
The House of Bonaparte is a former imperial and royal European dynasty of Italian origin. It was founded in 1804 by Napoleon I, the son of Corsican nobleman Carlo Buonaparte and Letizia Buonaparte. Napoleon was a French military leader who rose to power during the French Revolution and who, in 1804, transformed the French First Republic into the First French Empire, five years after his coup d'état of November 1799. Napoleon and the Grande Armée had to fight against every major European power and dominated continental Europe through a series of military victories during the Napoleonic Wars. He installed members of his family on the thrones of client states, expanding the power of the dynasty.

The word emperor can mean the male ruler of an empire. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife, mother/grandmother, or a woman who rules in her own right and name. Emperors are generally recognized to be of the highest monarchic honour and rank, surpassing kings. In Europe, the title of Emperor has been used since the Middle Ages, considered in those times equal or almost equal in dignity to that of Pope due to the latter's position as visible head of the Church and spiritual leader of the Catholic part of Western Europe. The emperor of Japan is the only currently reigning monarch whose title is translated into English as "Emperor".
A prince is a male ruler or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. Prince is also a title of nobility, often hereditary, in some European states. The female equivalent is a princess. The English word derives, via the French word prince, from the Latin noun prīnceps, from primus (first) and caput (head), meaning "the first, foremost, the chief, most distinguished, noble ruler, prince".

Napoleon II was the disputed Emperor of the French for a few weeks in 1815. He was the son of Emperor Napoleon I and Empress Marie Louise, daughter of Emperor Francis I of Austria. Napoleon II had been Prince Imperial of France and King of Rome since birth. After the fall of his father, he lived the rest of his life in Vienna and was known in the Austrian court as Franz, Duke of Reichstadt for his adult life. He was posthumously given the nickname L'Aiglon after the popular Edmond Rostand play, L'Aiglon.

Jérôme-Napoléon Bonaparte was the youngest brother of Napoleon I and reigned as Jerome Napoleon I, King of Westphalia, between 1807 and 1813.

Prince Napoléon Joseph Charles Paul Bonaparte, usually called Napoléon-Jérôme Bonaparte or Jérôme Bonaparte, was the second son of Jérôme, King of Westphalia, youngest brother of Napoleon I, and his second wife Catharina of Württemberg. Following the death of his nephew Louis-Napoléon, Prince Imperial in 1879, he claimed headship of the House of Bonaparte until his death in 1891. An outspoken liberal however, he was passed over as heir in his cousin's final will, which instead chose his elder son Victor, who was favored by most Bonapartists. From the 1880s onwards, he was one of the stronger supporters of General Georges Boulanger, together with other monarchist forces.

Joseph Cardinal Fesch, Prince of the Empire was a French priest and diplomat, who was the maternal half-uncle of Napoleon Bonaparte. In the wake of his nephew, he became Archbishop of Lyon and cardinal. He was also one of the most famous art collectors of his period, remembered for having established the Musée Fesch in Ajaccio, which remains one of the most important Napoleonic collections of art.
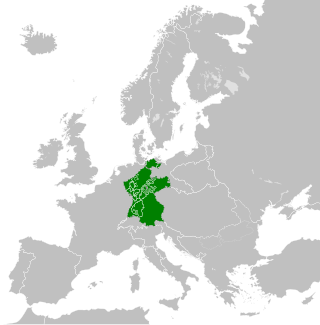
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine or Rhine Confederation, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austria and Russia at the Battle of Austerlitz. Its creation brought about the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire shortly afterward. The Confederation of the Rhine lasted for 7 years, from 1806 to 1813.

The Grand Dignitaries of the French Empire were created in 1804 by the Constitution of the Year XII, which established Napoleon Bonaparte, previously First Consul for Life, as Emperor of the French. The seven Grand Dignitaries broadly paralleled the Great Officers of the Crown which had existed under the Ancien Régime and were essentially honorific, although several limited functions were ascribed to them in the new constitution of the Empire. In the imperial nobility, the Grand Dignitaries ranked in status directly behind the Princes of France, although in practice, most Grand Dignitaries also held the title of Prince.

German mediatisation was the major redistribution and reshaping of territorial holdings that took place between 1802 and 1814 in Germany by means of the subsumption and secularisation of a large number of Imperial Estates, prefiguring, precipitating, and continuing after the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire. Most ecclesiastical principalities, free imperial cities, secular principalities, and other minor self-ruling entities of the Holy Roman Empire lost their independent status and were absorbed by the remaining states. By the end of the mediatisation process, the number of German states had been reduced from almost 300 to just 39.

Victor, Prince Napoléon, titular 3rd Prince of Montfort, was the Bonapartist pretender to the French throne from 1879 until his death in 1926. He was known as Napoléon V by those who supported his claim.

Charles, Prince Napoléon is a French politician who is the disputed head of the Imperial House of France and, as such, heir to the legacy of his great-great-granduncle, Emperor Napoléon I.

Jean-Christophe, Prince Napoléon, Prince of Montfort is the disputed head of the Imperial House of France, and as such the heir of Napoleon Bonaparte, the first Emperor of the French. He would be known as Napoleon VII.

The Princes of Canino and Musignano formed the genealogically senior line of the Bonaparte family following the death of Joseph Bonaparte in 1844. The line was succeeded by one of Emperor Napoleon's younger brothers, Lucien Bonaparte. It became extinct in the male line in 1924. The dynastic Bonapartist pretenders descend in the male line from Prince Jérôme Napoléon, Napoleon's youngest brother.

The Electorate of Bavaria was a quasi-independent hereditary electorate of the Holy Roman Empire from 1623 to 1806, when it was succeeded by the Kingdom of Bavaria.

The succession to the throne of the French Empire was vested by Bonapartist emperors in the descendants and selected male relatives of Napoleon I. Following the end of the Second French Empire in 1870, Bonapartist pretenders descended from Napoleon I's brothers have maintained theoretical claims to the imperial office.

As Emperor of the French, Napoleon I created titles in a newly established noblesse impériale to institute a stable elite in the First French Empire, after the instability resulting from the French Revolution.

The Faesch family, also spelled Fesch, is a prominent Swiss, French, Belgian, Corsican and Italian noble family, originally a patrician family of Basel. Known since the early 15th century, the family received a confirmation of nobility from the Holy Roman Emperor in 1563. It was continuously represented in the governing bodies of the city-republic of Basel for centuries, and three members served as Burgomasters, i.e. heads of state, namely Remigius Faesch (1541–1610), Johann Rudolf Faesch (1572–1659) and Johann Rudolf Faesch (1680–1762). The family was at times the richest family of Basel, and its rise was partially the result of clever marriage policies.

Prince Imperial of France was a title originally created under the Constitution of the Year XII, in 1804, to designate the eldest son of the Emperor of the French under the First French Empire. The title was, furthermore, revived under the Sénatus-Consulte of 25 December 1852, to serve the same role under the Second French Empire. Unlike the similar titles of Prince Imperial of Brazil and Prince Imperial of Mexico, however, the title could not be kept in use by the House of Bonaparte after the death of Napoléon, Prince Imperial, as the wording both of the Constitution of the Year XII and the Sénatus-Consulte of 25 December 1852 explicitly specifies that the title shall be borne by the eldest son of the Emperor.







































