A Trombe wall is a massive equator-facing wall that is painted a dark color in order to absorb thermal energy from incident sunlight and covered with a glass on the outside with an insulating air-gap between the wall and the glaze. A Trombe wall is a passive solar building design strategy that adopts the concept of indirect-gain, where sunlight first strikes a solar energy collection surface in contact with a thermal mass of air. The sunlight absorbed by the mass is converted to thermal energy (heat) and then transferred into the living space.

In passive solar building design, windows, walls, and floors are made to collect, store, reflect, and distribute solar energy, in the form of heat in the winter and reject solar heat in the summer. This is called passive solar design because, unlike active solar heating systems, it does not involve the use of mechanical and electrical devices.
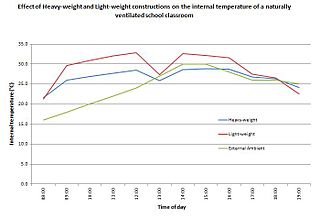
In building design, thermal mass is a property of the matter of a building that requires a flow of heat in order for it to change temperature. In scientific writing the term "heat capacity" is preferred. It is sometimes known as the thermal flywheel effect. The thermal mass of heavy structural elements can be designed to work alongside a construction's lighter thermal resistance components to create energy efficient buildings.

The R-value is a measure of how well a two-dimensional barrier, such as a layer of insulation, a window or a complete wall or ceiling, resists the conductive flow of heat, in the context of construction.. R-value is the temperature difference per unit of heat flux needed to sustain one unit of heat flux between the warmer surface and colder surface of a barrier under steady-state conditions. The measure is therefore equally relevant for lowering energy bills for heating in the winter, for cooling in the summer, and for general comfort.

Solar water heating (SWH) is heating water by sunlight, using a solar thermal collector. A variety of configurations are available at varying cost to provide solutions in different climates and latitudes. SWHs are widely used for residential and some industrial applications.

An energy-plus building produces more energy from renewable energy sources, over the course of a year, than it imports from external sources. This is achieved using a combination of microgeneration technology and low-energy building techniques, such as: passive solar building design, insulation and careful site selection and placement. A reduction of modern conveniences can also contribute to energy savings, however many energy-plus houses are almost indistinguishable from a traditional home, preferring instead to use highly energy-efficient appliances, fixtures, etc., throughout the house.

Passive house is a voluntary standard for energy efficiency in a building, which reduces the building's carbon footprint. Conforming to these standards results in ultra-low energy buildings that require less energy for space heating or cooling. A similar standard, MINERGIE-P, is used in Switzerland. Standards are available for residential properties and several office buildings, schools, kindergartens and a supermarket have also been constructed to the standard. Energy efficiency is not an attachment or supplement to architectural design, but a design process that integrates with architectural design. Although it is generally applied to new buildings, it has also been used for refurbishments.

Superinsulation is an approach to building design, construction, and retrofitting that dramatically reduces heat loss by using much higher insulation levels and airtightness than average. Superinsulation is one of the ancestors of the passive house approach.
Renewable heat is an application of renewable energy referring to the generation of heat from renewable sources; for example, feeding radiators with water warmed by focused solar radiation rather than by a fossil fuel boiler. Renewable heat technologies include renewable biofuels, solar heating, geothermal heating, heat pumps and heat exchangers. Insulation is almost always an important factor in how renewable heating is implemented.
Domestic housing in the United Kingdom presents a possible opportunity for achieving the 20% overall cut in UK greenhouse gas emissions targeted by the Government for 2010. However, the process of achieving that drop is proving problematic given the very wide range of age and condition of the UK housing stock.

Building insulation is material used in a building to reduce the flow of thermal energy. While the majority of insulation in buildings is for thermal purposes, the term also applies to acoustic insulation, fire insulation, and impact insulation. Often an insulation material will be chosen for its ability to perform several of these functions at once.
Manfred Siebald is a German singer-songwriter and lecturer in American studies in Mainz.

Building insulation materials are the building materials that form the thermal envelope of a building or otherwise reduce heat transfer.

Pipe Insulation is thermal or acoustic insulation used on pipework.

The Steingraeber Piano Manufactory is a major German manufacturer of grand and upright pianos. The family business was founded 1852 in Bayreuth, where the instruments are still manufactured today. It has its headquarters in Steingraeber Haus, a historic Rococo palace. Fanny and Alban Steingraeber run the company in the seventh generation.
Thomas Herzog is a German architect from Munich known for his focus on climate and energy use through the use of technologically advanced architectural skins. He began with an interest in pneumatics and became Germany's youngest architecture professor at the age of 32. He established his firm Herzog + Partner in 1983.

The Solar Settlement at Schlierberg is a 59-home PlusEnergy housing community in Freiburg, Germany. Solar architect Rolf Disch wanted to apply his PlusEnergy concept, created originally with his Heliotrope home, to mass residential production. The residential complex won awards, including House of the Year (2002), Residential PV solar integration award (2002), and "Germany's most beautiful housing community" (2006). It is one of the first housing communities in the world in which all the homes produce a positive energy balance and which is emissions-free and CO2 neutral.

Belvedere 21, formerly 21er Haus or Einundzwanziger Haus, is a modernist style steel and glass building designed by Austrian architect Karl Schwanzer (1918–1975). Originally constructed as the Austrian pavilion or temporary showroom for the Expo 58 in Brussels, it was later transferred to Vienna to house the Museum of the 20th Century, which explains why it was first nicknamed "20er Haus". Between 1979 and 2001, the building also acted as a depository for contemporary art works. From 2009 to 2011, it was remodeled by the architect Adolf Krischanitz and consequently renamed 21er Haus to reflect the 21st century. It was renamed Belvedere 21 in 2018.
Zero-carbon housing is housing that does not emit greenhouse gasses (GHGs) into the atmosphere, either directly, or indirectly due to consumption electricity produced using fossil fuels. Most commonly zero-carbon housing is taken to mean zero emissions of carbon dioxide, which is the main climate pollutant from homes, although fugitive methane may also be emitted from natural gas pipes and appliances.

The Hans Stieber Prize is a promotional prize for composers of serious and light music, which is awarded by the fiduciary trust Hans Stieber Foundation of the Landesverband Sachsen-Anhalt Deutscher Komponistenverband based in Halle (Saale). The name giver and dedicatee is Hans Stieber (1886–1969), composer and founding director of the Staatliche Hochschule für Theater und Musik Halle.














