
Porphyria is a group of liver disorders in which substances called porphyrins build up in the body, negatively affecting the skin or nervous system. The types that affect the nervous system are also known as acute porphyria, as symptoms are rapid in onset and short in duration. Symptoms of an attack include abdominal pain, chest pain, vomiting, confusion, constipation, fever, high blood pressure, and high heart rate. The attacks usually last for days to weeks. Complications may include paralysis, low blood sodium levels, and seizures. Attacks may be triggered by alcohol, smoking, hormonal changes, fasting, stress, or certain medications. If the skin is affected, blisters or itching may occur with sunlight exposure.

Heme, or haem, is a precursor to hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver.

Hereditary coproporphyria (HCP) is a disorder of heme biosynthesis, classified as an acute hepatic porphyria. HCP is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme coproporphyrinogen oxidase, coded for by the CPOX gene, and is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion, although homozygous individuals have been identified. Unlike acute intermittent porphyria, individuals with HCP can present with cutaneous findings similar to those found in porphyria cutanea tarda in addition to the acute attacks of abdominal pain, vomiting and neurological dysfunction characteristic of acute porphyrias. Like other porphyrias, attacks of HCP can be induced by certain drugs, environmental stressors or diet changes. Biochemical and molecular testing can be used to narrow down the diagnosis of a porphyria and identify the specific genetic defect. Overall, porphyrias are rare diseases. The combined incidence for all forms of the disease has been estimated at 1:20,000. The exact incidence of HCP is difficult to determine, due to its reduced penetrance.

Porphyria cutanea tarda is the most common subtype of porphyria. The disease is named because it is a porphyria that often presents with skin manifestations later in life. The disorder results from low levels of the enzyme responsible for the fifth step in heme production. Heme is a vital molecule for all of the body's organs. It is a component of hemoglobin, the molecule that carries oxygen in the blood.

Erythropoietic protoporphyria is a form of porphyria, which varies in severity and can be very painful. It arises from a deficiency in the enzyme ferrochelatase, leading to abnormally high levels of protoporphyrin in the red blood cells (erythrocytes), plasma, skin, and liver. The severity varies significantly from individual to individual.
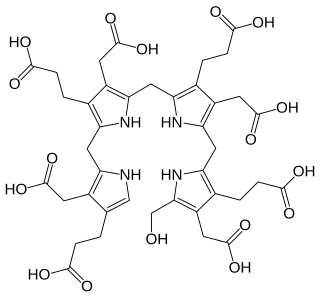
Gunther disease is a congenital form of erythropoietic porphyria. The word porphyria originated from the Greek word porphura. Porphura actually means "purple pigment", which, in suggestion, the color that the body fluid changes when a person has Gunther's disease. It is a rare, autosomal recessive metabolic disorder affecting heme, caused by deficiency of the enzyme uroporphyrinogen cosynthetase. It is extremely rare, with a prevalence estimated at 1 in 1,000,000 or less. There have been times that prior to birth of a fetus, Gunther's disease has been shown to lead to anemia. In milder cases patients have not presented any symptoms until they have reached adulthood. In Gunther's disease, porphyrins are accumulated in the teeth and bones and an increased amount are seen in the plasma, bone marrow, feces, red blood cells, and urine.
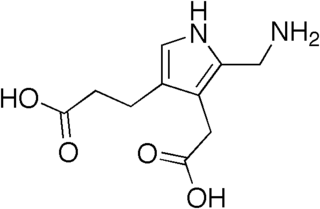
Acute intermittent porphyria (AIP) is a rare metabolic disorder affecting the production of heme resulting from a deficiency of the porphobilinogen deaminase. It is the most common of the acute porphyrias.

Protoporphyrinogen oxidase or protox is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PPOX gene.

Uroporphyrinogen III synthase is an enzyme involved in the metabolism of the cyclic tetrapyrrole compound porphyrin. It is involved in the conversion of hydroxymethyl bilane into uroporphyrinogen III. This enzyme catalyses the inversion of the final pyrrole unit of the linear tetrapyrrole molecule, linking it to the first pyrrole unit, thereby generating a large macrocyclic structure, uroporphyrinogen III. The enzyme folds into two alpha/beta domains connected by a beta-ladder, the active site being located between the two domains.

Uroporphyrinogen III is a tetrapyrrole, the first macrocyclic intermediate in the biosynthesis of heme, chlorophyll, vitamin B12, and siroheme. It is a colorless compound, like other porphyrinogens.
Erythropoietic porphyria is a type of porphyria associated with erythropoietic cells. In erythropoietic porphyrias, the enzyme deficiency occurs in the red blood cells.

Hepatoerythropoietic porphyria is a very rare form of hepatic porphyria caused by a disorder in both genes which code Uroporphyrinogen III decarboxylase (UROD).

Uroporphyrinogen I is an isomer of uroporphyrinogen III, a metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of heme. A type of porphyria is caused by production of uroporphyrinogen I instead of III.

Coproporphyrinogen I is an isomer of coproporphyrinogen III, a metabolic intermediate in the normal biosynthesis of heme. The compound is not normally produced by the human body; its production and accumulation causes a type of porphyria.

Aminolevulinic acid dehydratase deficiency porphyria is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that results from inappropriately low levels of the enzyme delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (ALAD), which is required for normal heme synthesis. This deficiency results in the accumulation of a toxic metabolic precursor in the heme synthesis pathway called aminolevulinic acid (ALA). Lead poisoning can also disrupt ALAD and result in elevated ALA causing the same symptoms. Heme is a component of hemoglobin which carries oxygen in red blood cells.

Harderoporphyria is a rare disorder of heme biosynthesis, inherited in an autosomal recessive manner caused by specific mutations in the CPOX gene. Mutations in CPOX usually cause hereditary coproporphyria, an acute hepatic porphyria, however the K404E mutation in a homozygous or compound heterozygous state with a null allele cause the more severe harderoporphyria. Harderoporphyria is the first known metabolic disorder where the disease phenotype depended on the type and location of the mutations in a gene associated with multiple disorders.
Erythrodontia is the red discoloration of teeth. It can be seen in congenital erythropoietic porphyria.
Ephraim Y. Levin,. 1957 BA and MA, 1953, MD, 1957, all at Johns Hopkins University. Internship and residencies at Johns Hopkins Hospital and Sinai Hospital of Baltimore. Married Ruth Lee Shefferman June 17, 1956; Four children: Joshua, Rebecca, Daniel, and Michael. Served in USPHS 1953-1998, on active duty 1958-1960 and 1974-1998. With Seymour Kaufman discovered the role of ascorbic acid in the enzymatic hydroxylation of dopamine to form norepinephrine, the first evidence for a specific metabolic function for this vitamin[./Ephraim_Levin#cite_note-1 [1]][./Ephraim_Levin#cite_note-1 [1]]. Fellowship with Konrad Bloch at Harvard University 1961-1963, under auspices of Sinai Hospital. On Faculty of Pediatrics at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine 1963-1974. Along with Vagn Flyger, demonstrated the partial deficiency of uroporphyrinogen cosynthetase in congenital erythropoietic porphyria of cattle and human beings, its occurrence in asymptomatic carriers of the disease, in fibroblasts as well as in bone marrow, and its probable cause of red bones in fox squirrels[./Ephraim_Levin#cite_note-4 [4]][./Ephraim_Levin#cite_note-4 [4]]. He once beat Solomon Golumb in a chess game.
Givosiran, sold under the brand name Givlaari, is a medication used for the treatment of adults with acute hepatic porphyria. Givosiran is a small interfering RNA (siRNA) directed towards delta-aminolevulinate synthase 1 (ALAS1), an important enzyme in the production of heme.













