
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly popular in the Ancient Roman world.

Dewlish is a village and civil parish in the county of Dorset in southern England, and is situated approximately 7 miles (11 km) north-east of the county town Dorchester. The village is sited in the valley of the small Devil's Brook among the chalk hills of the Dorset Downs; the parish covers about 2,100 acres (850 ha) and extends west to include part of the valley of the small Cheselbourne stream, and east to include a dry valley at Dennet's Bottom. The surrounding area is part of the Dorset Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB). In the 2011 census the parish had a population of 284.

Rudston is a small village and civil parish in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It is situated between Driffield and Bridlington approximately 6 miles west of Bridlington, and lies on the B1253 road. The Gypsey Race runs through the village, which lies in the Great Wold Valley. There are a number of Neolithic sites associated with the stream and its valley. It is the current Seat of the Clan Macdonald of Sleat, the head of the family residing at Thorpe Hall.

Brantingham is a village and civil parish in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England, about 2 miles (3 km) north of Brough, 12 miles (19 km) west of Hull and north of the A63 road. The 2011 UK Census gave the parish had a population of 370, marking a decrease from the 2001 UK census figure of 410. The 2019 estimate was 319.

The Villa Romana del Casale is a large and elaborate Roman villa or palace located about 3 km from the town of Piazza Armerina, Sicily. Excavations have revealed one of the richest, largest, and most varied collections of Roman mosaics in the world, for which the site has been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The villa and artwork contained within date to the early 4th century AD.

Chedworth Roman Villa is located near Chedworth, Gloucestershire, England and is a scheduled monument. It is one of the largest and most elaborate Roman villas so far discovered in Britain and one with the latest occupation beyond the Roman period. The villa was built in phases from the early 2nd century to the 5th century, with the 4th-century construction transforming the building into an elite dwelling arranged around three sides of a courtyard. The 4th-century building included a heated and furnished west wing containing a dining-room (triclinium) with a fine mosaic floor, as well as two separate bathing suites: one for damp-heat and one for dry-heat.

Littlecote Roman Villa is an extensive and exceptional Roman villa, with associated religious complex, at Littlecote Park just over a mile west of Hungerford, Berkshire. It has been excavated and is on display to the public in the grounds of the estate.

The Low Ham Roman Villa was a Roman courtyard villa located near Low Ham in the civil parish of High Ham in the English county of Somerset. It is best known for the extraordinary figured mosaic depicting the story of Aeneas and Dido.
Petuaria was originally a Roman fort situated where the town of Brough in the East Riding of Yorkshire now stands. Petuaria means something like 'quarter' or 'fourth part', incorporating the archaic Brythonic *petuar, 'four'.

Orpheus mosaics are found throughout the Roman Empire, normally in large Roman villas. The scene normally shown is Orpheus playing his lyre, and attracting birds and animals of many species to gather around him. Orpheus was a popular subject in classical art, and was also used in Early Christian art as a symbol for Christ.

A Roman mosaic is a mosaic made during the Roman period, throughout the Roman Republic and later Empire. Mosaics were used in a variety of private and public buildings, on both floors and walls, though they competed with cheaper frescos for the latter. They were highly influenced by earlier and contemporary Hellenistic Greek mosaics, and often included famous figures from history and mythology, such as Alexander the Great in the Alexander Mosaic.

North Leigh Roman Villa was a Roman courtyard villa in the Evenlode Valley about 0.5 miles (800 m) north of the hamlet of East End in North Leigh civil parish in Oxfordshire. It is a scheduled monument in the care of English Heritage and is open to the public.

Horkstow is a village and civil parish in North Lincolnshire, England, 4 miles (6.4 km) south-west from Barton-upon-Humber, 1 mile (1.6 km) south from South Ferriby and 9 miles (14.5 km) north from Brigg. It lies on the B1204, and 1 mile (1.6 km) east from the navigable River Ancholme. It is one of the five "Low Villages" – Worlaby, Bonby, Saxby All Saints, Horkstow and South Ferriby – between Brigg and the Humber estuary, so-called because of their position below the northern edge of the Lincolnshire Wolds. Horkstow was previously part of Glanford administrative district, and before that, the North Lindsey division of Lindsey, Lincolnshire.

Spoonley Wood Roman Villa is an ancient Roman villa located 2 km south-east of Sudeley Castle near the town of Winchcombe, in Gloucestershire, England. It was a courtyard-type villa excavated in 1882. Some remains of the villa, partly reconstructed, can still be seen in Spoonley Wood, and one mosaic is viewable under a corrugated iron roof.

The Hull and East Riding Museum is located in the Museums Quarter of the Old Town in Kingston upon Hull, England. It dates back to 1925 as the Museum of Commerce and Industry in a former Customs House but acquired its present name in 1989 with a major refurbishment and new entrance, with the transport section moving to a separate museum. It displays items from prehistoric to medieval in the area, many of them in life-size tableaux or reconstructions of rooms and buildings.

Dalton Parlours Roman villa is a Roman villa and scheduled monument near Collingham, West Yorkshire.

Winterton Roman villa is a Roman villa in Winterton, North Lincolnshire. It was discovered in 1747.

Rudston Roman villa is a Roman villa and scheduled monument near Rudston, East Riding of Yorkshire.
Brantingham Roman villa is a Roman villa and scheduled monument near Brantingham, East Riding of Yorkshire, England.
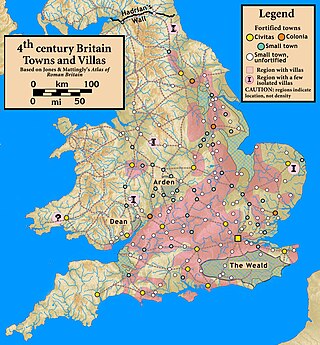
The Rutland Roman villa is a Romano-British villa site in Rutland, England. The site was listed as a scheduled monument by Historic England on 23 November 2021. The villa includes the first example of a mosaic in Britain which depicts scenes from Homer's Iliad.




















