
Historic preservation (US), built heritage preservation or built heritage conservation (UK), is an endeavor that seeks to preserve, conserve and protect buildings, objects, landscapes or other artifacts of historical significance. It is a philosophical concept that became popular in the twentieth century, which maintains that cities as products of centuries’ development should be obligated to protect their patrimonial legacy. The term refers specifically to the preservation of the built environment, and not to preservation of, for example, primeval forests or wilderness.

The Ontario Heritage Act, first enacted on March 5, 1975, allows municipalities and the provincial government to designate individual properties and districts in the Province of Ontario, Canada, as being of cultural heritage value or interest.

Grand-Pré National Historic Site is a park set aside to commemorate the Grand-Pré area of Nova Scotia as a centre of Acadian settlement from 1682 to 1755, and the British deportation of the Acadians that happened during the French and Indian War. The original village of Grand Pré extended four kilometres along the ridge between present-day Wolfville and Hortonville. Grand-Pré is listed as a World Heritage Site and is the main component of two National Historic Sites of Canada.

The Canadian Register of Historic Places, also known as Canada's Historic Places, is an online directory of historic sites in Canada which have been formally recognized for their heritage value by a federal, provincial, territorial or municipal authority.

The Heritage Lighthouse Protection Act is an Act of the Parliament of Canada for the designation and preservation of historically significant Canadian lighthouses. It was passed by the Canadian Parliament in May 2008. The act set up a public nomination process and sets heritage building conservation standards for lighthouses which are officially designated. First introduced in 2000 as Bill S-21 in the Senate of Canada the bill enjoyed consistent multi-party support despite the unpredictable legislative agendas of minority Parliaments and was repeatedly re-introduced. The final vote of approval was made by the Canadian Senate in 2008 and the bill received Royal Assent on May 29, 2008.
Heritage buildings in Edmonton, as elsewhere in Canada, may be designated by any of the three levels of government: the Government of Canada, the Government of Alberta, or the City of Edmonton.

A Cultural Property is administered by the Japanese government's Agency for Cultural Affairs, and includes tangible properties ; intangible properties ; folk properties both tangible and intangible; monuments historic, scenic and natural; cultural landscapes; and groups of traditional buildings. Buried properties and conservation techniques are also protected. Together these cultural properties are to be preserved and utilized as the heritage of the Japanese people.
The Quebec Cultural Heritage Directory is an online cultural heritage knowledge dissemination tool for the province of Quebec. The directory is maintained by the province's Ministry of Culture and Communications.
Protected areas of Ukraine are special areas of Ukraine established with the goal of protecting the natural and cultural heritage of the country from excessive changes as a result of human activity. The protection of the areas is the responsibility of the government of Ukraine, specifically the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine.
In Canada, heritage conservation deals with actions or processes that are aimed at safeguarding the character-defining elements of a cultural resource so as to retain its heritage value and extend its physical life. Historic objects in Canada may be granted special designation by any of the three levels of government: the federal government, the provincial governments, or a municipal government. The Heritage Canada Foundation acts as Canada's lead advocacy organization for heritage buildings and landscapes.
Archaeology and conservation of cultural resources in Ontario fall under the Ministry of Tourism, Culture and Sport. The Province of Ontario has created Acts to insure the protection archaeological and cultural resources. Acts such as the Ontario Heritage Act and Environmental Assessment Act provide the major legal documents that protect heritage and cultural resources. Additionally, Acts such as the Planning Act, the Aggregate Resource Act and the Ontario Cemeteries Act are also implemented when specific triggers occur during archaeological assessments.

The Heritage Conservation Act is a provincial statute which allows for the preservation of cultural heritage properties and areas in the province of New Brunswick, Canada.

Henry House is a two-and-a-half-storey stone house located on Barrington Street in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada. The house is designated a National Historic Site, and is both a Provincially Registered Property and a Municipally Registered Property under the provincial Heritage Property Act.

The Heritage Property Act is a provincial statute which allows for the preservation of cultural heritage properties, archaeological sites and palaeontological sites in the province of Saskatchewan, Canada.

The Heritage Places Protection Act is a provincial statute which allows for the recognition and protection of cultural heritage and natural heritage properties in the province of Prince Edward Island, Canada.
Heritage management in the Philippines is guided by laws and agencies that create regulations for potentially destructive behaviors such as excavations and demolition. Legislation pertaining to heritage management consists of Republic Acts and Presidential Decrees. Organizations such as UNESCO, the National Commission for Culture and the Arts, and the Heritage Conservation Society are also referred to in laws.
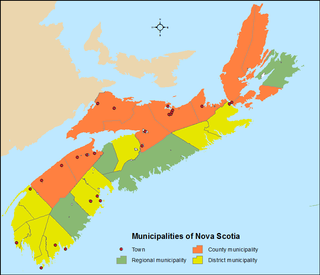
The Canadian province of Nova Scotia is divided into 49 municipalities, of which there are three types: regional (4), town (25), and county or district municipality (20).












