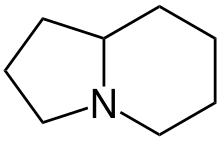


Indolizidine alkaloids are natural products from various alkaloid groups whose structure can be derived from indolizidine. [1]



Indolizidine alkaloids are natural products from various alkaloid groups whose structure can be derived from indolizidine. [1]
Indolizidine alkaloids are present in various plant families, including Elaeocarpaceae, Asclepiadaceae, and are also produced as metabolites by fungi and bacteria. [2] For instance, Slaframine and swainsonine were identified in the fungus Rhizoctonia leguminicola , [3] while Castanospermine was extracted from Castanospermum australe. [2] Notably, this alkaloid group includes pumiliotoxins, which are the toxins of the strawberry poison-dart frog . [2]
The polyhydroxy alkaloids include compounds like castanospermine and swainsonine. [1]
The primary alkaloids within the pumiliotoxin category are pumiliotoxin A and pumiliotoxin B. [2] Other representatives include gephyrotoxin 223 AB and gephyrotoxin. [3]
Representatives of this alkaloid group include tylophorine, tylocrebrine and tylophorinidine. [4] [5]
Representatives of this group include Elaeocanine A, Elaeocarpine and Elaeocarpidine. [6]
The main alkaloid in this category is securinine. Others are securinol A and norsecurinine. [7]
Most of the Tylophora alkaloids belong to the phenanthroindolizidine alkaloid family, including tylophorine, septicin, and hispidine. [8]
Main alkaloids of this group are Ipalbin and Ipomin. Furthermore, Ipalbidine and Ipohardine occur. [9]
Swainsonine-type compounds are currently under investigation for their potential as active agents against AIDS. Swainsonine and castanospermine function as inhibitors of sugar-splitting enzymes. Castanospermine also exhibits anti-cancer and anti-HIV properties, [2] while Slaframine acts as a parasympathomimetic agent. Pumiliotoxin A enhances the contraction of striated muscle, and gephyrotoxin has similar effects to pumiliotoxin A. Due to their multifaceted impacts on the nervous system, these alkaloids are in high demand. However, their natural availability through frog skin extraction is severely limited due to species protection measures. [3]

Toxiferine is a curare toxin. It is a bisindole alkaloid derived from Strychnos toxifera and a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist. This alkaloid is the main toxic component of Calabash curare, and one of the most toxic plant alkaloids known. The lethal dose (LD50) for mice has been determined as 10 - 60 µg/kg by intravenous administration. It is a muscle relaxant that causes paralysis of skeletal muscle, which takes approximately 2 hours to recovery for a moderate dose, and 8 hours of total paralysis with a 20-fold paralytic dose. The paralysis can be antagonized by neostigmine

Steroidal alkaloids have the basic steroidal skeleton with nitrogen-based functional groups attached to the skeleton. More specifically, they are distinguished by their tetracyclic cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene skeleton that marks their close relationship with sterols. They fall in two major categories: Solanum alkaloids and Veratrum alkaloids. A Steroidal alkaloid has also been found in Chonemorpha fragrans, 'chonemorphine' was used to treat intestinal infections in Wistar rats..

Pyridine alkaloids are a class of alkaloids, nitrogen-containing chemical compounds widely found in plants, that contain a pyridine ring. Examples include nicotine and anabasine which are found in plants of the genus Nicotiana including tobacco.

Piperidine alkaloids are naturally occurring chemical compounds from the group of alkaloids, which are chemically derived from piperidine.

Acridone alkaloids are natural products derived from acridone.

Isoquinoline alkaloids are natural products of the group of alkaloids, which are chemically derived from isoquinoline. They form the largest group among the alkaloids.
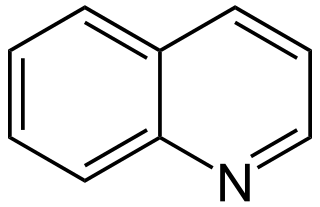
Quinoline alkaloids are naturally occurring chemical compounds from the group of alkaloids, which are chemically derived from quinoline. Some quinoline alkaloids show antiseptic, convulsive or antineoplastic effects.
Erythrina alkaloids, generally containing benzyl-tetrahydroisoquinoline structure, are widely distributed in Erythrina species, a genus of plants which belong to the Fabaceae family in tropical and subtropical regions. The Erythrina alkaloids can be found in several organs of Erythrina trees but are primarily found in their seeds. They display several unique properties, and are the subject of active scientific research relating to their synthesis and bioactivity.

The carbazole alkaloids are natural products of the indole alkaloid type, derived from carbazole.

Conium alkaloids are natural products of the piperidine alkaloid type.
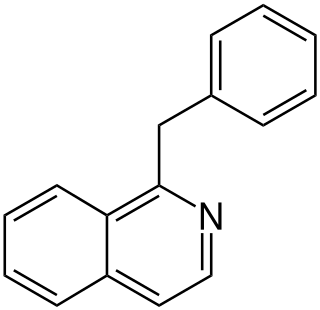
The benzylisoquinoline alkaloids are natural products that can be classified as isoquinoline alkaloids and are derived from benzylisoquinoline. They also include the benzyl(tetrahydro)isoquinoline alkaloids.

Bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids are natural products found primarily in the plant families of the barberry family, the Menispermaceae, the Monimiaceae, and the buttercup family.

Cephalotaxus alkaloids are natural products characterized by pentacyclic structure.
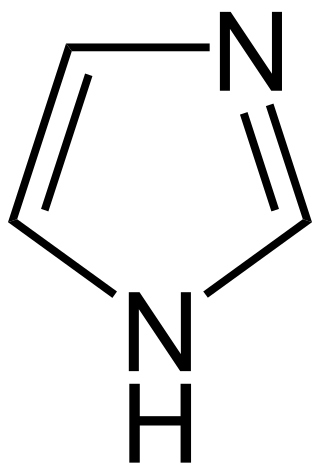
Imidazole alkaloids are a group of alkaloidss whose basic structure contains the imidazole ring system.

Corydalis Alkaloids are categorized as natural products of the isoquinoline alkaloid type.

Diterpene alkaloids are natural products of the terpene alkaloid type.

Dendrobium alkaloids are natural products and so-called pseudoalkaloids.

The pyrrolidine alkaloids are natural products chemically derived from pyrrolidine.

Areca alkaloids are a group of piperidine alkaloids found in the areca nut, the seeds of the areca palm.
Apocynaceae alkaloids are natural products found in the plant family of the dogbane family (Apocynaceae).
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)