
Leukotriene C4 synthase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the LTC4S gene.
The isoprenylcysteine o-methyltransferase carries out carboyxl methylation of cleaved eukaryotic proteins that terminate in a CaaX motif. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae this methylation is carried out by Ste14p, an integral endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein. Ste14p is the founding member of the isoprenylcysteine carboxyl methyltransferase (ICMT) family, whose members share significant sequence homology.
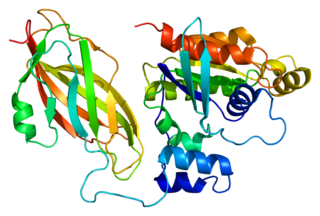
Rac2 is a small signaling G protein, and is a member of the Rac subfamily of the family Rho family of GTPases. It is encoded by the gene RAC2.

A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADAMTS1 gene.

Ras GTPase-activating protein-binding protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the G3BP1 gene.

Glucosidase 2 subunit beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKCSH gene.

DNA methyltransferase 1-associated protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DMAP1 gene.

Protein-L-isoaspartate(D-aspartate) O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PCMT1 gene.

DnaJ homolog subfamily B member 11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAJB11 gene.

DnaJ homolog subfamily B member 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAJB9 gene.

Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 16 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the USP16 gene.

Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 G1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UBE2G1 gene.

Ras GTPase-activating protein nGAP is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RASAL2 gene.

GPI transamidase component PIG-S is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIGS gene. This gene encodes a protein that is involved in GPI-anchor biosynthesis.

Leucine carboxyl methyltransferase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the LCMT2 gene.

Putative rRNA methyltransferase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FTSJ3 gene.

Ras-specific guanine nucleotide-releasing factor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RASGRF2 gene.

CAAX prenyl protease 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RCE1 gene.

N6-adenosine-methyltransferase 70 kDa subunit (METTL3) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the METTL3 gene.
Protein methylation is a type of post-translational modification featuring the addition of methyl groups to proteins. It can occur on the nitrogen-containing side-chains of arginine and lysine, but also at the amino- and carboxy-termini of a number of different proteins. In biology, methyltransferases catalyze the methylation process, activated primarily by S-adenosylmethionine. Protein methylation has been most studied in histones, where the transfer of methyl groups from S-adenosyl methionine is catalyzed by histone methyltransferases. Histones that are methylated on certain residues can act epigenetically to repress or activate gene expression.





















