Related Research Articles

The breast is one of two prominences located on the upper ventral region of a primate's torso. Both females and males develop breasts from the same embryological tissues.

The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neural control center for all endocrine systems.

The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, the elephant shrew and the Cairo spiny mouse. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus. The speculated presence of an endometrial microbiota has been argued against.

The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus. There is an ovary found on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries also secrete hormones that play a role in the menstrual cycle and fertility. The ovary progresses through many stages beginning in the prenatal period through menopause. It is also an endocrine gland because of the various hormones that it secretes.

A secondary sex characteristic is a physical characteristic of an organism that is related to or derived from its sex, but not directly part of its reproductive system. In humans, these characteristics typically start to appear during puberty. In animals, they can start to appear at sexual maturity. In humans, secondary sex characteristics include enlarged breasts and widened hips of females, facial hair and Adam's apples on males, and pubic hair on both. In non-human animals, secondary sex characteristics include, for example, the manes of male lions, the bright facial and rump coloration of male mandrills, and horns in many goats and antelopes.

The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus is located in the upper front part of the chest, in the anterior superior mediastinum, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. It is made up of two lobes, each consisting of a central medulla and an outer cortex, surrounded by a capsule.
Development of the human body is the process of growth to maturity. The process begins with fertilization, where an egg released from the ovary of a female is penetrated by a sperm cell from a male. The resulting zygote develops through mitosis and cell differentiation, and the resulting embryo then implants in the uterus, where the embryo continues development through a fetal stage until birth. Further growth and development continues after birth, and includes both physical and psychological development that is influenced by genetic, hormonal, environmental and other factors. This continues throughout life: through childhood and adolescence into adulthood.

A mammary gland is an exocrine gland in humans and other mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the Latin word mamma, "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primates, the udder in ruminants, and the dugs of other animals. Lactorrhea, the occasional production of milk by the glands, can occur in any mammal, but in most mammals, lactation, the production of enough milk for nursing, occurs only in phenotypic females who have gestated in recent months or years. It is directed by hormonal guidance from sex steroids. In a few mammalian species, male lactation can occur. With humans, male lactation can occur only under specific circumstances.

The female reproductive system is made up of the internal and external sex organs that function in the reproduction of new offspring. In humans, the female reproductive system is immature at birth and develops to maturity at puberty to be able to produce gametes, and to carry a fetus to full term. The internal sex organs are the vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. The female reproductive tract includes the vagina, uterus, and fallopian tubes and is prone to infections. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and childbirth, and is connected to the uterus at the cervix. The uterus or womb accommodates the embryo which develops into the fetus. The uterus also produces secretions which help the transit of sperm to the fallopian tubes, where sperm fertilize ova produced by the ovaries. The external sex organs are also known as the genitals and these are the organs of the vulva including the labia, clitoris, and vaginal opening.

Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations, poor nourishment, poor circulation, loss of hormonal support, loss of nerve supply to the target organ, excessive amount of apoptosis of cells, and disuse or lack of exercise or disease intrinsic to the tissue itself. In medical practice, hormonal and nerve inputs that maintain an organ or body part are said to have trophic effects. A diminished muscular trophic condition is designated as atrophy. Atrophy is reduction in size of cell, organ or tissue, after attaining its normal mature growth. In contrast, hypoplasia is the reduction in the cellular numbers of an organ, or tissue that has not attained normal maturity.
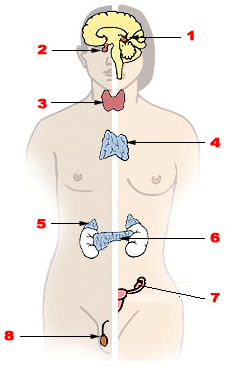
Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testicles, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, hypothalamus and adrenal glands. The hypothalamus and pituitary glands are neuroendocrine organs.
Reproductive biology includes both sexual and asexual reproduction.

The human reproductive system includes the male reproductive system which functions to produce and deposit sperm; and the female reproductive system which functions to produce egg cells, and to protect and nourish the fetus until birth. Humans have a high level of sexual differentiation. In addition to differences in nearly every reproductive organ, there are numerous differences in typical secondary sex characteristics.

Kurloff cells were described as mononuclear cells in the peripheral blood and organs of the guinea pig, capybara, paca, agouti and cavie. The Kurloff cell contains a characteristic proteoglycan-containing inclusion body. In the guinea pig, Kurloff cells are more numerous in the adult female than the adult male. A marked increase in the number of circulating Kurloff cells is present in the peripheral blood during pregnancy and after estrogen treatment in male and female animals. A relatively smaller number of cells take place in immature, non-pregnant, and non-estrogen-treated animals. The exact function of Kurloff cells remains unknown, but it has some of the characteristics of both monocytes and lymphocytes. In guinea-pigs, it has been proposed that Kurloff cells mainly involve in the function of the immune system, such as acting as a natural killer cell and preventing damage to the trophoblast by maternal defensive cells. Also, Kurloff cells present antibody-dependent cytotoxic activity in vitro.

Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The process of feeding milk in all female creatures is called nursing, and in humans it is also called breastfeeding. Newborn infants often produce some milk from their own breast tissue, known colloquially as witch's milk.
Breast development, also known as mammogenesis, is a complex biological process in primates that takes place throughout a female's life.
Thymic involution is the shrinking (involution) of the thymus with age, resulting in changes in the architecture of the thymus and a decrease in tissue mass. Thymus involution is one of the major characteristics of vertebrate immunology, and occurs in almost all vertebrates, from birds, teleosts, amphibians to reptiles, though the thymi of a few species of sharks are known not to involute. This process is genetically regulated, with the nucleic material responsible being an example of a conserved sequence — one maintained through natural selection since it arose in a common ancestor of all species now exhibiting it, via a phenomenon known to bioinformaticists as an orthologic sequence homology.

Maternal physiological changes in pregnancy are the adaptations that take place during pregnancy that enable the accommodation of the developing embryo and fetus. These are normal physiological adaptations that cause changes in behavior, the functioning of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, metabolism including increases in blood sugar levels, kidney function, posture, and breathing. During pregnancy numerous hormones and proteins are secreted that also have a broad range of effects.

Most mammals are viviparous, giving birth to live young. However, the five species of monotreme, the platypuses and the echidnas, lay eggs. The monotremes have a sex determination system different from that of most other mammals. In particular, the sex chromosomes of a platypus are more like those of a chicken than those of a therian mammal.
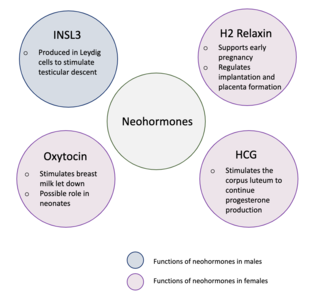
Neohormones are a group of recently evolved hormones primarily associated to the success of mammalian development. These hormones are specific to mammals and are not found in other vertebrates—this is because neohormones are evolved to enhance specific mammalian functions. In males, neohormones play important roles in regulating testicular descent and preparing the sperm for internal fertilisation. In females, neohormones are essential for regulating early pregnancy, mammary gland development lactation, and viviparity. Neohormones superimpose their actions on the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and are not associated with other core bodily functions.
References
- ↑ Sutherland, J. S.; Goldberg, G. L.; et al. (August 4, 2005). "Activation of Thymic Regeneration in Mice and Humans following Androgen Blockade". The Journal of Immunology. 175 (4): 2741–2753. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.4.2741 . PMID 16081852.
