
Remipedia is a class of blind crustaceans found in coastal aquifers which contain saline groundwater, with populations identified in almost every ocean basin so far explored, including in Australia, the Caribbean Sea, and the Atlantic Ocean. The first described remipede was the fossil Tesnusocaris goldichi. Since 1979, at least seventeen living species have been identified in subtropical regions around the world.

Cylindroleberididae is a family of ostracods that shows remarkable morphological diversity. The defining feature is the possession of gills: 7–8 leaf-like pairs at the posterior of the body. Other features common to all species in the family include a "baleen-comb" on both the maxilla and the fifth limb, a sword-shaped coxal endite on the mandible, and the triaenid bristles on the basal endites of the mandible.
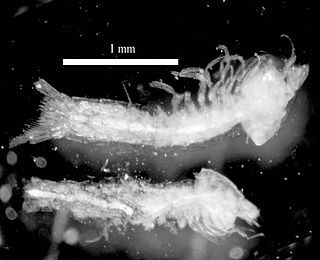
Thermosbaenacea is a group of crustaceans that live in thermal springs in fresh water, brackish water and anchialine habitats. They have occasionally been treated as a distinct superorder (Pancarida), but are generally considered to belong to the Peracarida. Due to their troglobitic lifestyle, thermosbaenaceans lack visual pigments and are therefore blind.
Polycopidae is a family of marine ostracods. Its members are related to animals in the suborder Halocypridina, but are sufficiently distinct to be placed in the sub-order Cladocopina. There is even some speculation that a separate order may be warranted. The genera in the family differ from the other suborder, Halocypridina, in several features: the central adductor muscle scars are in a triangular or half-rosette pattern, they lack sixth and seventh limbs, and the maxilla has both an exopod and endopod.
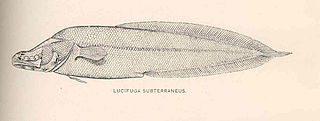
Lucifuga is a genus of viviparous brotulas. Most of the species are native to caves and sinkholes in Cuba and the Bahamas; L. inopinata from deep water off the Galápagos Islands is the only exception. The four species rated by the IUCN are all considered vulnerable. The largest species in the genus reaches about 15 cm (5.9 in) in length.
Leucocythere is a genus of ostracods in family Limnocytheridae. It contains at least the following species:
Spelaeoecia is a genus of crustaceans in the family Thaumatocyprididae. One species, the Bermudan endemic S. bermudensis, is listed as critically endangered on the IUCN Red List. It contains the following species:
Speleophria is a genus of marine copepods in the family Speleophriidae. It contains the following species:

Cypridinidae is a family of ostracods, containing the following genera:

Kornicker Glacier is a glacier draining northeastwards from the cirque bounded by Mount Liptak, Mount Southwick, Mount Milton and Mount Mullen in the southern Sentinel Range of the Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica. The glacier flows along the northwestern side of Petvar Heights and merges with the terminus of the southeast-flowing Thomas Glacier as both glaciers emerge from the range.
Halicyclops is a genus of copepods belonging to the family Cyclopidae. There are currently 94 described species found in brackish habitats throughout the world:

Limbodessus is a genus of beetles in the family Dytiscidae, first described by Félix Guignot in 1939. It contains the following species:
Nirripirti is a genus of beetles in the family Dytiscidae. However the Australian Faunal Directory considers it a synonym of the genus, Paroster, on the basis of work by Leys and Watts, and Toussaint, Hendrich and others.
Paroster is a genus of beetles in the family Dytiscidae, containing the following species:
Pleomothra is a genus of crustacean found in the Caribbean. First described in 1989, the genus has 2 identified species as of 2008. It is the sole member of family Pleomothridae, but was previously placed in family Godzilliidae.

The clade Multicrustacea constitutes the largest superclass of crustaceans, containing approximately four-fifths of all described crustacean species, including crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrimp, krill, prawns, woodlice, barnacles, copepods, amphipods, mantis shrimp and others. The largest branch of multicrustacea is the class Malacostraca.
Thaumatocyprididae is a family of ostracods in the order Halocyprida which contains seven genera and one subfamily. It first appeared in the Lopingian Epoch, 259.9 million years ago.
Cytherella is a genus of seed shrimp in the family Cytherellidae.
Tulumella is a genus of crustaceans belonging to the monotypic family Tulumellidae.
An anchialine system is a landlocked body of water with a subterranean connection to the ocean. Depending on its formation, these systems can exist in one of two primary forms: pools or caves. The primary differentiating characteristics between pools and caves is the availability of light; cave systems are generally aphotic while pools are euphotic. The difference in light availability has a large influence on the biology of a given system. Anchialine systems are a feature of coastal aquifers which are density stratified, with water near the surface being fresh or brackish, and saline water intruding from the coast at depth. Depending on the site, it is sometimes possible to access the deeper saline water directly in the anchialine pool, or sometimes it may be accessible by cave diving.







