
The gluteus maximus is the main extensor muscle of the hip in humans. It is the largest and outermost of the three gluteal muscles and makes up a large part of the shape and appearance of each side of the hips. It is the single largest muscle in the human body. Its thick fleshy mass, in a quadrilateral shape, forms the prominence of the buttocks. The other gluteal muscles are the medius and minimus, and sometimes informally these are collectively referred to as the glutes.

The bench press, or chest press, is a weight training exercise where a person presses a weight upwards while lying horizontally on a weight training bench. Although the bench press is a full-body exercise, the muscles primarily used are the pectoralis major, the anterior deltoids, and the triceps, among other stabilizing muscles. A barbell is generally used to hold the weight, but a pair of dumbbells can also be used.

The push-up is a common calisthenics exercise beginning from the prone position. By raising and lowering the body using the arms, push-ups exercise the pectoral muscles, triceps, and anterior deltoids, with ancillary benefits to the rest of the deltoids, serratus anterior, coracobrachialis and the midsection as a whole. Push-ups are a basic exercise used in civilian athletic training or physical education and commonly in military physical training. They are also a common form of punishment used in the military, school sport, and some martial arts disciplines. Variations of push-ups, such as wide-arm push-ups, diamond push-ups target specific muscle groups and provide further challenges.

Lordosis is historically defined as an abnormal inward curvature of the lumbar spine. However, the terms lordosis and lordotic are also used to refer to the normal inward curvature of the lumbar and cervical regions of the human spine. Similarly, kyphosis historically refers to abnormal convex curvature of the spine. The normal outward (convex) curvature in the thoracic and sacral regions is also termed kyphosis or kyphotic. The term comes from the Greek lordōsis, from lordos.
Bicep curls are a group of weight training exercises in which a person bends their arm towards their body at the elbow in order to make their biceps stronger.

A squat is a strength exercise in which the trainee lowers their hips from a standing position and then stands back up. During the descent, the hip and knee joints flex while the ankle joint dorsiflexes; conversely the hip and knee joints extend and the ankle joint plantarflexes when standing up. Squats also help the hip muscles.

The deadlift is a weight training exercise in which a loaded barbell or bar is lifted off the ground to the level of the hips, torso perpendicular to the floor, before being placed back on the ground. It is one of the three powerlifting exercises, along with the squat and bench press, as well as a frequent lift in strongman.
In strength training, rowing is an exercise where the purpose is to strengthen the muscles that draw the rower's arms toward the body as well as those that retract the scapulae and those that support the spine. When done on a rowing machine, rowing also exercises muscles that extend and support the legs. In all cases, the abdominal and lower back muscles must be used in order to support the body and prevent back injury.
The good-morning is a weight training exercise. It is known as a good morning because of the movement in the erector spinae which resembles the bow that traditionally begins a schoolday in some East-Asian countries. The erector spinae muscles of the lower back work isometrically to keep the spine in an extended position while the hamstrings and gluteus maximus work isotonically to perform hip extension. Other muscles are involved in stabilizing weight on the back and maintaining balance.

In combat sports, a spinal lock is a multiple joint lock applied to the spinal column, which is performed by forcing the spine beyond its normal ranges of motion. This is typically done by bending or twisting the head or upper body into abnormal positions. Commonly, spinal locks might strain the spinal musculature or result in a mild spinal sprain, while a forcefully and/or suddenly applied spinal lock may cause severe ligament damage or damage to the vertebrae, and possibly result in serious spinal cord injury, stroke, or death. Spinal locks and cervical locks are forbidden in IBJJF Brazilian jiu-jitsu competitions, amateur mixed martial arts (MMA), multiple forms of no Gi jiu-jitsu, judo, and other martial arts. However, professional MMA and some Brazilian jiu-jitsu competitions do permit spinal locks and, particularly, neck cranks, and such moves are trained in various MMA and Brazilian jiu-jitsu schools.
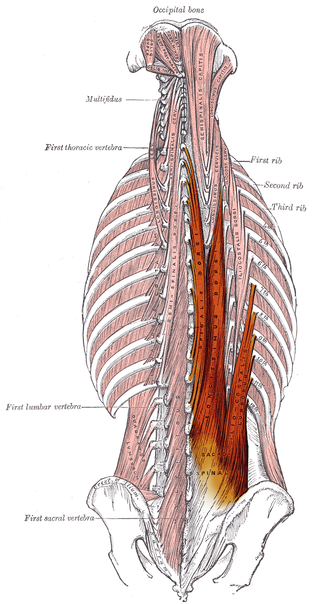
The erector spinae or spinal erectors is a set of muscles that straighten and rotate the back. The spinal erectors work together with the glutes to maintain stable posture standing or sitting.

Weighted clothing are garments that have heavy materials incorporated into them, to add weight to various parts of the body, usually as part of resistance training. The effect is achieved through attaching weighted pieces to the body which leave the hands free to grasp objects. Unlike with held weights or machines, weighted clothing can leave users more able to do a variety of movements and manual labour. In some cases certain weighted clothing can be worn under normal clothing, to disguise its use to allow exercise in casual environments.
A bent-over row is a weight training exercise that targets a variety of back muscles. Which ones are targeted varies on form. The bent over row is often used for both bodybuilding and powerlifting.

The acetabular labrum is a fibrocartilaginous ring which surrounds the circumference of the acetabulum of the hip, deepening the acetabulum. The labrum is attached onto the bony rim and transverse acetabular ligament. It is triangular in cross-section.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to exercise:

A fly or flye is a strength training exercise in which the hand and arm move through an arc while the elbow is kept at a constant angle. Flies are used to work the muscles of the upper body. Because these exercises use the arms as levers at their longest possible length, the amount of weight that can be moved is significantly less than equivalent press exercises for the same muscles . Due to this leverage, fly exercises of all types have a large potential to damage the shoulder joint and its associated ligaments and the tendons of the muscles connecting to it. They should be done with caution and their effects first tested while using very light weights; which are gradually incremented after more strength is gained.

The Roman chair is a piece of exercise equipment. It is mainly used for the lower back, but can also target the buttocks, hamstrings, and abdomen. The definition of the equipment, and what 'Roman chair exercise' specifically means, is not clear.
The rear delt raise, also known as the rear deltoid raise, or rear shoulder raise is an exercise in weight training. This exercise is an isolation exercise that heavily works the posterior deltoid muscle. The movement is primarily limited to the two shoulder joints: the glenohumeral joint and the scapulothoracic joint. Scapular movement will also cause movement in the sternoclavicular joint and acromioclavicular joint. If the elbow bends during the extension exercises, it gravitates into a rowing motion.

The leg raise is a strength training exercise which targets the iliopsoas. Because the abdominal muscles are used isometrically to stabilize the body during the motion, leg raises are also often used to strengthen the rectus abdominis muscle and the internal and external oblique muscles.
















