International human rights instruments are the treaties and other international texts that serve as legal sources for international human rights law and the protection of human rights in general. There are many varying types, but most can be classified into two broad categories: declarations, adopted by bodies such as the United Nations General Assembly, which are by nature declaratory, so not legally-binding although they may be politically authoritative and very well-respected soft law;, and often express guiding principles; and conventions that are multi-party treaties that are designed to become legally binding, usually include prescriptive and very specific language, and usually are concluded by a long procedure that frequently requires ratification by each states' legislature. Lesser known are some "recommendations" which are similar to conventions in being multilaterally agreed, yet cannot be ratified, and serve to set common standards. There may also be administrative guidelines that are agreed multilaterally by states, as well as the statutes of tribunals or other institutions. A specific prescription or principle from any of these various international instruments can, over time, attain the status of customary international law whether it is specifically accepted by a state or not, just because it is well-recognized and followed over a sufficiently long time.
International human rights law (IHRL) is the body of international law designed to promote human rights on social, regional, and domestic levels. As a form of international law, international human rights law are primarily made up of treaties, agreements between sovereign states intended to have binding legal effect between the parties that have agreed to them; and customary international law. Other international human rights instruments, while not legally binding, contribute to the implementation, understanding and development of international human rights law and have been recognized as a source of political obligation.

The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime is a United Nations office that was established in 1997 as the Office for Drug Control and Crime Prevention by combining the United Nations International Drug Control Program (UNDCP) and the Crime Prevention and Criminal Justice Division in the United Nations Office at Vienna. and was renamed the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime in 2002.

The International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC) is a 1951 multilateral treaty overseen by the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization that aims to secure coordinated, effective action to prevent and to control the introduction and spread of pests of plants and plant products. The Convention extends beyond the protection of cultivated plants to the protection of natural flora and plant products. It also takes into consideration both direct and indirect damage by pests, so it includes weeds.
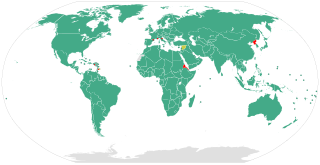
The United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC) is the only legally binding international anti-corruption multilateral treaty. Negotiated by member states of the United Nations (UN) it has been adopted by the UN General Assembly in October 2003 and entered into force in December 2005. The treaty recognise the importance of both preventive and punitive measures, addresses the cross-border nature of corruption with provisions on international cooperation and on the return of the proceeds of corruption. The UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) in Vienna serves as Secretariat for the UNCAC. UNCAC's goal is to reduce various types of corruption that can occur across country borders, such as trading in influence and abuse of power, as well as corruption in the private sector, such as embezzlement and money laundering. Another goal of the UNCAC is to strengthen international law enforcement and judicial cooperation between countries by providing effective legal mechanisms for international asset recovery.
Inter-American can refer to:

The Inter-American Convention to Prevent and Punish Torture (IACPPT) is an international human rights instrument, created in 1985 within the Western Hemisphere Organization of American States and intended to prevent torture and other similar activities.

The Group of States against Corruption, the Council of Europe’s anti-corruption monitoring body with its Headquarters in Strasbourg (France), was established, in 1999, as an enlarged Partial Agreement by 17 Council of Europe member States.
The Fiji Independent Commission Against Corruption (FICAC) is the country's mandated law enforcement agency to investigate and prosecute public sector corruption, as well as educate society on understanding and reporting corruption.
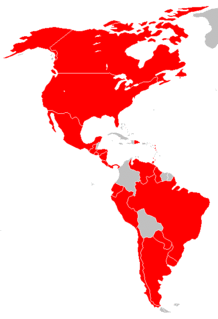
The Inter-American Convention Against Terrorism was adopted by the member countries of the Organization of American States (OAS) at its General Assembly held in Bridgetown, Barbados, on 3 June 2002. The Convention, negotiated pursuant to a mandate from the OAS Foreign Ministers shortly after the terrorist attacks of 11 September 2001 in the United States, reflects the Americas' hemispheric-wide commitment to enhancing cooperation in the fight against terrorism.
Convention against Corruption could refer to:

A few nations have codified ecocide as a crime. Activities that might constitute ecocide in these nations include substantially damaging or destroying ecosystems or by harming the health and well-being of a species, including humans.

International asset recovery is any effort by governments to repatriate the proceeds of corruption hidden in foreign jurisdictions. Such assets may include monies in bank accounts, real estate, vehicles, arts and artifacts, and precious metals. As defined under the United Nations Convention against Corruption, asset recovery refers to recovering the proceeds of corruption, rather than broader terms such as asset confiscation or asset forfeiture which refer to recovering the proceeds or instrumentalities of crime in general.
The African Union Convention on Preventing and Combating Corruption (AUCPCC) was adopted in Maputo on 11 July 2003 to fight rampant political corruption on the African continent. It represents regional consensus on what African states should do in the areas of prevention, criminalization, international cooperation and asset recovery. Going beyond other similar conventions, the AUCPCC calls for the eradication of corruption in the private and public sector. The Convention covers a wide range of offences including bribery, diversion of property by public officials, trading in influence, illicit enrichment, money laundering and concealment of property and primarily consists of mandatory provisions. It also obliges the signatories to introduce open and converted investigations against corruption. Those measures attracted criticism in the Journal of African Law, where Peter Schroth argued that the convention disregards other aspects of the rule of law, like e.g. data protection and the presumption of innocence.
The Declaration on the Elimination of Violence Against Women was adopted without a vote by the United Nations General Assembly in the 48/104 resolution of 20 December 1993. Contained within it is the recognition of "the urgent need for the universal application to women of the rights and principles with regard to equality, security, liberty, integrity and dignity of all human beings". It recalls and embodies the same rights and principles as those enshrined in such instruments as the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, and Articles 1 and 2 provide the most widely used definition of violence against women.
The Council of Europe Convention on preventing and combating violence against women and domestic violence, better known as the Istanbul Convention, is a human rights treaty of the Council of Europe against violence against women and domestic violence which was opened for signature on 11 May 2011, in Istanbul, Turkey. The convention aims at prevention of violence, victim protection and to end the impunity of perpetrators. As of March 2019, it has been signed by 45 countries and the European Union. On 12 March 2012, Turkey became the first country to ratify the convention, followed by 34 other countries from 2013 to 2021. The Convention came into force on 1 August 2014. In 2021, Turkey became the first and only country to withdraw from the convention, after denouncing it on 20 March 2021. The convention ceased to be effective in Turkey on 1 July 2021, following its denunciation.
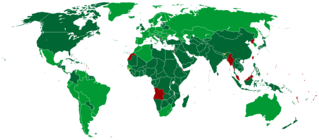
The International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination (ICERD) is a United Nations convention. A third-generation human rights instrument, the Convention commits its members to the elimination of racial discrimination and the promotion of understanding among all races. The Convention also requires its parties to criminalize hate speech and criminalize membership in racist organizations.
Anti-corruption comprise activities that oppose or inhibit corruption. Just as corruption takes many forms, anti-corruption efforts vary in scope and in strategy. A general distinction between preventive and reactive measures is sometimes drawn. In such framework, investigative authorities and their attempts to unveil corrupt practices would be considered reactive, while education on the negative impact of corruption, or firm-internal compliance programs are classified as the former.

The Inter-American Convention on the Prevention, Punishment, and Eradication of Violence against Women, better known as the Belém do Pará Convention, is an international human rights instrument adopted by the Inter-American Commission of Women (CIM) of the Organization of American States at a conference held in Belém do Pará, Brazil, on 9 June 1994. It is the first legally binding international treaty that criminalises all forms of violence against women, especially sexual violence. On 26 October 2004, the Follow-Up Mechanism (MESECVI) agency was established to ensure the State parties' compliance with the Convention.









