Related Research Articles

The humerus is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes. The body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prismatic below. The lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes, and 3 fossae. As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons.

The brachioradialis is a muscle of the forearm that flexes the forearm at the elbow. It is also capable of both pronation and supination, depending on the position of the forearm. It is attached to the distal styloid process of the radius by way of the brachioradialis tendon, and to the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus.

The brachialis is a muscle in the upper arm that flexes the elbow. It lies beneath the biceps brachii, and makes up part of the floor of the region known as the cubital fossa. It originates from the anterior aspect of the distal humerus; it inserts onto the tuberosity of the ulna. It is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve, and commonly also receives additional innervation from the radial nerve. The brachialis is the prime mover of elbow flexion generating about 50% more power than the biceps.

The musculocutaneous nerve is a mixed branch of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus derived from cervical spinal nerves C5-C7. It arises opposite the lower border of the pectoralis major. It provides motor innervation to the muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm: the coracobrachialis, biceps brachii, and brachialis. It provides sensory innervation to the lateral forearm. It courses through the anterior part of the arm, terminating 2 cm above elbow; after passing the lateral edge of the tendon of biceps brachii it is becomes known as the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm.
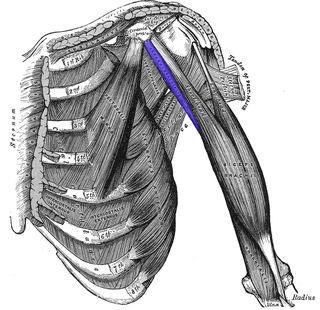
The coracobrachialis muscle is a muscle in the upper medial part of the arm. It is located within the anterior compartment of the arm. It originates from the coracoid process of the scapula; it inserts onto the middle of the medial aspect of the body of the humerus. It is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve. It acts to adduct and flex the arm.

The radial recurrent artery arises from the radial artery immediately below the elbow.

The inferior ulnar collateral artery is an artery in the arm. It arises about 5 cm. above the elbow from the brachial artery.
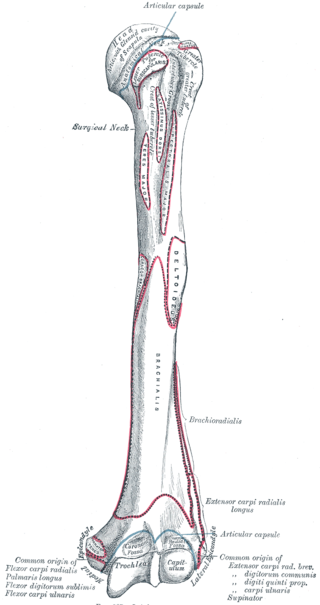
The inferior third of the medial border of the humerus is raised into a slight ridge, the medial supracondylar ridge, which becomes very prominent below; it presents an anterior lip for the origins of the Brachialis and Pronator teres, a posterior lip for the medial head of the Triceps brachii, and an intermediate ridge for the attachment of the medial intermuscular septum.

The fascial compartments of arm refers to the specific anatomical term of the compartments within the upper segment of the upper limb of the body. The upper limb is divided into two segments, the arm and the forearm. Each of these segments is further divided into two compartments which are formed by deep fascia – tough connective tissue septa (walls). Each compartment encloses specific muscles and nerves.
The coronoid process of the ulna is a triangular process projecting forward from the anterior proximal portion of the ulna.

The tuberosity of the ulna is a rough eminence on the proximal end of the ulna. It occurs at the junction of the antero-inferior surface of the coronoid process with the front of the body. It provides an insertion point to a tendon of the brachialis.

The humeroulnar joint is part of the elbow-joint. It is composed of two bones, the humerus and ulna, and is the junction between the trochlear notch of ulna and the trochlea of humerus. It is classified as a simple hinge-joint, which allows for movements of flexion, extension and circumduction. Owing to the obliquity of the trochlea of the humerus, this movement does not take place in the antero-posterior plane of the body of the humerus.

The cervical spinal nerve 6 (C6) is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment.
Iquiracetima is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae, containing the following species:
Iquiracetima aspasia is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Galileo and Martins in 1995. It is known from Ecuador and Peru.
Iquiracetima cerari is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Galileo and Martins in 2008. It is known from Brazil.
Canarana brachialis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Félix Édouard Guérin-Méneville in 1855. It is known from Bolivia, Brazil, Peru and Ecuador.

Bruchus brachialis, the vetch bruchid, is a species of leaf beetle in the family Chrysomelidae. It is found in Europe & Northern Asia and North America.
Demeijerea brachialis is a species of midge in the family Chironomidae.

Episcirrus brachialis is a species of hidden snout weevil in the beetle family Curculionidae. It is found in North America.
References
- ↑ BioLib.cz - Iquiracetima brachialis. Retrieved on 8 September 2014.