfax.

Aïn M'lila is a town and commune in Oum El Bouaghi Province, Algeria. According to the 2008 census it has a population of 65,371. It is the home-town of Larbi Ben M'hidi, one of the most prominent Algerian leaders during the war of independence. It is the home of football club AS Ain M'lila that currently play in the Algerian Ligue Professionnelle 1.

El Amiria is a town and commune in Oum El Bouaghi Province, Algeria. According to the 1998 census it has a population of 9795.

The Sfax medina is the medina quarter of the Tunisian city of Sfax. It was built by Aghlabid prince Abu Abbass Muhammad between 849 and 851. The medina is home to about 113,000 residents, and is dominated by the Great Mosque of Sfax.

Vicus Turris is a former Roman and Byzantine town of Africa and a titular see of the Roman Catholic Church.
Henchir-Mâtria is an archaeological and prehistoric site in northern Tunisia. Henchir-Mâtria is at 36°31′23.4″N9°13′11.1″E, between Béja and Dougga and elevation of 407 metres. It is on the Oued el Beida River.

Henchir-Sidi-Salah is a rural locality and archaeological site in the hinterland behind Sfax, Tunisia.
Oued Sidi Salah is a wadi of eastern Tunisia. It rises in the hinterland behind the city of Sfax and empties into the Chott El Merdasia near Sidi Mansour, on the Mediterranean coast. The wadi takes its name from Dar Mahommed Salah which it flows past.
Oglet Khefifa is a locality in Sfax Governorate southern Tunisia, located in the semi arid area south of Sfax.
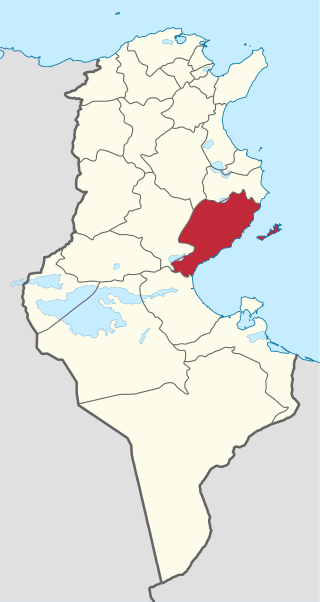
Henchir Bou Doukhane is a village in Sfax Governorate, Eastern Tunisia.

The Compagnie des chemins de fer Bône-Guelma built and operated railway lines in Algeria and Tunisia between 1875 and 1923 during the French colonial period. In 1923 it became the Compagnie fermière des chemins de fer tunisiens.
Numidia was a Roman province on the North African coast, comprising roughly the territory of northeastern Algeria.














