In organic chemistry, amines (, UK also ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group (these may respectively be called alkylamines and arylamines; amines in which both types of substituent are attached to one nitrogen atom may be called alkylarylamines). Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline; see Category:Amines for a list of amines. Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine (NClH2).
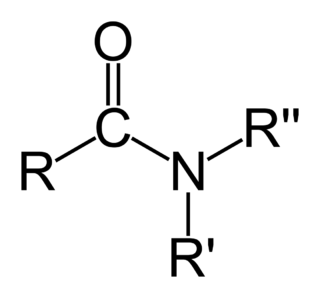
In organic chemistry, an amide ( or or, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula RC NR′R″, where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is part of the main chain of a protein, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain, such as in the amino acids asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a derivative of a carboxylic acid RC OH with the hydroxyl group –OH replaced by an amine group –NR′R″; or, equivalently, an acyl group RC – joined to an amine group.

Monoamine neurotransmitters are neurotransmitters and neuromodulators that contain one amino group connected to an aromatic ring by a two-carbon chain (such as -CH2-CH2-). Examples are dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin.
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry. Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous structural formula can be created. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry.

An imine is a functional group or chemical compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond. The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen (H) or an organic group (R). If this group is not a hydrogen atom, then the compound can sometimes be referred to as a Schiff base. The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. The term "imine" was coined in 1883 by the German chemist Albert Ladenburg.
Methylamine is an organic compound with a formula of CH3NH2. This colorless gas is a derivative of ammonia, but with one hydrogen atom being replaced by a methyl group. It is the simplest primary amine.
Trimethylamine (TMA) is an organic compound with the formula N(CH3)3. It is a colorless, hygroscopic, and flammable tertiary amine. It is a gas at room temperature but is usually sold as a 40% solution in water. (It is also sold in pressurized gas cylinders.) TMA is a nitrogenous base and can be readily protonated to give the trimethylammonium cation. Trimethylammonium chloride is a hygroscopic colorless solid prepared from hydrochloric acid. Trimethylamine is a good nucleophile, and this reaction is the basis of most of its applications. TMA is widely used in industry: it is used in the synthesis of choline, tetramethylammonium hydroxide, plant growth regulators or herbicides, strongly basic anion exchange resins, dye leveling agents, and a number of basic dyes. At higher concentrations it has an ammonia-like odor, and can cause necrosis of mucous membranes on contact. At lower concentrations, it has a "fishy" odor, the odor associated with rotting fish.
Ethylenediamine (abbreviated as en when a ligand) is the organic compound with the formula C2H4(NH2)2. This colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor is a basic amine. It is a widely used building block in chemical synthesis, with approximately 500,000 tonnes produced in 1998. Ethylenediamine readily reacts with moisture in humid air to produce a corrosive, toxic and irritating mist, to which even short exposures can cause serious damage to health (see safety). Ethylenediamine is the first member of the so-called polyethylene amines.
Ethylamine also known as Ethanamine is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH2NH2. This colourless gas has a strong ammonia-like odor. It condenses just below room temperature to a liquid miscible with virtually all solvents. It is a nucleophilic base, as is typical for amines. Ethylamine is widely used in chemical industry and organic synthesis.
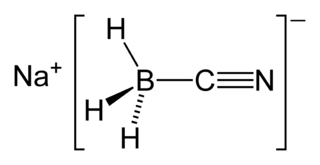
Sodium cyanoborohydride is the chemical compound with the formula NaBH3CN. It is a colourless salt, but commercial samples can appear tan. It is widely used in organic synthesis for the reduction of imines. The salt tolerates aqueous conditions.
Chloramines refer to derivatives of ammonia and organic amines wherein one or more N-H bonds have been replaced by N-Cl bonds. Two classes of compounds are considered: inorganic chloramines and organic chloramines.

Benzylamine is an organic chemical compound with the condensed structural formula C6H5CH2NH2 (sometimes abbreviated as PhCH2NH2 or BnNH2). It consists of a benzyl group, C6H5CH2, attached to an amine functional group, NH2. This colorless water-soluble liquid is a common precursor in organic chemistry and used in the industrial production of many pharmaceuticals. The hydrochloride salt was used to treat motion sickness on the Mercury-Atlas 6 mission in which NASA astronaut John Glenn became the first American to orbit the Earth.
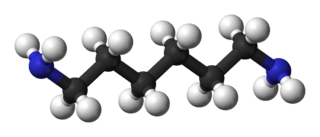
Hexamethylenediamine is the organic compound with the formula H2N(CH2)6NH2. The molecule is a diamine, consisting of a hexamethylene hydrocarbon chain terminated with amine functional groups. The colorless solid (yellowish for some commercial samples) has a strong amine odor. About 1 billion kilograms are produced annually.

n-Butylamine is an organic compound (specifically, an amine) with the formula CH3(CH2)3NH2. This colourless liquid is one of the four isomeric amines of butane, the others being sec-butylamine, tert-butylamine, and isobutylamine. It is a liquid having the fishy, ammonia-like odor common to amines. The liquid acquires a yellow color upon storage in air. It is soluble in all organic solvents.

Dimethylbenzylamine is the organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2N(CH3)2. The molecule consists of a benzyl group, C6H5CH2, attached to a dimethylamino functional group. It is a colorless liquid. It is used as a catalyst for the formation of polyurethane foams and epoxy resins.

tert-Butylamine is an organic chemical compound with the formula (CH3)3CNH2. It is a colorless liquid with a typical amine-like odor. tert-Butylamine is one of the four isomeric amines of butane, the others being n-butylamine, sec-butylamine and isobutylamine.

sec-Butylamine is an organic chemical compound (specifically, an amine) with the formula CH3CH2CH(NH2)CH3. It is a colorless liquid. sec-Butylamine is one of the four isomeric amines of butane, the others being n-butylamine, tert-butylamine, and isobutylamine. sec-Butylamine is chiral and therefore can exist in either of two enantiomeric forms.

Tris(2-aminoethyl)amine is the organic compound with the formula N(CH2CH2NH2)3. This colourless liquid is soluble in water and is highly basic, consisting of a tertiary amine center and three pendant primary amine groups. Abbreviated tren or TREN it is a crosslinking agent in the synthesis of polyimine networks and a tripodal ligand in coordination chemistry.

Cyclam (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane) is an organic compound with the formula (NHCH2CH2NHCH2CH2CH2)2. Classified as an aza-crown ether, it is a white solid that is soluble in water. As a macrocyclic ligand, it binds strongly to many transition metal cations. The compound was first prepared by the reaction of 1,3-dibromopropane and ethylenediamine.
A polyamine is an organic compound having more than two amino groups. Alkyl polyamines occur naturally but are also synthetic. Alkylpolyamines are colorless, hygroscopic, and water soluble. Near neutral pH, they exist as the ammonium derivatives. Most aromatic polyamines are crystalline solids at room temperature.













