
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, and maintain mechanical systems. It is one of the oldest and broadest of the engineering branches.

William John Macquorn Rankine was a Scottish mechanical engineer who also contributed to civil engineering, physics and mathematics. He was a founding contributor, with Rudolf Clausius and William Thomson, to the science of thermodynamics, particularly focusing on its First Law. He developed the Rankine scale, an equivalent to the Kelvin scale of temperature, but in degrees Fahrenheit rather than Celsius.

The Missouri Botanical Garden is a botanical garden located at 4344 Shaw Boulevard in St. Louis, Missouri. It is also known informally as Shaw's Garden for founder and philanthropist Henry Shaw. Its herbarium, with more than 6.6 million specimens, is the second largest in North America, behind that of the New York Botanical Garden. The Index Herbariorum code assigned to the herbarium is MO and it is used when citing housed specimens.

In materials science, fatigue is the initiation and propagation of cracks in a material due to cyclic loading. Once a fatigue crack has initiated, it grows a small amount with each loading cycle, typically producing striations on some parts of the fracture surface. The crack will continue to grow until it reaches a critical size, which occurs when the stress intensity factor of the crack exceeds the fracture toughness of the material, producing rapid propagation and typically complete fracture of the structure.
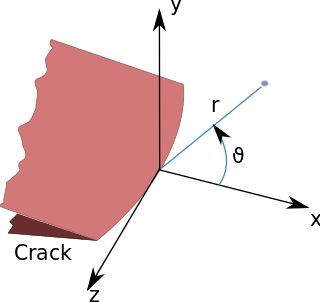
In fracture mechanics, the stress intensity factor is used to predict the stress state near the tip of a crack or notch caused by a remote load or residual stresses. It is a theoretical construct usually applied to a homogeneous, linear elastic material and is useful for providing a failure criterion for brittle materials, and is a critical technique in the discipline of damage tolerance. The concept can also be applied to materials that exhibit small-scale yielding at a crack tip.
Failure analysis is the process of collecting and analyzing data to determine the cause of a failure, often with the goal of determining corrective actions or liability. According to Bloch and Geitner, ”machinery failures reveal a reaction chain of cause and effect… usually a deficiency commonly referred to as the symptom…”. failure analysis can save money, lives, and resources if done correctly and acted upon. It is an important discipline in many branches of manufacturing industry, such as the electronics industry, where it is a vital tool used in the development of new products and for the improvement of existing products. The failure analysis process relies on collecting failed components for subsequent examination of the cause or causes of failure using a wide array of methods, especially microscopy and spectroscopy. Nondestructive testing (NDT) methods are valuable because the failed products are unaffected by analysis, so inspection sometimes starts using these methods.
Dr. Ramulu Mamidala is a mechanical engineering professor at University of Washington. Usually goes by the name 'Ram', or 'M.R.', he is recognized for his leadership and outstanding record in promoting collaborative education and research with industry. He is currently the director of Manufacturing Science and Technology Laboratory (MSTL) at Mechanical Engineering Department, University of Washington. He has designed and developed manufacturing methods for a wide range of systems, from the B2 bomber to the Boeing 787. Additionally, in collaboration with industry, he established and directed two interdisciplinary graduate educational programs in engineering and management and a certificate program in composites tooling and manufacturing. His exemplary collaborative efforts motivated working engineers to pursue doctoral studies and he is a leader in using emerging technologies in distance education to reach non-traditional students.
AFGROW is a Damage Tolerance Analysis (DTA) computer program that calculates crack initiation, fatigue crack growth, and fracture to predict the life of metallic structures. Originally developed by the Air Force Research Laboratory, AFGROW is mainly used for aerospace applications, but can be applied to any type of metallic structure that experiences fatigue cracking.
Daniel Charles Drucker was American civil and mechanical engineer and academic, who served as president of the Society for Experimental Stress Analysis in 1960–1961, as president of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers in the year 1973–74, and as president of the American Academy of Mechanics in 1981–82.
James Robert Rice is an American engineer, scientist, geophysicist, and Mallinckrodt Professor of Engineering Sciences and Geophysics at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences,.

Roark's Formulas for Stress and Strain is a mechanical engineering design book written by Richard G. Budynas and Ali M. Sadegh. It was first published in 1938 and the most current ninth edition was published in March 2020.
Tim Andreas Osswald is a mechanical engineer and the K. K. and Cindy Wang Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. He is also honorary professor at the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg in Germany and the National University of Colombia. Osswald has authored 12 books in the field of polymer engineering and teaches polymer processing and designing with polymers. His research includes modeling and simulation in polymer processing, engineering design with plastics, sustainability and biopolymers.

Wiesław Kazimierz Binienda is a Polish-American scientist, PhD, and professor and chairman of the Department of Civil Engineering at the University of Akron.
Ramarathnam Narasimhan is an Indian materials engineer and a professor at the Department of Mechanical Engineering of the Indian Institute of Science. He is known for his pioneering researches on fracture mechanics and is an elected fellow of the Indian Academy of Sciences, Indian National Science Academy and the Indian National Academy of Engineering. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards for his contributions to Engineering Sciences in 1999.
Paul Croce Paris was an American academic, engineering consultant and researcher in the field of mechanics and fatigue. He was known particularly for introducing fracture mechanics methods to the aviation industry, and for the empirical Paris' law relating crack growth rate to the amplitude of the stress intensity factor.
Tada is a Japanese surname. It has also been used as a given name. Notable people with the name include:
Reginald Irenee Vachon was an American mechanical engineer, business executive, lawyer and inventor, known as former president of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers.
John William Fisher is a professor emeritus of civil engineering.
Albert Satoshi Kobayashi is an American engineer and scientist.

David Beauregard Bogy is the William S. Floyd, Jr. Distinguished Professor of the Graduate School at the University of California, Berkeley (UCB). He is also the founder and head of the Computer Mechanics Laboratory (CML) at UCB.. He has made particular contributions in air-bearing analysis and design for the sliders that support the read/write heads in hard disk drives (HDD).







