The Rohingya people are a stateless Indo-Aryan ethnic group who reside in Rakhine State, Myanmar. There were an estimated 1 million Rohingya living in Myanmar before the 2016–17 crisis. By December 2017, an estimated 625,000 refugees from Rakhine, Myanmar, had crossed the border into Bangladesh since August 2017. The majority are Muslim while a minority are Hindu. Described by the United Nations in 2013 as one of the most persecuted minorities in the world, the Rohingya population is denied citizenship under the 1982 Myanmar nationality law. According to Human Rights Watch, the 1982 laws "effectively deny to the Rohingya the possibility of acquiring a nationality". Despite being able to trace Rohingya history to the 8th century, Myanmar law does not recognize the ethnic minority as one of the eight "national indigenous races". They are also restricted from freedom of movement, state education and civil service jobs. The legal conditions faced by the Rohingya in Myanmar have been widely compared to apartheid by many international academics, analysts and political figures, including Nobel laureate Bishop Desmond Tutu, a South African anti-apartheid activist.

The Rakhine people are an ethnic group in Myanmar (Burma) forming the majority along the coastal region of present-day Rakhine State. They possibly constitute 5.53% or more of Myanmar's total population, but no accurate census figures exist. Arakanese people also live in the southeastern parts of Bangladesh, especially in Chittagong Division and Barisal Division. A group of Arakanese descendants, living in the Chittagong Hill Tracts of Bangladesh at least since the 16th century, are known as the Marma people or Mog people.
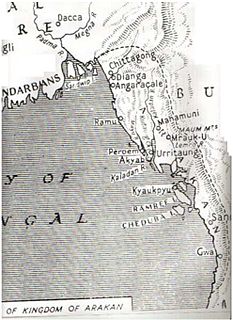
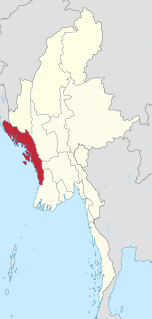
Rakhine State occupies the northern coastline of Myanmar up to the border with Bangladesh and corresponds to the historical Kingdom of Arakan. The history of Rakhine is divided into 7 parts - the independent kingdoms of Dhanyawadi, Waithali, Lemro, Mrauk U, Burmese occupation from 1784 to 1826, British rule from 1826 to 1948 and as a part of independent Burma from 1948.

General elections were held in Burma over several months between June 1951 and April 1952 due to internal conflict within the country.

The Arakan League for Democracy is a political party active in Rakhine State, Myanmar (Burma).

The Communist Party (Burma), sometimes referred to as the Red Flag Communist Party, was a communist party in Burma. The party was formed after a more radical faction broke away from the Communist Party of Burma in 1946. In the same year, it began a protracted armed insurgency; first against British rule, then against the Burmese government. The party was led by Thakin Soe, a firebrand communist leader. In the mid to late 1970s, the party lost influence and was militarily defeated after the capture of Thakin Soe in 1978.

The Rakhine Nationalities Development Party was a political party in Myanmar (Burma), representing the interests of the Rakhine people in Rakhine State and Yangon Region. The party contested 44 seats, of which it won 35. RNDP was the largest party in the Rakhine State Hluttaw, the sole State or Region Hluttaw whose largest party was not the Union Solidarity and Development Party following the 2010 General Election. The party was at times accused of stirring up anti-Muslim feelings.

The Kingdom of Mrauk-U was an independent coastal kingdom of Arakan which existed for over 350 years. It was based in the city of Mrauk-U, near the eastern coast of the Bay of Bengal. The kingdom from 1429 to 1785 ruled over what is now Rakhine State, Myanmar and Chittagong Division, Bangladesh. From 1429 to 1531 it was a protectorate of the Bengal Sultanate at different time periods. After gaining independence from Bengal, it prospered with help from the Portuguese settlement in Chittagong. In 1666, it lost control of Chittagong after a war with the Mughal Empire. Its reign continued until the 18th century, when it fell to the invasion of the Burmese Empire.
Narameikhla Min Saw Mon was the last king of Launggyet Dynasty and the founder of Mrauk-U Dynasty of Arakan.
The Kamein, also known as the Kaman (ကမန်), are a predominantly Muslim ethnic group that primarily reside in Rakhine State, Myanmar. The name Kaman comes from Persian, meaning a "bow." The Kaman are formally recognized by the Burmese government and classified as one of the 7 ethnic groups comprising the Rakhine national race. The Kaman are considered indigenous and are widely acknowledged as Burmese citizens who hold national identity cards.

The Arakan National Party, is a political party in Myanmar (Burma), representing the interests of the Rakhine people in Rakhine State and Yangon Region. The party was founded on 13 January 2014 and registered with the election commission on 6 March 2014. The chairman of the ANP is Dr. Aye Maung.

The Arakanese Muslim Association was a political party in Burma.
Sultan Mahmud was a politician from Arakan, Burma. In the British Raj, Mahmud served as cabinet secretary in the Central Legislative Assembly. After Burmese independence, he was elected to the Parliament of Burma through a by election from Buthidaung in 1957. He was re-elected in 1960. He served as Minister of Health of the Union of Burma from 1960 till the 1962 Burmese coup d'état.
Sultan Ahmed was one of the longest serving legislators from Arakan, Burma. Ahmed was the president of the Jamiat-e-Ulema party, which was allied with the Anti-Fascist People's Freedom League, the founding political party of Burma. Ahmed served in the Burmese parliament until the 1962 Burmese coup d'état.

The Mayu Frontier District was a short-lived administrative zone of Burma which existed between 1961 and 1964. It covered the Maungdaw District of present-day Rakhine State in the historical region of Arakan. The zone was administered directly from the capital Rangoon.
The Communist Party of Arakan, also known as the Arakanese Communist Party, was a far-left political party and armed insurgent group in Arakan, Burma. It was founded in 1962 after a faction under the leadership of Arakanese political leaders Kyaw Zan Rhee and Bo Maung Han broke away from the Red Flag Communist Party (RFCP).