
Elasmobranchii is a subclass of Chondrichthyes or cartilaginous fish, including sharks, rays, skates, and sawfish. Members of this subclass are characterised by having five to seven pairs of gill clefts opening individually to the exterior, rigid dorsal fins and small placoid scales on the skin. The teeth are in several series; the upper jaw is not fused to the cranium, and the lower jaw is articulated with the upper. The details of this jaw anatomy vary between species, and help distinguish the different elasmobranch clades. The pelvic fins in males are modified to create claspers for the transfer of sperm. There is no swim bladder; instead, these fish maintain buoyancy with large livers rich in oil.

The New Zealand smooth skate is a skate of the genus Dipturus, found around New Zealand at depths between 15 and 1,300 m.
The Madagascar skate is a species of fish in the family Rajidae. It is endemic to Madagascar. Its natural habitat is open seas. It is threatened by habitat loss. The IUCN describes the species as "a relatively small, poorly known, rare, deepwater skate with a limited distribution in the Western Indian Ocean off the west coast of Madagascar. [It is b]enthic on the continental slope at depths of 300 to 850 m. Virtually nothing is known of the biology of the species."
The maugean skate or Port Davey Skate is a species of fish in the family Rajidae. Its natural habitat is estuarine waters. It is endemic to Tasmania, only found in Macquarie Harbour and Bathurst Harbour. The species was discovered in 1988 by Dr Graham Edgar.
The Maltese skate or Maltese ray, is a species of fish in the family Rajidae. It is found in the Mediterranean Sea off the coasts of Algeria, Italy, Malta, and Tunisia. Its natural habitat is open seas. It is threatened by habitat loss.

The big skate is the largest species of skate in the waters off North America. They are found along the Pacific Coast from Alaska to Baja California, typically from the intertidal zone to a depth of 120 m (390 ft), and feed on benthic invertebrates and small fishes. They are unusual among skates in that their egg cases may contain up to seven eggs each. This species is one of the most commercially important skates off California and is sold for food.
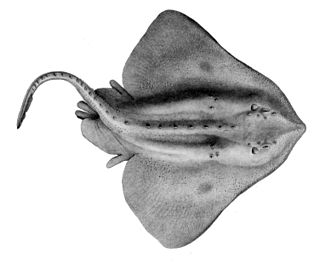
The Arctic skate is a species of fish in the family Rajidae. It lives near the seabed between 140 and 2,500 m deep in the Arctic Ocean and waters around Canada and northern and north-western Europe, in the northern Pacific Ocean, and in waters surrounding Antarctica and New Zealand.

Pavoraja nitida, commonly known as the peacock skate, is a species of fish in the family Arhynchobatidae. It lives near the soft bottoms of the continental shelf near the coasts of southeastern Australia in depths ranging from 30 to 390 metres. It produces oblong egg capsules which have stiff horns in each corner and lays them in sandy or muddy flats. Its maximum size is 36.8 cm.
Pavoraja mosaica, commonly known as the mosaic skate, is a species of fish in the family Arhynchobatidae. It lives in depths ranging from 300 meters to 450 meters off the northeastern coast of Australia. It can reach up to 27.9 cm (11.0 in) in total length.
Pavoraja arenaria, commonly known as the sandy skate or yellow skate, is a species of fish in the family Arhynchobatidae. It lives in depths ranging from 192 to 712 meters but is usually found at 300 to 400 meters depth off the coast of western Australia. Its maximum size is 34.3 cm (13.5 in) total length. It is a little-known species that could be threatened by being taken as by-catch in trawl fisheries.
Pavoraja pseudonitida, commonly known as the false peacock skate, is a species of fish in the family Arhynchobatidae. It lives in depths ranging from 212 to 512 meters in the western Pacific Ocean off the coast of north-eastern Australia. Its maximum size is 37.2 cm (14.6 in) total length.
Pavoraja umbrosa, commonly known as the dusky skate, is a species of fish in the family Arhynchobatidae. It lives off the coast of north-eastern Australia in depths ranging from 360 to 731 meters. Its maximum size is 36.9 cm (14.5 in) total length.

Neoraja caerulea, also known as the blue ray or blue pygmy skate, is a species of fish in the family Rajidae. This small ray reaches a total length of approximately fish 30 centimetres (12 in) and is endemic to the north-eastern Atlantic Ocean off Ireland and Iceland, and south to the Bay of Biscay. It occurs at depths of 600 to 1,262 metres.
Insentiraja is a genus of skates in the family Arhynchobatidae commonly known as looseskin skates. The genus contains two known species, both of which occur in deep water in the western-central Pacific Ocean.
The Norwegian skate, or black skate, is a species of skate found at depths of 200 m (660 ft) to over 1,000 m (3,300 ft) in the East Atlantic region. Initially its range was believed to be restricted to the Norwegian Sea and North Sea to the Bay of Biscay. It is occasionally encountered off the western coast of Ireland, and historically has been found near Rockall and in the Norwegian Deep, though recent surveys have not identified the species there. The species has frequently been confused with other skates, and since the late 1980s it has been confirmed to occur more widely, ranging from Iceland to Morocco, as well as off South Africa and in the Mediterranean Sea.
Amblyraja taaf, commonly known as the whiteleg skate or thorny skate, is a little-known skate found at depths ranging from 150 to 600 m. It has been located off Crozet and Kerguelen Islands. Other specimens have been found off the coast of South Africa and Madagascar, but may be unrepresentative of the skate's native regions. Because of the limited knowledge of its biology and extent of capture in fisheries, this species is assessed as data deficient.
Brochiraja aenigma, also known as the Enigmaskate, is a skate known from a single specimen recently identified in 2006. Based on the single specimen, its range includes at least the Wanganella Bank on the Norfolk Ridge. It is rare with further searches finding no specimens, and while it is not commonly fished or reported in commercial distribution, it can be used for fish meal.

Fenestraja plutonia is a species of cartilaginous fish in the family Gurgesiellidae. It is commonly known as the underworld windowskate or Pluto pygmy skate. The underworld windowskate is known from patches of continental slope in the western Atlantic Ocean between the coasts of the southern United States and Suriname.

Insentiraja subtilispinosa, commonly known as the western looseskin skate or velvet skate, is a common deep water skate in the family Arhynchobatidae.
Gurgesiella atlantica, commonly known as the Atlantic pygmy skate, Atlantic finless skate, or simply the Atlantic skate, is a skate species in the family Gurgesiellidae. It lives in the western central and southwest Atlantic Ocean, from Nicaragua to Brazil. It grows to 49 centimetres (19 in) – 52 centimetres (20 in) long and is distinguished from other skates by its long, slender tail and absence of dorsal fins.








