Grus is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the crane, a type of bird. It is one of twelve constellations conceived by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. Grus first appeared on a 35-centimetre-diameter (14-inch) celestial globe published in 1598 in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius and was depicted in Johann Bayer's star atlas Uranometria of 1603. French explorer and astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille gave Bayer designations to its stars in 1756, some of which had been previously considered part of the neighbouring constellation Piscis Austrinus. The constellations Grus, Pavo, Phoenix and Tucana are collectively known as the "Southern Birds".

A nebula is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral, or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the "Pillars of Creation" in the Eagle Nebula. In these regions, the formations of gas, dust, and other materials "clump" together to form denser regions, which attract further matter and eventually become dense enough to form stars. The remaining material is then thought to form planets and other planetary system objects.

A planetary nebula is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.

The Ring Nebula is a planetary nebula in the northern constellation of Lyra.[C] Such a nebula is formed when a star, during the last stages of its evolution before becoming a white dwarf, expels a vast luminous envelope of ionized gas into the surrounding interstellar space.

The Cat's Eye Nebula is a planetary nebula in the northern constellation of Draco, discovered by William Herschel on February 15, 1786. It was the first planetary nebula whose spectrum was investigated by the English amateur astronomer William Huggins, demonstrating that planetary nebulae were gaseous and not stellar in nature. Structurally, the object has had high-resolution images by the Hubble Space Telescope revealing knots, jets, bubbles and complex arcs, being illuminated by the central hot planetary nebula nucleus (PNN). It is a well-studied object that has been observed from radio to X-ray wavelengths.

The Eskimo Nebula, also known as the Clown-faced Nebula, Lion Nebula, or Caldwell 39, is a bipolar double-shell planetary nebula (PN). It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel in 1787. The formation resembles a person's head surrounded by a parka hood. It is surrounded by gas that composed the outer layers of a Sun-like star. The visible inner filaments are ejected by a strong wind of particles from the central star. The outer disk contains unusual, light-year-long filaments.

IC 418, also known as the Spirograph Nebula, is a planetary nebula located in the constellation of Lepus about 3,600 ly away from Earth. It spans 0.3 light-years across. The central star of the planetary nebula, HD 35914, is an O-type star with a spectral type of O7fp. The nebula formed a few thousand years ago during the stars last stages of its red giant phase. Material from the star’s outer layers was ejected from the star into the surrounding space. The nebula’s glow is caused by the central star’s ultraviolet radiation interacting with the gas.

NGC 5189 is a planetary nebula in the constellation Musca. It was discovered by James Dunlop on 1 July 1826, who catalogued it as Δ252. For many years, well into the 1960s, it was thought to be a bright emission nebula. It was Karl Gordon Henize in 1967 who first described NGC 5189 as quasi-planetary based on its spectral emissions.

NGC 7027, also known as the Jewel Bug Nebula, is a very young and dense planetary nebula located around 3,000 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cygnus. Discovered in 1878 by Édouard Stephan using the 800 mm (31 in) reflector at Marseille Observatory, it is one of the smallest planetary nebulae and by far the most extensively studied.

NGC 6751, also known as the Glowing Eye Nebula, is a planetary nebula in the constellation Aquila. It is estimated to be about 6,500 light-years away.
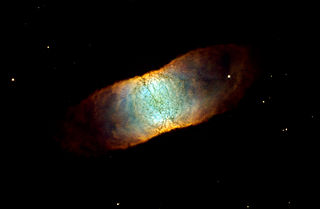
IC 4406, sometimes known as the Retina Nebula, is a planetary nebula near the western border of the constellation Lupus, the Wolf. It has dust clouds and has the shape of a torus. Despite this, it looks somewhat rectangular because it is seen from its side as viewed from Earth, almost in the plane of its equator.

NGC 5882 is a small planetary nebula in the southern constellation of Lupus, positioned about 1.5° to the southwest of the star Epsilon Lupi. It was discovered by English astronomer John Herschel on July 2, 1834 from the Cape of Good Hope observatory. John L. E. Dreyer described it as "very small, round, quite sharp". It is located at a distance of approximately 7.7 kilolight-years from the Sun.

NGC 5307 is a planetary nebula in the southern constellation of Centaurus, positioned less than 3° to the northeast of the star Epsilon Centauri. It was discovered by English astronomer John Herschel on April 15, 1836. The nebula is located at a distance of approximately 10.6 kilolight-years from the Sun. The central star, designated PNG 312.3+10.5, is a weak emission-line star, superficially similar to the WC subtype of Wolf–Rayet stars. It has a spectral class of O(H)3.5 V.

Abell 39 is a low surface brightness planetary nebula in the constellation of Hercules. It is the 39th entry in George Abell's 1966 Abell Catalog of Planetary Nebulae of 86 old planetary nebulae which either Abell or Albert George Wilson discovered before August 1955 as part of the National Geographic Society - Palomar Observatory Sky Survey. It is estimated to be about 3,800 light-years from earth and thus 2,600 light-years above the Galactic plane. It is almost perfectly spherical and also one of the largest known spheres with a radius of about 1.4 light-years.

NGC 2899 is a planetary nebula in the southern constellation of Vela. It was discovered by English astronomer John Herschel on February 27, 1835. This nebula can be viewed with a moderate-sized amateur telescope, but requires a larger telescope to resolve details. NGC 2899 is located at a distance of 3,350 ± 670 light-years (1,026 ± 205 pc) from the Sun and 25,894 ± 3 light-years (7,939 ± 1 pc) from the Galactic Center.

IC 2177 is a region of nebulosity that lies along the border between the constellations Monoceros and Canis Major. It is a roughly circular H II region centered on the Be star HD 53367. This nebula was discovered by Welsh amateur astronomer Isaac Roberts and was described by him as "pretty bright, extremely large, irregularly round, very diffuse."

Abell 36 is a planetary nebula located 780 light years away in the constellation of Virgo.

NGC 6445, also known as the Little Gem Nebula or Box Nebula, is a planetary nebula in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by William Herschel on May 28, 1786. The distance of NGC 6445 is estimated to be slightly more than 1,000 parsecs based on the parallax measured by Gaia, which was measured at 0.9740±0.3151 mas.

Hen 2-131 is a planetary nebula in the southern constellation of Apus. It was discovered by Andrew David Thackeray in 1950 and added to the Catalogues of Hα-emission Stars and Nebulae in the Magellanic Clouds by Karl Gordon Henize in 1967.

IC 4997 is a planetary nebula located in the constellation of Delphinus. It was discovered in 1896 by Edward Charles Pickering and Williamina Fleming, and independently by Gustav Gruss the same year. This nebula is about 14,000 light-years from Earth. It looks like an ordinary star in smaller telescopes, and only detailed study of its spectrum reveals its nebular characteristics.




















