
Fernando Affonso Collor de Mello is a Brazilian politician who served as the 32nd president of Brazil from 1990 to 1992, when he resigned in a failed attempt to stop his impeachment trial by the Brazilian Senate. Collor was the first president democratically elected after the end of the Brazilian military dictatorship. He became the youngest president in Brazilian history, taking office at the age of 40. After he resigned from the presidency, the impeachment trial on charges of corruption continued. Collor was found guilty by the Senate and disqualified from holding elected office for eight years (1992–2000). He was later acquitted of ordinary criminal charges in his judicial trial before Brazil's Supreme Federal Court, for lack of valid evidence.

Aécio Neves da Cunha is a Brazilian economist, politician and former president of the Brazilian Social Democracy Party (PSDB). He was the 17th Governor of Minas Gerais from 1 January 2003 to 31 March 2010, and is currently a member of the Brazilian Chamber of Deputies. He lost in the runoff presidential election against Dilma Rousseff in 2014.
Paulo Cesar Siqueira Cavalcante Farias commonly known as Paulo Cesar Farias or PC Farias, was the political campaign treasurer of Brazilian President Fernando Collor de Mello and a central figure in the corruption scandal that resulted in Collor's 1992 removal from Brazil's presidential office.

Ciro Ferreira Gomes, known mononymously as Ciro, is a Brazilian politician, lawyer, and academic. Ciro is currently affiliated with and vice-president of the Democratic Labour Party (PDT).

The Brazilian Labour Renewal Party is a conservative Brazilian political party. It was founded in 1994 and its electoral number is 28. According to the party's official website, the PRTB's main ideology is participatory economics: "to establish an economic system based on participatory decision making as the primary economic mechanism for allocation in society".

José Renan Vasconcelos Calheiros is a Brazilian politician and former President of the Federal Senate of Brazil. He has represented the state of Alagoas in the senate as a member of the Brazilian Democratic Movement. since 1 February 1995. Renan's presidency of the Brazilian Senate, a term that started 1 February 2013, was revoked on 5 December 2016 by a minister of the Brazilian Supreme Court, Marco Aurélio Mello, who said that a person under investigation could not be in the line of succession for the presidency. However the Supreme Court decided 7 December 2016 that Renan could remain senate president, without being in the succession.
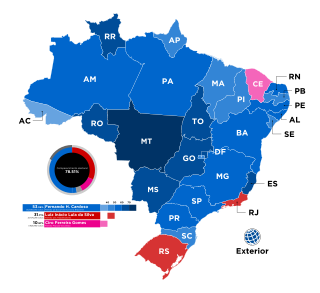
General elections were held in Brazil on 4 October 1998 to elect the President, National Congress and state governorships. If no candidate in the presidential election received more than 50% of the vote in the first round, a second-round runoff would have been held on 25 October. The election saw voting machines used for the first time in Brazilian history.

Marco Aurélio Mendes de Farias Mello is a Brazilian former justice of the Supreme Federal Court of Brazil, appointed to the position by his cousin, former President of Brazil Fernando Collor de Mello.
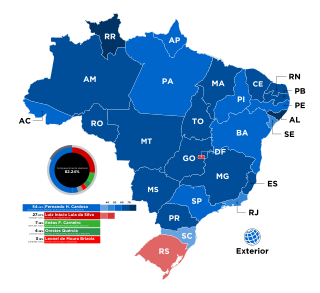
General elections were held in Brazil on October 3, 1994, the second to take place under the provisions of the 1988 constitution and the second direct presidential election since 1960.
Lei da Ficha Limpa or Complementary Law no. 135 of 2010 is a Brazilian act that amended the Conditions of Ineligibility Act. It was the fourth bill proposed by direct people's initiative as law in Brazil. It was devised by Judge Marlon Reis and received about 1.3 million signatures before being submitted to the National Congress. The act makes a candidate who has been impeached, has resigned to avoid impeachment, or been convicted by a decision of a collective body ineligible to hold public office for eight years, even if possible appeals remain.

Corruption in Brazil exists on all levels of society from the top echelons of political power to the smallest municipalities. Operation Car Wash showed central government members using the prerogatives of their public office for rent-seeking activities, ranging from political support to siphoning funds from state-owned corporation for personal gain. The Mensalão scandal for example used taxpayer funds to pay monthly allowances to members of congress from other political parties in return for their support and votes in congress. Politicians also used the state-owned and state-run oil company Petrobras to raise hundreds of millions of reais for political campaigns and personal enrichment.

Luiz Lindbergh Farias Filho, commonly known only as Lindbergh Farias, is a Brazilian former student union leader and politician.

Events in the year 1992 in Brazil.

Events in the year 1994 in Brazil.

General elections were held in Brazil on 7 October 2018 to elect the president, National Congress and state governors. As no candidate in the presidential election received more than 50% of the vote in the first round, a runoff round was held of those offices on 28 October. On that day, right-wing outsider candidate Jair Bolsonaro defeated leftist Fernando Haddad and was elected President of Brazil.

Benevenuto Daciolo Fonseca dos Santos, known as Cabo Daciolo, is a Brazilian military firefighter, pastor and politician affiliated to Republicans. In 2014, he was elected federal deputy. He was expelled from the Socialism and Liberty Party (PSOL) in 2015 and later affiliated to the Labour Party of Brazil, Patriota, Podemos (PODE), Liberal Party and the Brazilian Woman's Party (PMB).

Janaina Conceição Paschoal is a Brazilian jurist and politician. She is a member of the Progressistas (PP) since 2024, having been elected state representative of the State of São Paulo by the Social Liberal Party (PSL) from 2019 to 2023. She is also a lawyer and a law professor at the University of São Paulo.

Ubirajara Dettmar was a Brazilian photographer. He documented a wide range of events, including weddings, funerals, revolutions, and armed conflicts, both within Brazil and internationally. Dettmar served as the official photographer for President Fernando Collor de Mello.

The presidency of Itamar Franco began on 29 December 1992, with the resignation of Fernando Collor de Mello, and ended on 1 January 1995, when Fernando Henrique Cardoso took office.
TV Gazeta de Alagoas is a Brazilian television station based in Maceió, capital of the state of Alagoas, carrying TV Globo for the state, owned-and-operated by locally based Organização Arnon de Mello, a communications group linked to the former President of the Republic Fernando Collor de Mello.

















