
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at the Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus. The geological detritus originated from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies. Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipitate from water solution.
Sedimentology encompasses the study of modern sediments such as sand, silt, and clay, and the processes that result in their formation, transport, deposition and diagenesis. Sedimentologists apply their understanding of modern processes to interpret geologic history through observations of sedimentary rocks and sedimentary structures.

Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks. Stratigraphy has two related subfields: lithostratigraphy and biostratigraphy.
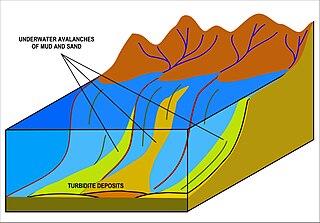
A turbidite is the geologic deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean.

The exposed geology of the Capitol Reef area presents a record of mostly Mesozoic-aged sedimentation in an area of North America in and around Capitol Reef National Park, on the Colorado Plateau in southeastern Utah.
Cyclic sediments are sequences of sedimentary rocks that are characterised by repetitive patterns of different rock types (strata) or facies within the sequence. Processes that generate sedimentary cyclicity can be either autocyclic or allocyclic, and can result in piles of sedimentary cycles hundreds or even thousands of metres thick. The study of sequence stratigraphy was developed from controversies over the causes of cyclic sedimentation.

The Santos Basin is an approximately 352,000 square kilometres (136,000 sq mi) large mostly offshore sedimentary basin. It is located in the south Atlantic Ocean, some 300 kilometres (190 mi) southeast of Santos, Brazil. The basin is one of the Brazilian basins to have resulted from the break-up of Gondwana since the Early Cretaceous, where a sequence of rift basins formed on both sides of the South Atlantic; the Pelotas, Santos, Campos and Espírito Santo Basins in Brazil, and the Namibia, Kwanza and Congo Basins in southwestern Africa.
The Triassic Lockatong Formation is a mapped bedrock unit in Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and New York. It is named after the Lockatong Creek in Hunterdon County, New Jersey.
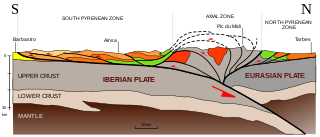
The Pyrenees are a 430-kilometre-long, roughly east–west striking, intracontinental mountain chain that divide France, Spain, and Andorra. The belt has an extended, polycyclic geological evolution dating back to the Precambrian. The chain's present configuration is due to the collision between the microcontinent Iberia and the southwestern promontory of the European Plate. The two continents were approaching each other since the onset of the Upper Cretaceous (Albian/Cenomanian) about 100 million years ago and were consequently colliding during the Paleogene (Eocene/Oligocene) 55 to 25 million years ago. After its uplift, the chain experienced intense erosion and isostatic readjustments. A cross-section through the chain shows an asymmetric flower-like structure with steeper dips on the French side. The Pyrenees are not solely the result of compressional forces, but also show an important sinistral shearing.

The Bass Formation, also known as the Bass Limestone, is a Mesoproterozoic rock formation that outcrops in the eastern Grand Canyon, Coconino County, Arizona. The Bass Formation erodes as either cliffs or stair-stepped cliffs. In the case of the stair-stepped topography, resistant dolomite layers form risers and argillite layers form steep treads. In general, the Bass Formation in the Grand Canyon region and associated strata of the Unkar Group-rocks dip northeast (10°-30°) toward normal faults that dip 60+° toward the southwest. This can be seen at the Palisades fault in the eastern part of the main Unkar Group outcrop area. In addition, thick, prominent, and dark-colored basaltic sills intrude across the Bass Formation.
One of the major depositional strata in the Himalaya is the Lesser Himalayan Strata from the Paleozoic to Mesozoic eras. It had a quite different marine succession during the Paleozoic, as most parts of it are sparsely fossiliferous or even devoid of any well-defined fossils. Moreover, it consists of many varied lithofacies, making correlation work more difficult. This article describes the major formations of the Paleozoic – Mesozoic Lesser Himalayan Strata, including the Tal Formation, Gondwana Strata, Singtali Formation and Subathu Formation.

The Nam Con Son Basin formed as a rift basin during the Oligocene period. This basin is the southernmost sedimentary basin offshore of Vietnam, located within coordinates of 6°6'-9°45'N and 106°0-109°30'E in the East Vietnam Sea. It is the largest oil and gas bearing basin in Vietnam and has a number of producing fields.
The geology of Morocco formed beginning up to two billion years ago, in the Paleoproterozoic and potentially even earlier. It was affected by the Pan-African orogeny, although the later Hercynian orogeny produced fewer changes and left the Maseta Domain, a large area of remnant Paleozoic massifs. During the Paleozoic, extensive sedimentary deposits preserved marine fossils. Throughout the Mesozoic, the rifting apart of Pangaea to form the Atlantic Ocean created basins and fault blocks, which were blanketed in terrestrial and marine sediments—particularly as a major marine transgression flooded much of the region. In the Cenozoic, a microcontinent covered in sedimentary rocks from the Triassic and Cretaceous collided with northern Morocco, forming the Rif region. Morocco has extensive phosphate and salt reserves, as well as resources such as lead, zinc, copper and silver.
The geology of Nigeria formed beginning in the Archean and Proterozoic eons of the Precambrian. The country forms the Nigerian Province and more than half of its surface is igneous and metamorphic crystalline basement rock from the Precambrian. Between 2.9 billion and 500 million years ago, Nigeria was affected by three major orogeny mountain-building events and related igneous intrusions. Following the Pan-African orogeny, in the Cambrian at the time that multi-cellular life proliferated, Nigeria began to experience regional sedimentation and witnessed new igneous intrusions. By the Cretaceous period of the late Mesozoic, massive sedimentation was underway in different basins, due to a large marine transgression. By the Eocene, in the Cenozoic, the region returned to terrestrial conditions.
The geology of South Korea includes rocks dating to the Archean and two large massifs of metamorphic rock as the crystalline basement, overlain by thick sedimentary sequences, younger metamorphic rocks and volcanic deposits.
The geology of Afghanistan includes nearly one billion year old rocks from the Precambrian. The region experienced widespread marine transgressions and deposition during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic, that continued into the Cenozoic with the uplift of the Hindu Kush mountains.

The geology of Uzbekistan consists of two microcontinents and the remnants of oceanic crust, which fused together into a tectonically complex but resource rich land mass during the Paleozoic, before becoming draped in thick, primarily marine sedimentary units.
The geology of Saudi Arabia includes Precambrian igneous and metamorphic basement rocks, exposed across much of the country. Thick sedimentary sequences from the Phanerozoic dominate much of the country's surface and host oil.

The Antalo Limestone, also known as the Antalo Sequence, is a geological formation in Ethiopia. It is between 300 and 800 metres thick and comprises fossiliferous limestones and marls that were deposited in a reef. Marine microfossils have shown an age between 165 and 150 million years.
The Officer Basin is an intracratonic sedimentary basin that covers roughly 320,000 km2 along the border between southern and western Australia. Exploration for hydrocarbons in this basin has been sparse, but the geology has been examined for its potential as a hydrocarbon reservoir. This basin's extensive depositional history, with sedimentary thicknesses exceeding 6 km and spanning roughly 350 Ma during the Neoproterozoic, make it an ideal candidate for hydrocarbon production.










