In chemistry, azide is a linear, polyatomic anion with the formula N−3 and structure −N=N+=N−. It is the conjugate base of hydrazoic acid HN3. Organic azides are organic compounds with the formula RN3, containing the azide functional group. The dominant application of azides is as a propellant in air bags.

In organosulfur chemistry, a sulfonate is a salt or ester of a sulfonic acid. It contains the functional group R−S(=O)2−O−, where R is an organic group. Sulfonates are the conjugate bases of sulfonic acids. Sulfonates are generally stable in water, non-oxidizing, and colorless. Many useful compounds and even some biochemicals feature sulfonates.

Imidazole (ImH) is an organic compound with the formula C3N2H4. It is a white or colourless solid that is soluble in water, producing a mildly alkaline solution. In chemistry, it is an aromatic heterocycle, classified as a diazole, and has non-adjacent nitrogen atoms in meta-substitution.

Sodium azide is the inorganic compound with the formula NaN3. This colorless salt is the gas-forming component in legacy car airbag systems. It is used for the preparation of other azide compounds. It is an ionic substance, is highly soluble in water and is very acutely poisonous.
The diazogroup is an organic moiety consisting of two linked nitrogen atoms (azo) at the terminal position. Overall charge neutral organic compounds containing the diazo group bound to a carbon atom are called diazo compounds or diazoalkanes and are described by the general structural formula R2C=N+=N–. The simplest example of a diazo compound is diazomethane, CH2N2. Diazo compounds (R2C=N2) should not be confused with azo compounds of the type R-N=N-R or with diazonium compounds of the type R-N2+.

Hydrazoic acid, also known as hydrogen azide or azoimide, is a compound with the chemical formula HN3. It is a colorless, volatile, and explosive liquid at room temperature and pressure. It is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen, and is therefore a pnictogen hydride. It was first isolated in 1890 by Theodor Curtius. The acid has few applications, but its conjugate base, the azide ion, is useful in specialized processes.

The Bamford–Stevens reaction is a chemical reaction whereby treatment of tosylhydrazones with strong base gives alkenes. It is named for the British chemist William Randall Bamford and the Scottish chemist Thomas Stevens Stevens (1900–2000). The usage of aprotic solvents gives predominantly Z-alkenes, while protic solvent gives a mixture of E- and Z-alkenes. As an alkene-generating transformation, the Bamford–Stevens reaction has broad utility in synthetic methodology and complex molecule synthesis.
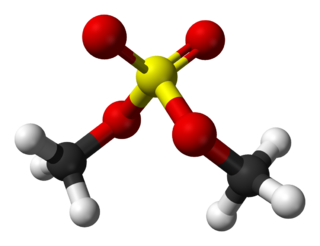
Dimethyl sulfate (DMS) is a chemical compound with formula (CH3O)2SO2. As the diester of methanol and sulfuric acid, its formula is often written as (CH3)2SO4 or Me2SO4, where CH3 or Me is methyl. Me2SO4 is mainly used as a methylating agent in organic synthesis.
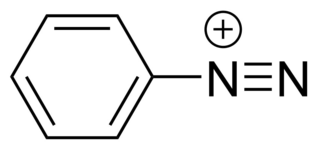
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group [R−N+≡N]X− where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halide.
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms within the ring.

The Seyferth–Gilbert homologation is a chemical reaction of an aryl ketone 1 with dimethyl (diazomethyl)phosphonate 2 and potassium tert-butoxide to give substituted alkynes 3. Dimethyl (diazomethyl)phosphonate 2 is often called the Seyferth–Gilbert reagent.
In organic chemistry, the Baudisch reaction is a process for the synthesis of nitrosophenols using metal ions. Although the products are of limited value, the reaction is of historical interest as an example of metal-promoted functionalization of aromatic substrates.

Trifluoromethanesulfonyl azide or triflyl azideCF3SO2N3 is an organic azide used as a reagent in organic synthesis.
Electrophilic amination is a chemical process involving the formation of a carbon–nitrogen bond through the reaction of a nucleophilic carbanion with an electrophilic source of nitrogen.

Methyl azide is an organic compound with the formula CH3N3. It is a white solid and it is the simplest organic azide.

Tosyl azide is a reagent used in organic synthesis.
A tosylhydrazone in organic chemistry is a functional group with the general structure RR'C=N-NH-Ts where Ts is a tosyl group. Organic compounds having this functional group can be accessed by reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with tosylhydrazine.
Nickel boride is the common name of materials composed chiefly of the elements nickel and boron that are widely used as catalysts in organic chemistry. Their approximate chemical composition is Ni2.5B, and they are often incorrectly denoted "Ni
2B" in organic chemistry publications.

Cyanogen azide, N3CN or CN4, is an azide compound of carbon and nitrogen which is an oily, colourless liquid at room temperature. It is a highly explosive chemical that is soluble in most organic solvents, and normally handled in dilute solution in this form. It was first synthesised by F. D. Marsh at DuPont in the early 1960s.
An organic azide is an organic compound that contains an azide functional group. Because of the hazards associated with their use, few azides are used commercially although they exhibit interesting reactivity for researchers. Low molecular weight azides are considered especially hazardous and are avoided. In the research laboratory, azides are precursors to amines. They are also popular for their participation in the "click reaction" and in Staudinger ligation. These two reactions are generally quite reliable, lending themselves to combinatorial chemistry.