
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula NH3. A stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to fertilisers. Around 70% of ammonia produced industrially is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil.
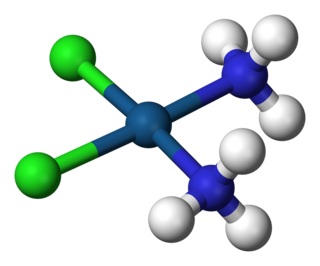
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the coordination centre, and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals, are coordination complexes.
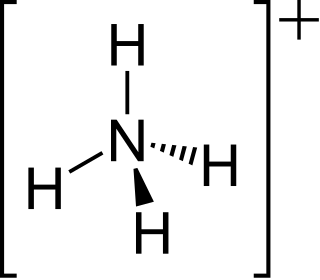
Ammonium is a modified form of ammonia that has an extra hydrogen atom. It is a positively charged (cationic) molecular ion with the chemical formula NH+4 or [NH4]+. It is formed by the addition of a proton to ammonia. Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged (protonated) substituted amines and quaternary ammonium cations, where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic or other groups. Not only is ammonium a source of nitrogen and a key metabolite for many living organisms, but it is an integral part of the global nitrogen cycle. As such, human impact in recent years could have an effect on the biological communities that depend on it.

Cisplatin is a chemical compound with formula cis-[Pt(NH3)2Cl2]. It is a coordination complex of platinum that is used as a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of cancers. These include testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, esophageal cancer, lung cancer, mesothelioma, brain tumors and neuroblastoma. It is given by injection into a vein.

Strontium chloride (SrCl2) is a salt of strontium and chloride. It is a 'typical' salt, forming neutral aqueous solutions. As with all compounds of strontium, this salt emits a bright red colour in flame, and is commonly used in fireworks to that effect. Its properties are intermediate between those for barium chloride, which is more toxic, and calcium chloride.

Rhodium(III) chloride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula RhCl3(H2O)n, where n varies from 0 to 3. These are diamagnetic red-brown solids. The soluble trihydrated (n = 3) salt is the usual compound of commerce. It is widely used to prepare compounds used in homogeneous catalysis.

Iridium(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula IrCl3. The anhydrous compound is relatively rare, but the related hydrate is much more commonly encountered. The anhydrous salt has two polymorphs, α and β, which are brown and red colored respectively. More commonly encountered is the hygroscopic dark green trihydrate IrCl3(H2O)3 which is a common starting point for iridium chemistry.

In coordination chemistry, metal ammine complexes are metal complexes containing at least one ammonia ligand. "Ammine" is spelled this way for historical reasons; in contrast, alkyl or aryl bearing ligands are spelt with a single "m". Almost all metal ions bind ammonia as a ligand, but the most prevalent examples of ammine complexes are for Cr(III), Co(III), Ni(II), Cu(II) as well as several platinum group metals.

Platinum(II) chloride describes the inorganic compounds with the formula PtCl2. They are precursor used in the preparation of other platinum compounds. Platinum(II) chloride exists in two crystalline forms (polymorphs), but the main properties are somewhat similar: dark brown, insoluble in water, diamagnetic, and odorless.

Hexaamminecobalt(III) chloride is the chemical compound with the formula [Co(NH3)6]Cl3. It is the chloride salt of the coordination complex [Co(NH3)6]3+, which is considered an archetypal "Werner complex", named after the pioneer of coordination chemistry, Alfred Werner. The cation itself is a metal ammine complex with six ammonia ligands attached to the cobalt(III) ion.
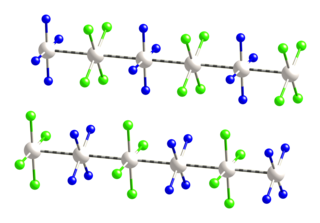
Magnus's green salt is the inorganic compound with the formula [Pt(NH3)4][PtCl4]. This salt is named after Heinrich Gustav Magnus, who, in the early 1830s, first reported the compound. The compound is a linear chain compound, consisting of a chain of platinum atoms. It is dark green, which is unusual for platinum compounds.

Potassium tetrachloroplatinate(II) is the chemical compound with the formula K2PtCl4. This reddish orange salt is an important reagent for the preparation of other coordination complexes of platinum. It consists of potassium cations and the square planar dianion PtCl42−. Related salts are also known including Na2PtCl4, which is brown-colored and soluble in alcohols, and quaternary ammonium salts, which are soluble in a broader range of organic solvents.

Potassium hexachloroplatinate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2PtCl6. It is a yellow solid that is an example of a comparatively insoluble potassium salt. The salt features the hexachloroplatinate(IV) dianion, which has octahedral coordination geometry.

Sodium hexachloroplatinate(IV), the sodium salt of chloroplatinic acid, is an inorganic compound with the formula Na2[PtCl6], consisting of the sodium cation and the hexachloroplatinate anion. As explained by Cox and Peters, anhydrous sodium hexachloroplatinate, which is yellow, tends to form the orange hexahydrate upon storage in humid air. The latter can be dehydrated upon heating at 110 °C.

Metal amides (systematic name metal azanides) are a class of coordination compounds composed of a metal center with amide ligands of the form NR2−. Amido complexes of the parent amido ligand NH2− are rare compared to complexes with diorganylamido ligand, such as dimethylamido. Amide ligands have two electron pairs available for bonding.
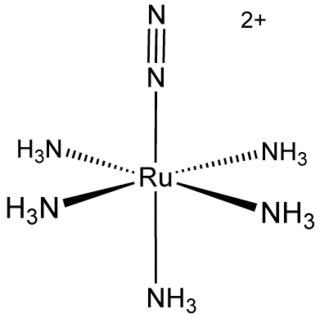
Pentaamine(nitrogen)ruthenium(II) chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula [Ru(NH3)5(N2)]Cl2. It is a nearly white solid, but its solutions are yellow. The cationic complex is of historic significance as the first compound with N2 bound to a metal center. [Ru(NH3)5(N2)]2+ adopts an octahedral structure with C4v symmetry.

Hexaamminenickel chloride is the chemical compound with the formula [Ni(NH3)6]Cl2. It is the chloride salt of the metal ammine complex [Ni(NH3)6]2+. The cation features six ammonia (called ammines in coordination chemistry) ligands attached to the nickel(II) ion.
Nitrate chlorides are mixed anion compounds that contain both nitrate (NO3−) and chloride (Cl−) ions. Various compounds are known, including amino acid salts, and also complexes from iron group, rare-earth, and actinide metals. Complexes are not usually identified as nitrate chlorides, and would be termed chlorido nitrato complexes.

In organometallic chemistry, transition metal complexes of nitrite describes families of coordination complexes containing one or more nitrite ligands. Although the synthetic derivatives are only of scholarly interest, metal-nitrite complexes occur in several enzymes that participate in the nitrogen cycle.
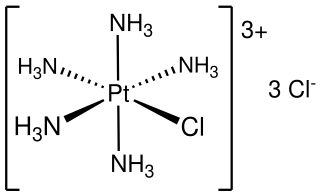
Chloropentammineplatinum chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula [PtCl(NH3)5]Cl3. It is a chloride salt of the coordination complex [PtCl(NH3)5]+. It is a white, water soluble solid.



















